Complete Hair Transplant Guide: Restore Your Hairline
Struggling with thinning hair or a receding hairline? This in-depth guide explores hair transplantation options, including FUE and FUT techniques, candidacy, risks, recovery timelines, costs, and maintenance tips. Learn what to expect and how to choose the right approach for lasting hair restoration results.
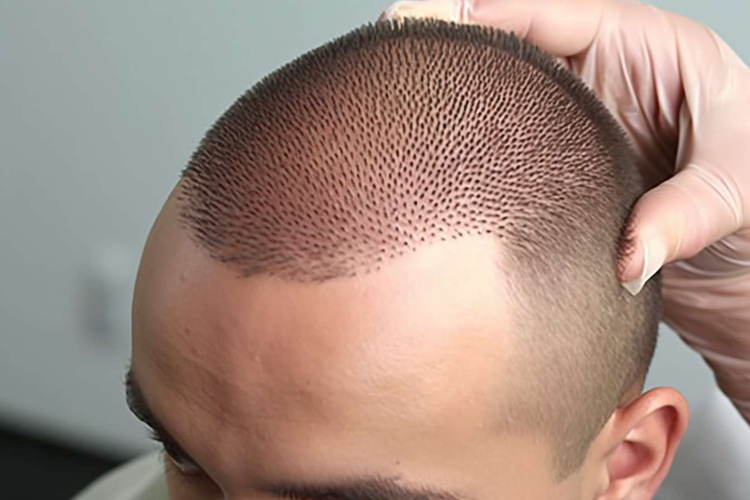
Hair transplantation can offer a long-term way to rebuild a natural-looking hairline for people affected by pattern baldness or localized hair loss. This guide walks through the main surgical approaches, who typically benefits, potential complications, the timeline for visible growth, cost comparisons, and practical aftercare advice to help you make an informed decision.
Surgical techniques: FUT and FUE explained
Two primary surgical methods are used today: Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE). FUT, sometimes called the strip method, involves removing a thin strip of skin from a donor area—usually the back of the scalp—then dissecting it into individual follicular units under magnification for implantation. This approach can yield a larger number of grafts in one session but leaves a linear scar where the strip was taken.
FUE takes a different approach by harvesting individual follicular units directly from the donor zone using a small punch instrument. Because grafts are removed one at a time, FUE typically results in tiny, dot-like scars that are less noticeable and allows patients to wear shorter hairstyles. Both techniques rely on careful planning and strategic placement of grafts to recreate a natural hairline and hair direction.
Who makes a good candidate?
Hair transplantation isn’t suitable for everyone. Ideal candidates often include:
- Men and women with androgenetic (male or female pattern) hair loss
- Individuals whose hair loss has stabilized rather than rapidly advancing
- People who have adequate donor hair to cover the areas of thinning
- Those in generally good health without medical issues that impede healing
- Patients with realistic expectations about the outcome and commitment to post-op care
A qualified hair restoration specialist will evaluate your hair pattern, donor density, medical history, and goals during a consultation to determine whether a transplant is appropriate.
Potential risks and side effects
As with any surgical procedure, hair transplants carry risks. Common complications and side effects include:
- Infection at donor or recipient sites
- Bleeding or the development of scars (linear with FUT, tiny punctate scars with FUE)
- Temporary or occasionally longer-lasting numbness in treated areas
- Irregular or unnatural hair growth patterns if grafts are poorly placed
- Folliculitis, an inflammation of hair follicles
- Shock loss—temporary shedding of existing native hair around grafts
- Failure of some transplanted follicles to establish and grow
Most side effects resolve with proper wound care and follow-up. Choosing an experienced surgeon and following pre- and post-operative instructions reduces risk and improves the chance of a satisfying result.
What to expect after surgery: timeline for growth
Hair transplant results develop gradually; patience is essential. Typical stages include:
- Weeks 1–2: Transplanted hairs often shed—a normal, expected phase as follicles transition.
- Months 2–3: Grafts enter a resting or dormant phase before active growth resumes.
- Months 3–6: New hairs begin to emerge from transplanted follicles.
- Months 6–12: Hair becomes thicker and more abundant as growth continues.
- 12–18 months: Most patients see the final cosmetic outcome, with full maturation of transplanted hairs.
Individual timelines vary by age, health status, and how closely post-op care guidelines are followed.
| Treatment | Provider Type | Estimated Cost Range | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| FUE Hair Transplant | Specialized Clinics | $4,000 - $15,000+ | Minimally invasive, natural-looking, permanent solution |
| FUT Hair Transplant | Specialized Clinics | $4,000 - $10,000+ | Can implant larger graft numbers, often lower cost per graft |
| Non-surgical Hair Systems | Hair Replacement Centers | $1,000 - $3,000+ (initial cost) | Immediate coverage, non-invasive, requires ongoing upkeep |
| Medication (e.g., Finasteride, Minoxidil) | Pharmacies, Doctors | $10 - $100+ per month | Non-invasive, may slow hair loss, needs continuous use |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Maintaining and protecting your results
Long-term success depends on both the surgery and how you care for your scalp afterward. Practical steps include:
- Adhere strictly to your surgeon’s post-operative care plan, including wound care and activity restrictions
- Use mild hair care products and avoid chemical or heat-heavy treatments until cleared by your doctor
- Protect the scalp from sun exposure in the early healing months
- Discuss medications such as finasteride or minoxidil with your physician to maintain native hair and support transplanted follicles
- Eat a balanced diet, manage stress, and maintain overall health to support hair growth
- Keep scheduled follow-up visits so your surgeon can monitor healing and address concerns
Choosing an experienced, credentialed surgeon and realistic planning help ensure the best cosmetic and functional results.
Deciding to pursue a hair transplant is a personal choice that requires careful evaluation. Speak with a board-qualified hair restoration specialist to review your pattern of hair loss, donor availability, and expectations before committing to surgery. This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.




