Effective Eczema Treatment for Skin Rash and Itching
Eczema is a common inflammatory condition that causes red, dry, and itchy patches on the skin. For many people it’s episodic — flaring in response to triggers like stress, allergens, or changes in weather — while for others it may be chronic and require ongoing management. This article explains what eczema is, how it affects the skin, why it causes rash and itching, when dermatology care is recommended, and practical treatment options you can discuss with a clinician. Note: an external API request for additional resources returned Service Unavailable: , so some supplementary checks could not be retrieved; rely on trusted clinical guidance and local services for the latest details.
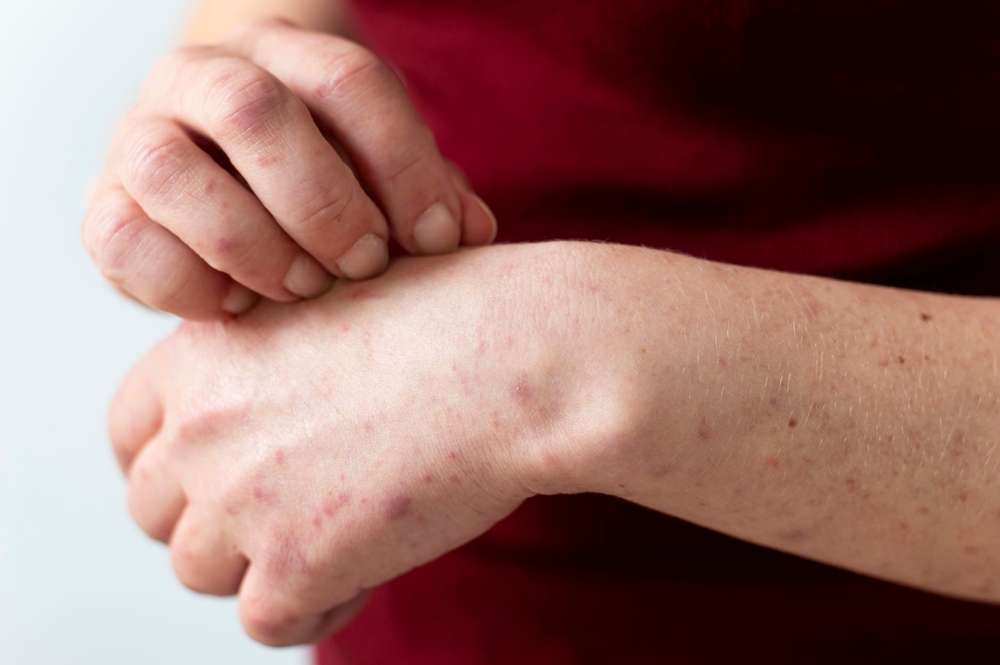
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.
What is eczema?
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis in many cases, is a group of inflammatory skin conditions characterized by dry, itchy, and often red or scaly patches. It’s linked to a combination of genetic and environmental factors that affect the skin’s barrier function and immune response. People with eczema may have a family history of allergic conditions such as asthma or hay fever. The condition can appear at any age but often starts in childhood; severity and pattern vary widely between individuals.
How does eczema affect the skin?
Eczema disrupts the skin’s protective barrier, allowing moisture to escape and irritants to enter more easily. This leads to dryness, cracking, and increased sensitivity. Repeated scratching can further damage the skin, increasing the risk of secondary infections. Affected areas commonly include the face, hands, inner elbows, and behind the knees, but eczema can appear almost anywhere. Restoring the barrier with moisturizers, avoiding known irritants, and treating inflammation are central strategies to manage how eczema impacts the skin.
Why does eczema cause rash and itching?
Itching in eczema is driven by immune activation and nerve signaling in damaged skin. When the barrier is compromised, environmental allergens and microbes trigger an immune response that releases inflammatory chemicals. These mediators make the nerves in the skin more sensitive, producing the persistent urge to scratch. Scratching worsens the rash and inflammation, creating a cycle of itching and skin damage. Effective management focuses on breaking that cycle using moisturization, anti-inflammatory treatments, and itch-relief strategies.
When should you see dermatology or local services?
You should consider seeing a dermatologist or qualified local services if symptoms are severe, widespread, recurrent despite basic care, or if you suspect skin infection (increasing redness, warmth, pain, or pus). Dermatology care is also important when eczema affects sleep, daily functioning, or mental health. A specialist can confirm the diagnosis, identify triggers, recommend prescription topical or systemic therapies, and advise on allergy testing or patch testing when relevant. If you’re unsure, primary care providers can often triage and refer to dermatology in your area.
Practical eczema treatment options
Treatment aims to restore the skin barrier, reduce inflammation, and control itching and triggers. First-line self-care includes regular fragrance-free emollients applied liberally and often, gentle cleansers, lukewarm baths, and avoiding harsh soaps or known irritants. Over-the-counter hydrocortisone 1% may help short-term for mild flares. Prescription options from dermatology include topical corticosteroids of varying strengths, topical calcineurin inhibitors (non-steroidal anti-inflammatories), and newer non-steroidal topical agents. For moderate to severe eczema, dermatologists may consider phototherapy or systemic medications, such as targeted biologic therapies or immunomodulators. Behavioral strategies — wet wraps, stress reduction, and avoiding triggers — are also valuable.
Managing rash, itching, and daily care
Daily routines and trigger management make a big difference for many people. Keep nails short to reduce damage from scratching, use humidifiers in dry environments, and choose cotton clothing to minimize irritation. For intense itching, non-sedating antihistamines sometimes help with allergic contributors, while sedating antihistamines may assist sleep in select cases under clinician advice. Watch for signs of infection (increased pain, spreading redness, or yellow crusting) and seek prompt care when they appear. Coordinate with a healthcare professional to develop a personalized plan that balances topical care, lifestyle adjustments, and, when needed, prescription therapies.
Conclusion
Eczema treatment is individualized: what works for one person may not work for another. Combining consistent skin care to restore the barrier, targeted anti-inflammatory treatments for flares, and practical strategies to limit irritation and scratching yields the best outcomes. If symptoms persist, worsen, or affect quality of life, consult a dermatologist or local services for assessment and a tailored treatment plan. “””




