Advancements in Cerebral Tumor Detection Methods
Detecting cerebral tumors at their earliest stages is a critical area of focus in modern medicine. Significant progress in diagnostic technologies and methodologies has transformed how these complex conditions are identified, offering new avenues for earlier intervention and improved understanding. These advancements encompass a range of innovations, from sophisticated imaging techniques to a deeper comprehension of subtle neurological indicators, all contributing to more precise and timely diagnoses.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.
Understanding Early Symptoms and Neurological Indicators
Early detection of a cerebral tumor often begins with recognizing subtle changes in a patient’s health. Neurological symptoms can vary widely depending on the tumor’s size, location, and growth rate within the brain. Common indicators might include persistent headaches, unexplained nausea, vision changes, seizures, or shifts in personality and cognitive function. These symptoms, while non-specific on their own, prompt further investigation when they persist or worsen. A thorough neurological examination helps clinicians assess motor skills, sensory function, reflexes, and coordination, providing initial clues that may lead to a suspected intracranial lesion.
Advanced Imaging Techniques for Cerebral Tumor Diagnosis
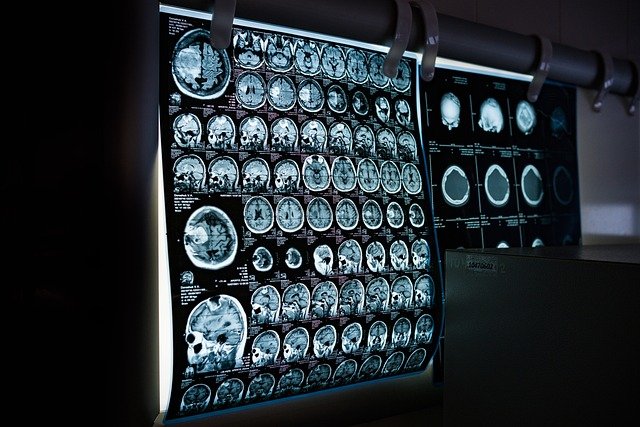
Modern medical imaging plays a pivotal role in the diagnosis of cerebral tumors. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is often the gold standard, offering highly detailed images of brain structures and allowing for differentiation between tumor types and surrounding healthy tissue. Specialized MRI sequences, such as perfusion MRI and diffusion tensor imaging, can provide additional information about blood flow and white matter integrity, aiding in characterizing the tumor. Computed Tomography (CT) scans are also valuable, particularly in emergency settings or for detecting calcifications and hemorrhage. Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scans, often combined with CT or MRI, can highlight metabolic activity, helping to distinguish between active tumor tissue and post-treatment changes or scar tissue.
The Role of Oncology Research in Improving Detection
Ongoing research in oncology is continuously pushing the boundaries of cerebral tumor detection. Scientists are exploring biomarkers—molecules found in blood, urine, or cerebrospinal fluid that can indicate the presence of a tumor. Liquid biopsies, for instance, aim to detect circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) or circulating tumor cells (CTCs), potentially offering a less invasive method for early detection and monitoring. Advances in artificial intelligence and machine learning are also being applied to analyze complex imaging data and patient symptoms, helping to identify patterns that might be missed by the human eye and improve diagnostic accuracy and speed. This interdisciplinary research is crucial for developing the next generation of diagnostic tools and improving patient outcomes.
Enhancing Patient Care Through Improved Detection and Awareness
Improved detection methods directly contribute to better patient care. Identifying cerebral tumors earlier can significantly impact treatment planning and potential for recovery. When a tumor is detected at an earlier stage, treatment options, which may include surgery, radiation therapy, or chemotherapy, can often be more effective and less invasive. Furthermore, increased public and medical professional awareness of the varied symptoms associated with intracranial lesions encourages timely consultation and investigation. This proactive approach ensures that individuals experiencing concerning neurological changes receive prompt attention, leading to earlier diagnosis and potentially better long-term prognoses. The integration of advanced diagnostics into routine clinical practice is vital for comprehensive patient management.
Conclusion
The landscape of cerebral tumor detection is continually evolving, driven by technological innovations and dedicated research. From refining the interpretation of neurological symptoms to developing highly sensitive imaging modalities and exploring novel biomarkers, these advancements are pivotal. The ongoing commitment to enhancing diagnostic accuracy and timeliness offers significant hope for individuals facing a cerebral tumor diagnosis, contributing to more effective interventions and improved quality of life.




