Egg Processing Careers: Industry Overview & Insights
Dive into the egg processing sector and learn how eggs travel from producers to consumers. This in-depth guide highlights roles, essential skills, and the technology transforming egg production. Ideal for job seekers and industry-curious readers seeking insights on food safety, automation, and career pathways in egg processing.
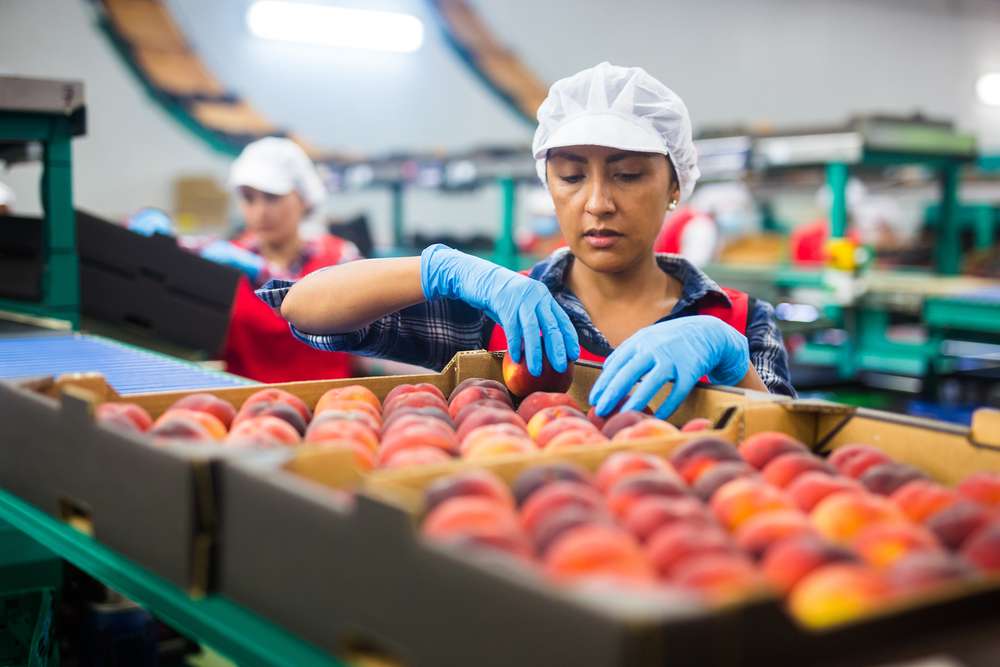

The egg processing industry is a key link in the food supply chain, responsible for making sure eggs arrive at retailers and kitchens in a safe, consistent, and efficient manner. This guide outlines the varied scales of operations, the working environment, the skills employers value, recent technological advances, potential career paths, and typical working conditions. Note: this overview provides general information about the sector and is not a source of specific job vacancies or employment guarantees.
Understanding the egg processing environment
Operations in this sector range from small family-run facilities to highly automated industrial plants. While smaller sites often rely more on hands-on processes, larger enterprises incorporate automated lines and sophisticated monitoring systems. No matter the size, precision, strict hygiene, and operational efficiency remain core priorities.
Key elements commonly found in egg processing settings include: 1. Temperature control: Facilities keep eggs in cool conditions to protect freshness and quality. 2. Sanitation protocols: Comprehensive cleaning and hygiene standards are enforced to reduce contamination risk. 3. Technology integration: Equipment can vary from simple conveyors to advanced optical graders and sorters. 4. Safety measures: Use of personal protective equipment such as hairnets, gloves, and other safeguards is standard practice.
Skills valued in egg processing
Entry-level roles may not demand formal qualifications, but several personal attributes and practical skills are frequently sought by employers: 1. Physical stamina: Positions often require standing for long periods and repeating tasks. 2. Attention to detail: Spotting cracks, foreign material, or size inconsistencies is critical to maintaining product quality. 3. Basic numeracy: Workers commonly perform counting, weighing, and simple calculations. 4. Food safety awareness: Knowledge of contamination risks and hygiene practices is essential. 5. Teamwork: Many processes depend on coordinated efforts across a production team. 6. Adaptability: Employees who can learn procedures and handle new technology are preferred.
Many businesses provide on-the-job training to teach specific machinery or processes. In larger establishments, certifications in food safety or related areas may be advantageous or required for some roles.
Technological advancements reshaping the industry
Recent innovation has altered how work is carried out in egg processing plants, shifting labor away from some manual tasks and creating demand for technical skills. Notable developments include: 1. Automated sorting and grading systems that classify eggs by size and quality. 2. Robotic packaging solutions that increase speed and consistency. 3. Advanced conveyor and material-handling networks that streamline flow through production stages. 4. Digital inventory and production management tools that improve traceability and planning. 5. Machine-vision quality control systems that detect surface defects and foreign matter.
As automation grows, roles focused on operating, programming, and maintaining machinery are becoming more prominent. Comfort with computerized systems and troubleshooting is increasingly valuable for workers.
Industry landscape and potential career pathways
The sector offers a range of positions and opportunities for progression. Depending on employer size and location, typical career trajectories might include: 1. Quality assurance specialist: Monitoring standards, conducting inspections, and ensuring compliance with safety protocols. 2. Production line supervisor: Overseeing day-to-day operations, coordinating staff, and managing workflow. 3. Equipment maintenance technician: Performing routine maintenance and repairs on mechanical and electrical systems. 4. Food safety coordinator: Implementing hygiene programs, conducting audits, and training staff. 5. Operations manager: Managing broader facility performance, budgeting, and strategic planning.
Skills gained in egg processing are transferable to other food production segments, agricultural technology roles, or positions in supply chain and logistics. The industry�s emphasis on food safety and quality control provides practical experience valued across the broader food and beverage sector.
Working conditions and practical considerations
Typical conditions in egg processing facilities include: 1. Climate-controlled environments to keep product quality intact. 2. Shift-based scheduling that may include overnight or weekend shifts to meet production demands. 3. Rigid hygiene and safety procedures, with mandatory use of protective clothing and adherence to cleaning routines. 4. Physically demanding or repetitive tasks that require stamina and attention. 5. Fast-paced production targets that require consistent productivity.
Employees should also be prepared for operational noise, strong smells associated with food processing, and the need to follow strict safety protocols around machinery. Employers generally strive to create safe and comfortable workplaces, but the nature of food production involves inherent challenges.
Conclusion
Egg processing remains an essential part of the food system, combining traditional practices with modern technology to deliver safe, high-quality products. This overview provides insight into the environments, skills, and roles commonly found in the sector and highlights how technological change is reshaping job functions. For those exploring careers in food production, the egg processing industry offers practical experience and several pathways for growth, though this article does not list specific job openings or guarantee employment.