Complete Hair Transplant Guide: Restore Hair with FUE & FUT
Explore a comprehensive guide to hair transplantation, including modern methods like FUE and FUT, candidacy criteria, recovery timelines, expected longevity, and cost estimates. Learn what to expect from eyebrow or scalp restoration and how to choose the right approach for lasting, natural results.
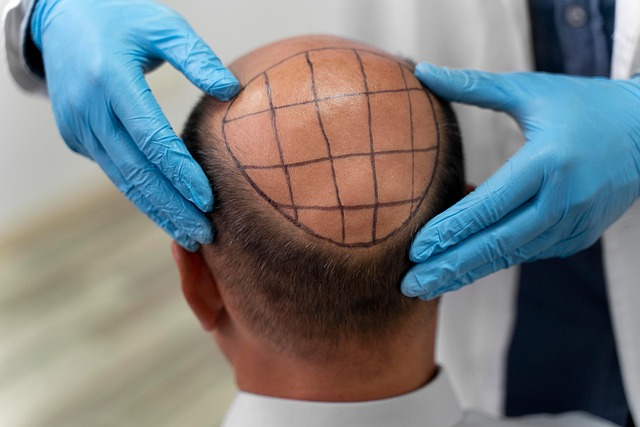
Hair transplantation rebuilds hair in areas affected by thinning or baldness by moving robust follicles from donor zones to places with reduced growth. Typically, grafts are taken from the back and sides of the scalp—areas genetically resistant to hair loss—and implanted into the recipient region. Once relocated, these follicles usually continue to produce hair in their new location, offering a long-term cosmetic improvement.
Contemporary methods: FUE and FUT
Two principal surgical techniques are commonly used today: Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE). Both seek the same outcome—natural-looking regrowth—but the way donor hair is harvested differs.
-
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT): FUT involves removing a narrow strip of scalp from the donor area, which is then dissected into individual follicular units under magnification. These grafts are placed into small recipient incisions. FUT often enables large graft numbers in a single session and can be cost-effective for extensive restorations. The main trade-off is a linear scar at the donor site that may be visible if hair is cut very short.
-
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE): With FUE, surgeons extract individual follicular units directly from the donor area using a tiny punch device. Each isolated graft is then transplanted into the thinning area. FUE produces minimal detectable scarring and generally allows faster donor healing. It can be more time-consuming and, depending on the clinic and tools used, sometimes more expensive for high graft counts.
Both approaches are reliable when performed by experienced specialists. Which one suits you best depends on factors like the extent of hair loss, how many grafts are needed, scalp tightness, scarring concerns, and patient preferences.
Who benefits from a transplant?
Hair transplantation can help a wide range of people, but it isn’t appropriate for everyone. Good candidates typically include:
- Men with male pattern baldness seeking permanent restoration
- Women with concentrated thinning or receding hairlines
- People with hair loss from injury, burns, or surgical scars
- Those seeking eyebrow, beard, or facial hair reconstruction
- Anyone with realistic expectations and enough healthy donor hair
A consultation with a board-certified hair restoration physician is crucial. The clinician will assess donor density, the pattern and progression of hair loss, overall health, and potential underlying causes that might influence results.
Recovery: a typical timeline
Healing varies between individuals and techniques, but many patients experience similar stages:
-
Immediate postoperative days: Mild discomfort, swelling, and tenderness are common. Surgeons often prescribe pain relief and may recommend antibiotics. Avoid strenuous exercise and prolonged sun exposure.
-
First week: Small scabs appear around implanted grafts. Patients should follow clinic instructions for gentle washing and resist picking at scabs.
-
Two to three weeks: The visible shafts of transplanted hair often shed in a process called shock loss. This is normal and clears the way for new growth.
-
Three to four months: New hair typically begins to emerge. Early growth may be fine and thin but will thicken over time.
-
Six to twelve months: Noticeable improvement in coverage and texture. Some patients continue to see maturation and increased density up to 12–18 months.
Adhering to postoperative directions enhances healing and outcomes. Factors like smoking, certain medications, and nutritional status can hinder recovery and should be reviewed with the surgeon.
Durability of results
A key benefit of transplantation is its permanence. Grafts are taken from scalp regions that are less susceptible to genetic hair loss, so transplanted follicles tend to retain that resistance and can last for many years or a lifetime. That said, natural hair loss may progress in untreated areas, and additional sessions could be desired later to increase density or address new thinning.
Cost overview
| Procedure Type | Average Cost Range | Factors Affecting Price |
|---|---|---|
| FUT (Strip Method) | $4,000 - $15,000 | Number of grafts; surgeon experience; clinic location |
| FUE | $4,000 - $20,000 | Graft count; technology used; extraction speed |
| Eyebrow Transplant | $3,000 - $8,000 | Procedure complexity; artistic skill required |
Prices are estimates and may vary by clinic, region, and patient needs. Independent research is recommended before making financial commitments.
Many clinics provide financing plans to spread the cost. In rare cases, such as reconstructive surgery after trauma, insurance may cover part or all of the expense.
Deciding if it’s right for you
Choosing hair transplantation is both a medical and personal decision. Prepare for consultations by reviewing before-and-after photos, asking about the surgeon’s experience with your chosen method, and clarifying what follow-up care is included. Expect an honest conversation about achievable density, possible scarring, and the potential need for future procedures. A customized plan and realistic expectations are essential for satisfaction.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.




