Guidance on Maintaining Fungal-Free Skin
Maintaining healthy skin involves understanding various conditions, including fungal infections like ringworm. This common skin condition, medically known as tinea, is caused by dermatophytes, a type of fungus that thrives on the dead tissues of the skin, hair, and nails. Recognizing the signs and implementing effective strategies for prevention and treatment are crucial steps in ensuring your skin remains clear and free from these persistent infections.
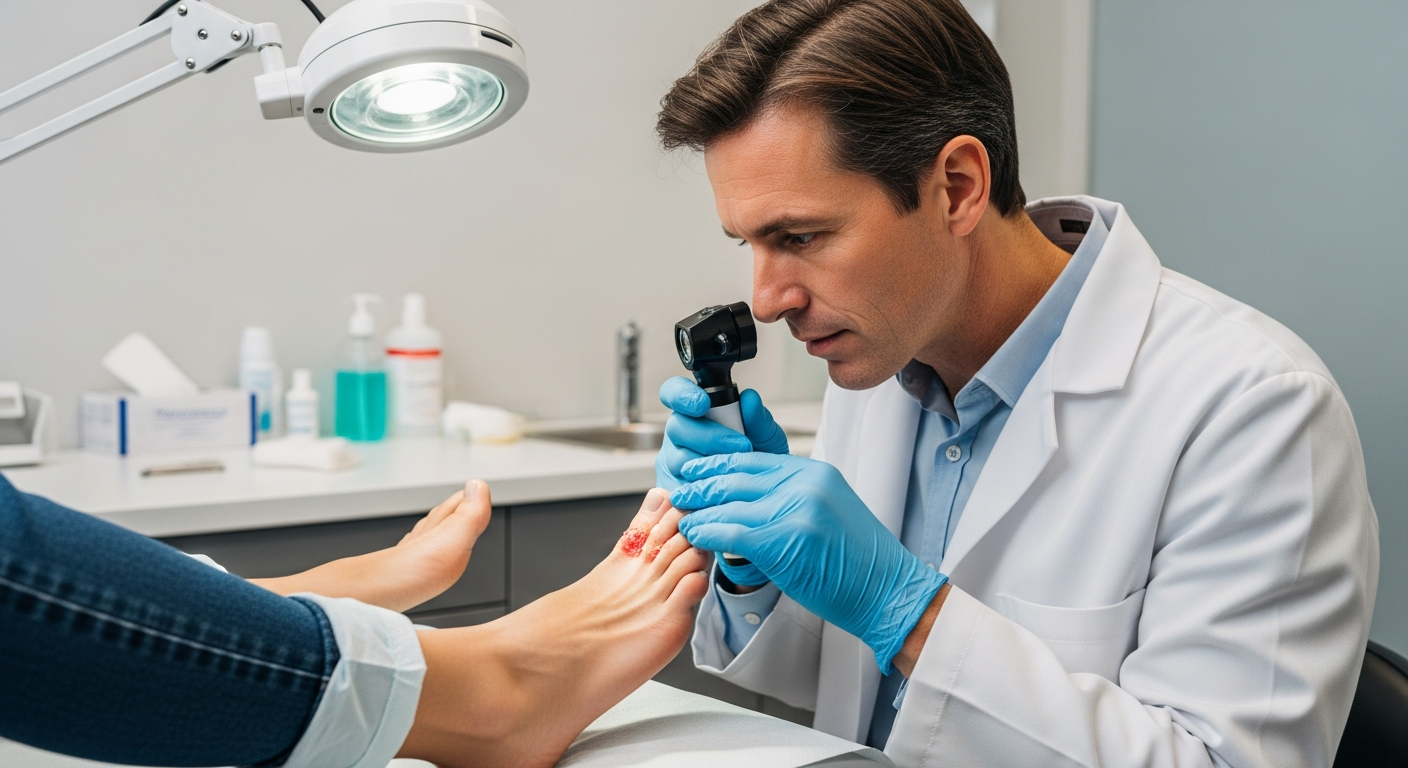
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.
What are the common symptoms of a fungal skin infection?
Fungal skin infections, often referred to as ringworm or tinea, manifest with distinct symptoms that can help in early identification. The most recognizable sign of a dermatophyte infection on the skin is a red, itchy, circular rash with raised edges and a clearer center, giving it a ring-like appearance. However, the exact presentation can vary depending on the affected body part. For instance, on the feet (tinea pedis or athlete’s foot), it might appear as scaling, redness, itching, or blistering between the toes. On the scalp (tinea capitis), it can lead to scaly patches, hair loss, and even inflammation.
