E-Bikes Powering Change: Reinventing Urban Transportation
Electric bicycles are reshaping how people move through cities. Combining pedal power with electric assistance, e-bikes make commuting faster, less strenuous, and more sustainable. Learn how these bikes cut congestion and emissions, save money over time, and fit into evolving urban infrastructure and transit networks.
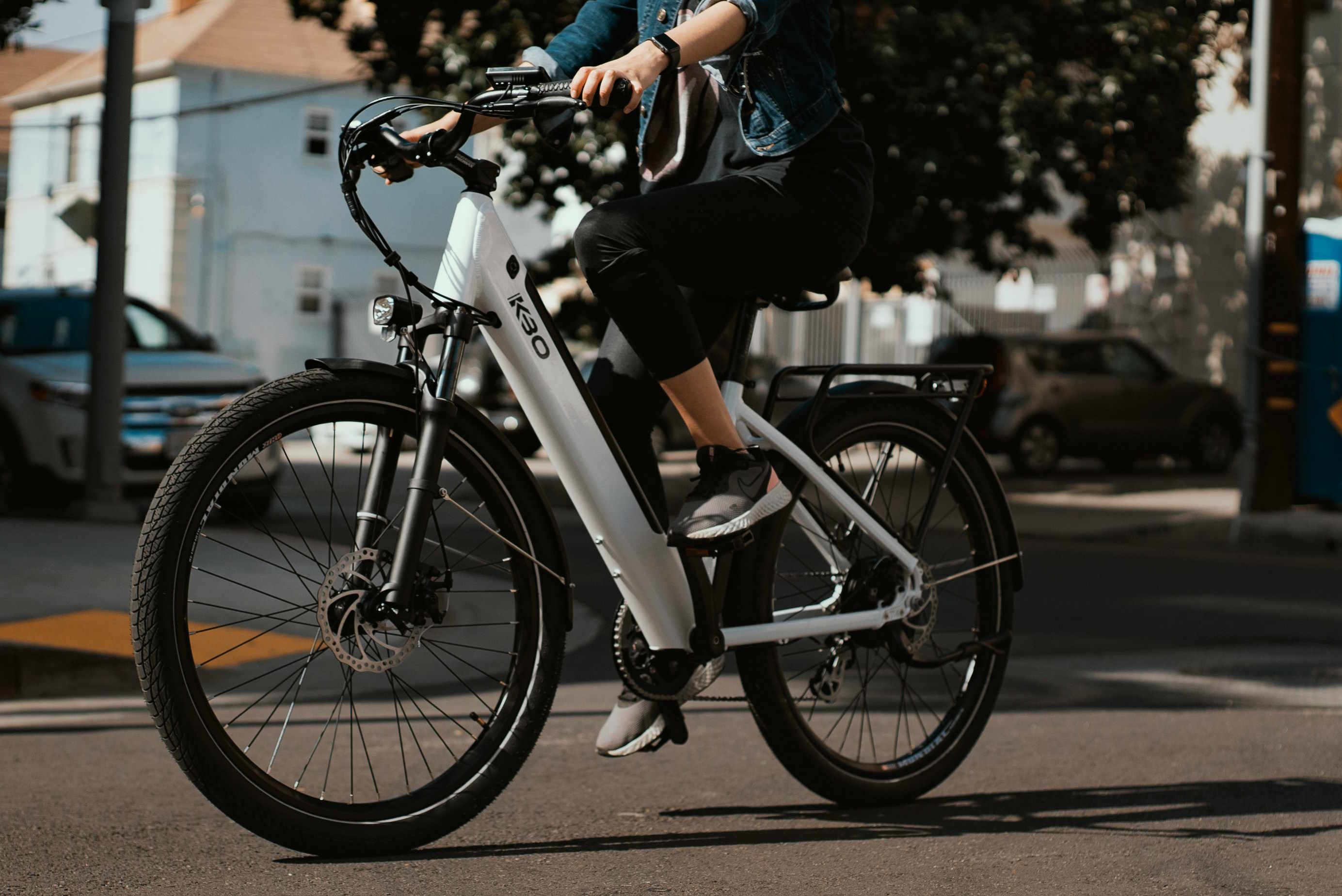
Cities around the world are witnessing a quiet revolution on two wheels. Electric bicycles, or e-bikes, blend traditional cycling with battery-powered assistance to create a transport option that is efficient, low-emission, and practical for daily use. As urban areas contend with traffic, air quality issues, and limited space, e-bikes are emerging as a compelling alternative to cars and even some public transit trips.
