Eczema Essentials: Tackling Atopic Dermatitis
Discover the ins and outs of atopic dermatitis, a widespread skin condition affecting millions globally. This comprehensive guide delves into the root causes, telltale signs, and cutting-edge treatment options for eczema. Whether you're grappling with this condition or supporting someone who is, gain valuable insights to effectively manage symptoms and enhance quality of life. Uncover expert strategies for soothing irritated skin and breaking the itch-scratch cycle.
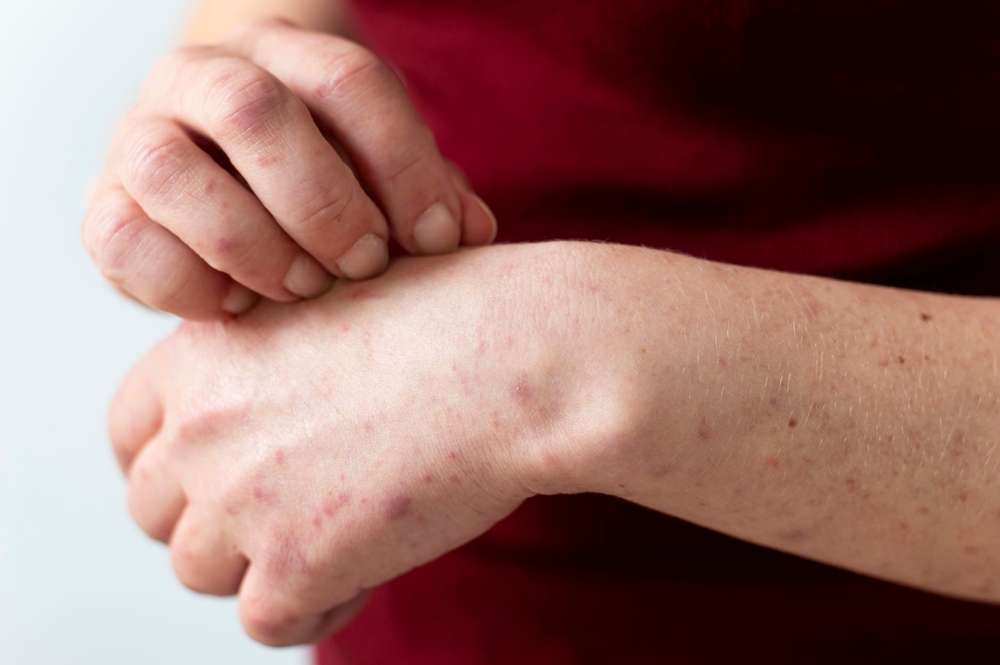
Living with atopic dermatitis, commonly known as eczema, can be a challenging experience. This chronic skin condition not only causes physical discomfort but can also take a toll on one’s emotional well-being. Let’s explore the complexities of atopic dermatitis and arm ourselves with knowledge to better manage this persistent skin ailment.
Recognizing the Signs: Beyond the Itch
While itching is a hallmark symptom of atopic dermatitis, it’s crucial to be aware of other indicators:
- Skin dryness and flakiness
- Redness and inflammation
- Rough, scaly patches
- Oozing or crusting in severe cases
- Skin thickening (lichenification)
- Heightened skin reactivity
These symptoms typically manifest in specific body areas, such as facial regions, hands, feet, and flexural zones like elbow and knee creases. Infants may experience rashes on their scalp and cheeks. The relentless itching associated with eczema often disrupts sleep patterns and daily activities, significantly impacting overall quality of life.
Unraveling the Mystery: Causes and Risk Factors
The precise etiology of atopic dermatitis remains elusive, but research points to a complex interplay of genetic predisposition and environmental triggers. Key factors contributing to its development include:
- Hereditary influences: A family history of atopic conditions elevates the risk.
- Immune system irregularities: An overactive immune response can lead to skin inflammation.
- Compromised skin barrier: Genetic mutations may impair the skin’s ability to retain moisture and ward off irritants.
- Environmental catalysts: Exposure to certain allergens, irritants, or climatic conditions can exacerbate symptoms.
While atopic dermatitis can affect individuals of all ages, it frequently emerges in early childhood, often before age five. Some people may experience symptom improvement or resolution as they mature, while others continue to face flare-ups throughout adulthood.
Navigating Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Diagnosing atopic dermatitis typically involves a comprehensive evaluation by a dermatologist or healthcare professional. The process includes:
- Thorough skin examination
- Review of medical history
- Potential allergy testing to identify triggers
Treatment strategies aim to alleviate symptoms, prevent flare-ups, and enhance overall skin health. A multifaceted approach may encompass:
- Diligent moisturizing: Regular use of emollients to hydrate skin and bolster its protective barrier.
- Topical medications: Prescription creams or ointments to reduce inflammation and itching.
- Systemic treatments: Oral antihistamines or immunosuppressants for severe cases.
- Light therapy: Controlled UV exposure to diminish inflammation.
- Lifestyle adjustments: Identifying and avoiding triggers, maintaining a consistent skincare regimen, and implementing stress management techniques.
When to Seek Professional Help
While mild eczema can often be managed with over-the-counter remedies and proper skincare, certain situations warrant medical attention:
- Persistent or severe symptoms unresponsive to home treatments
- Widespread rash coverage
- Significant sleep disturbances due to itching
- Signs of skin infection (increased redness, warmth, or purulent discharge)
- Substantial impact on daily functioning or quality of life
A healthcare provider can assess the condition’s severity, develop a tailored treatment plan, and offer guidance on long-term management strategies.
Empowering Self-Care: Home Management Techniques
In addition to medical interventions, individuals can take proactive steps to manage atopic dermatitis and minimize flare-ups:
- Establish a gentle skincare routine: Use fragrance-free cleansers and apply moisturizer liberally, especially after bathing.
- Identify and eliminate triggers: Be mindful of common culprits like certain fabrics, soaps, or environmental factors.
- Implement stress-reduction practices: Incorporate relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or mindfulness meditation.
- Utilize cool compresses: Apply damp, cool cloths to soothe itchy and inflamed areas.
- Practice proper nail care: Keep nails trimmed and consider wearing gloves at night to prevent inadvertent scratching during sleep.
- Choose skin-friendly attire: Opt for soft, breathable fabrics and avoid potential irritants like wool or synthetic materials.
By combining medical treatments with these self-care strategies, many individuals with atopic dermatitis can effectively manage their symptoms and improve their overall quality of life. Remember to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a comprehensive management plan tailored to your unique needs.
This article serves informational purposes only and should not be construed as medical advice. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider for personalized guidance and treatment options.