Other common symptoms across different areas include persistent itching, flaking or peeling skin, redness, and sometimes a burning sensation. The infection can also affect the groin (tinea cruris or jock itch), nails (tinea unguium or onychomycosis), and other parts of the body. Prompt recognition of these signs is vital for effective management and to prevent the spread of the fungus to other areas or individuals.
How does ringworm spread and what are prevention strategies?
Ringworm is highly contagious and spreads through direct contact with an infected person or animal, as well as indirectly through contaminated objects. Sharing personal items like towels, clothing, combs, or sports equipment can facilitate the transmission of the fungal infection. Warm, moist environments, such as locker rooms, public showers, and swimming pools, are common breeding grounds for dermatophytes, increasing the risk of exposure. Poor hygiene practices also contribute to its spread.
Effective prevention strategies involve maintaining good personal hygiene. Regularly washing the skin with soap and water, especially after sweating or participating in activities where exposure might occur, is fundamental. It is important to keep the skin dry, particularly in areas prone to moisture like between toes, in skin folds, and the groin. Wearing clean, breathable clothing, changing socks daily, and avoiding sharing personal items are also key measures. Inspecting pets for signs of fungal infection can also help prevent transmission, as animals are common carriers of this type of fungus.
What are effective remedies and solutions for ringworm?
Addressing a fungal skin infection effectively involves a range of remedies and solutions, depending on the severity and location of the infection. For localized and mild cases, over-the-counter (OTC) antifungal creams, lotions, powders, or sprays are often the first line of defense. These products typically contain active ingredients such as miconazole, clotrimazole, terbinafine, or tolnaftate, which work by inhibiting fungal growth or killing the fungus directly. Consistent application for the recommended duration, even after symptoms subside, is crucial for complete healing and to prevent recurrence.
In more widespread or persistent cases, or when the infection affects the scalp or nails, a healthcare professional may prescribe stronger topical medications or oral antifungal drugs. Oral medications are particularly effective for infections that are difficult to reach with topical treatments or those that are deeply embedded. These solutions aim to eradicate the fungus from within, promoting recovery and providing relief from symptoms. Adhering to the full course of prescribed medication is essential for successful management of the infection.
Understanding topical and oral treatments for fungal skin conditions
Topical treatments are applied directly to the affected skin area and are generally effective for superficial fungal infections. These creams, ointments, and sprays penetrate the outer layers of the skin to deliver antifungal agents directly to the site of the infection. They are typically used for several weeks, and continuous application is vital to ensure all fungal elements are eliminated, even if the visible symptoms of the tinea infection have improved. Proper application, often involving cleaning and drying the area before treatment, enhances their efficacy in promoting skin healing.
Oral antifungal medications are usually reserved for more severe, widespread, or stubborn fungal conditions, especially those affecting the hair, scalp, or nails, where topical treatments may not adequately penetrate. These medications, such as fluconazole, itraconazole, or griseofulvin, work systemically throughout the body to target the dermatophyte. While highly effective, oral treatments can have side effects and require careful monitoring by a healthcare provider. The duration of oral treatment can vary significantly, from weeks to several months, depending on the specific infection and its response to therapy, leading to a full recovery from the infection.
| Product/Service Type | Provider/Typical Brands | Cost Estimation (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Antifungal Cream (OTC) | Lotrimin AF, Lamisil AT, Tinactin | $8 - $20 |
| Antifungal Spray (OTC) | Desenex, Micatin | $10 - $25 |
| Antifungal Powder (OTC) | Zeasorb, Gold Bond | $7 - $15 |
| Prescription Topical Cream | Various (e.g., Ketoconazole, Econazole) | $15 - $50 (with insurance) |
| Prescription Oral Medication | Fluconazole, Terbinafine (Generic) | $10 - $100+ (with insurance, per course) |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Maintaining fungal-free skin requires a combination of vigilance, good hygiene practices, and appropriate treatment when an infection occurs. By understanding the symptoms of fungal infections, knowing how they spread, and utilizing effective remedies, individuals can protect their skin health. Whether through diligent prevention or timely intervention with topical or oral treatments, consistent care and attention are key to managing and overcoming dermatophyte infections, ensuring long-term skin health and comfort.