How do e-bikes differ from traditional bicycles?
At their core, e-bikes add an electric motor and a rechargeable battery to the familiar bicycle platform. This electric assist reduces the physical effort required to pedal, making it easier to climb hills, push through headwinds, and cover longer distances without fatigue. Most e-bikes use pedal-assist systems that amplify a rider’s pedaling, while some models also offer a throttle for on-demand power without pedaling.
Manufacturers typically include multiple assistance levels so riders can control how much motor support they receive, from a light boost to near full assistance. Despite the motor, many e-bikes still require pedaling in assisted modes, preserving the health benefits of cycling while extending range and convenience. This combination distinguishes e-bikes from purely manual bicycles and from motorized scooters or mopeds that rely solely on a throttle.
What are the benefits of using an e-bike for commuting?
E-bikes make urban commuting more accessible and attractive for a wide range of people. Key advantages include:
- Reduced exertion: Riders can travel longer distances or tackle steep terrain without arriving sweaty or exhausted, which is especially valuable for commuting to work.
- Faster trip times: Electric assistance often increases average speed versus a conventional bike, helping riders shorten commute times without the cost of driving.
- Cargo capacity: The extra power makes it easier to carry groceries, work gear, or child seats, turning a single vehicle into a versatile hauler for errands and family trips.
- Health and wellbeing: Because most e-bikes encourage pedaling, they still provide aerobic activity, improving fitness compared with passive transport modes.
- Environmental gains: Shifting short car trips to e-bikes reduces vehicle emissions and helps ease congestion, contributing to cleaner, more livable streets.
These benefits combine to make cycling a viable option for commuters who might otherwise avoid traditional bikes due to distance, topography, or the need to look professional on arrival.
Are e-bikes cost-effective compared to other transportation methods?
While an e-bike typically costs more up front than a standard bicycle, it can be far cheaper to operate than a car or long-term transit use. Major cost factors include:
- Purchase price: E-bikes range from a few hundred dollars for basic models to several thousand for premium builds with advanced motors and components.
- Running costs: Charging batteries is inexpensive compared with gasoline, and maintenance is similar to regular bikes with some added attention for electrical components.
- Savings on fees: Owners avoid parking costs, many tolls, and can significantly reduce public transit fares or ride-hailing expenses over time.
- Depreciation and lifespan: Quality e-bikes can provide years of reliable service; battery replacement is a periodic cost but is getting cheaper as technology improves.
Taken together, for people who replace regular car commutes or frequent short transit trips with an e-bike, total ownership costs can be substantially lower over several years.
| Model | Type | Key Features | Typical Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rad Power Bikes RadCity 5 Plus | Commuter | 750W motor, up to 50-mile range, built-in lights | $1,999 |
| Trek Verve+ 2 | Hybrid | Bosch drive system, long-range battery, comfort geometry | $2,699 |
| Specialized Turbo Vado 4.0 | Urban | Efficient 250W motor, extended range, integrated display | $3,500 |
| VanMoof S3 | Smart Bike | Automatic electronic shifting, anti-theft tech | $2,298 |
| Aventon Pace 500 | Cruiser | 750W motor, ~40-mile range, throttle option | $1,699 |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
How are e-bikes impacting urban transportation and infrastructure?
The growth of e-bikes is prompting cities to rethink mobility planning. Municipal responses include expanding protected bike lanes, integrating e-bikes into public bike-share programs, and revising traffic rules to account for higher average speeds and the unique performance of electric-assist cycles. These adaptations aim to increase safety and make active transportation a practical choice for more residents.
E-bike adoption also raises policy questions related to parking, charging infrastructure, and regulation. Cities are experimenting with curb management, secure bike parking, and fast-charging hubs, while lawmakers consider where e-bikes fit within vehicle classifications and helmet or speed rules. Transit agencies are exploring e-bikes as a complement to rail and bus systems, particularly for first- and last-mile connections that can expand the practical catchment area of transit stops.
As more commuters switch to e-bikes, the potential benefits include reduced car dependency, quieter streets, and improved urban air quality. These shifts support broader sustainability goals and can make cities more human-scaled and resilient.
E-bikes are not a silver bullet, but they offer a pragmatic, scalable way to transform everyday travel in dense environments. With continued improvements in battery technology, lower costs, and smarter urban planning, electric bicycles are positioned to play an increasingly central role in the future of city mobility.