Automotive Technician Training: Launch a Skilled Career
Automotive mechanic training prepares you for a durable, in-demand career in auto repair and maintenance. This guide explains education paths, typical program lengths, cost ranges, certification options, and job prospects — including work on hybrids and electric vehicles — so you can choose the right route to become a qualified automotive technician.
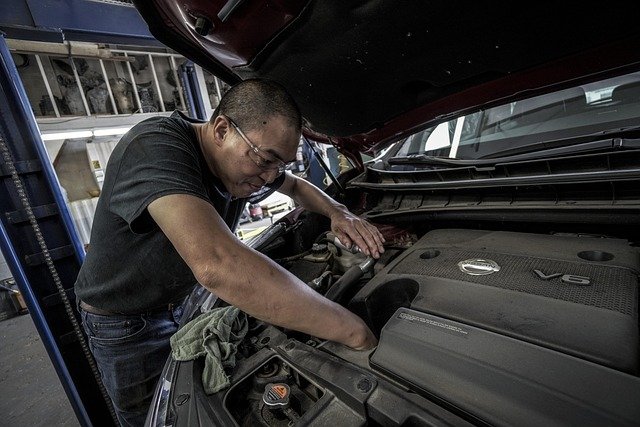

Many modern training programs go beyond hands-on vehicle repair to include customer service, shop management, and health and safety procedures — all essential skills for daily work in a garage. As vehicles grow more sophisticated, training curricula are regularly updated so graduates can diagnose and service the latest engines, electronics, and computer-controlled systems.
What are the educational requirements for becoming an automotive mechanic?
There are several common pathways into the trade, and requirements depend on the job level and employer. Typical options include:
-
High school diploma or equivalent: Most entry-level roles expect a high school diploma or GED. Relevant classes such as math, physics, and computer science provide a useful foundation.
-
Vocational or technical certificates: Short-term programs (often 6–12 months) offered by technical schools focus on core repair and maintenance skills and provide practical shop experience.
-
Associate degrees: Community colleges and technical institutes offer two-year associate degree programs in automotive technology that dive deeper into diagnostics, systems theory, and hands-on practice — often improving job prospects.
-
Apprenticeships: Employer- or union-run apprenticeships combine paid, on-the-job work with classroom instruction. These programs typically run 2–4 years and are an excellent way to learn while earning.
-
Manufacturer-specific training: Automakers and dealers sometimes provide specialized courses for their vehicle lines. Completing brand-specific programs can lead to certifications that are highly valued by employers.
How long does automotive mechanic training take?
Training duration varies by path and the level of expertise desired. Typical timelines include:
- Certificate programs: about 6–12 months
- Associate degree: usually 2 years
- Apprenticeships: commonly 2–4 years
- Bachelor’s degree (for management, engineering, or advanced technical roles): roughly 4 years
Learning doesn’t stop after graduation. Mechanics often take continuing education and manufacturer updates to keep pace with evolving automotive technologies and repair methods.
Career prospects for trained automotive mechanics
Job outlook for trained mechanics is steady. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projects about 4% employment growth for automotive service technicians and mechanics from 2021 to 2031 — roughly in line with the average for all occupations. Trained technicians can find roles in a wide array of settings, including:
- New and used automobile dealerships
- Independent repair and specialty shops
- Fleet maintenance operations (delivery, rental, municipal)
- Automotive parts retailers with service centers
- Government vehicle maintenance divisions
- Self-employment or owning a repair shop
With experience and extra certifications, technicians can progress into lead technician roles, shop supervisory or management positions, or specialize in niches like diesel engines, performance tuning, hybrid systems, or electric vehicle (EV) repair.
Costs associated with automotive mechanic training
Training expenses vary by program and institution. Typical cost ranges are:
- Certificate programs (technical schools): approximately $5,000–$20,000
- Associate degrees (community colleges): approximately $10,000–$25,000
- Bachelor’s degrees (universities): often $40,000–$100,000+ depending on school
- Apprenticeships: costs vary, but many apprenticeship routes pay participants while they learn
These estimates may cover tuition, required textbooks, tools, and lab fees. Many students qualify for financial aid, scholarships, or employer-sponsored programs that help offset costs. Apprenticeships are particularly attractive for those who prefer to earn pay while gaining real-world experience.
How to choose the right training program
When comparing programs, evaluate several important factors:
-
Accreditation: Verify the program is accredited by respected organizations such as the National Automotive Technicians Education Foundation (NATEF) or similar regional accrediting bodies.
-
Curriculum breadth: Ensure courses address modern automotive systems, including electronics, diagnostics, and alternative powertrains (hybrids and EVs).
-
Facilities and equipment: Look for up-to-date shops and diagnostic tools that reflect what’s used in the industry today.
-
Industry partnerships: Programs with ties to manufacturers, dealerships, or local businesses can offer internships, apprenticeships, or better job placement.
-
Instructor experience: Instructors with real-world shop experience and technical certifications typically deliver more practical, career-ready training.
-
Career services: Job placement help, resume support, and interview coaching ease the transition into the workforce.
-
Cost and financial aid: Compare total costs and available funding options to find a program that fits your budget.
Selecting a program that balances accreditation, modern curriculum, strong industry connections, and reasonable cost will help position you for success.
Conclusion
Completing quality automotive mechanic training can open the door to a stable, rewarding career in a field that continues to evolve. With the right combination of education, hands-on experience, and ongoing professional development, you can become a competent technician equipped to work on everything from traditional internal combustion engines to the latest hybrid and electric vehicles. Given steady demand for skilled technicians, now is a good time to explore training options and begin building your automotive career.