Hair Transplant Guide: Restore Your Hair with Surgery
Experiencing hair loss can dent confidence, but surgical hair restoration offers a durable path to regaining a fuller, natural-looking hairline. This guide explains FUE and FUT techniques, who benefits most, what to expect before and after surgery, recovery timelines, and typical costs to help you decide if a hair transplant is right for you.
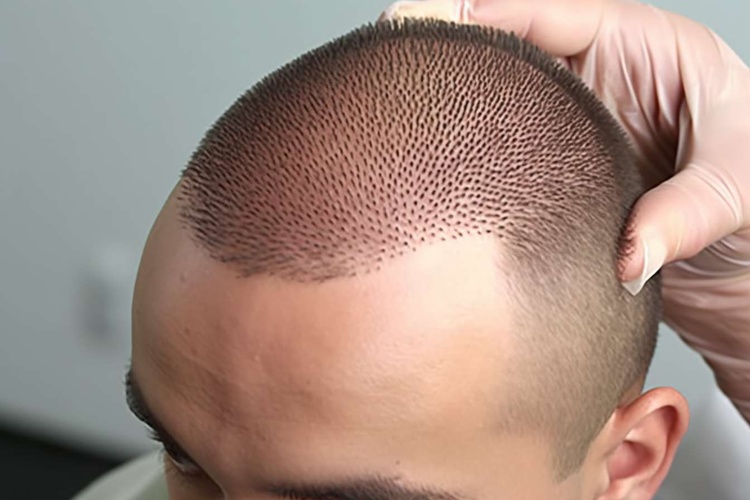
Hair loss affects many people and can impact self-image and confidence. Surgical hair restoration provides a reliable option for rebuilding hair where it has thinned or receded. This guide walks through the two primary transplant methods, who is suitable, benefits and risks, how to prepare, what recovery looks like, and the typical costs involved so you can make an informed choice.
Common surgical techniques: FUE and FUT
Two main approaches are used to harvest hair for transplantation. Follicular Unit Transplantation, or FUT, removes a narrow strip of scalp from the donor region, usually the back of the head, which is then dissected into individual follicular units for implantation. Follicular Unit Extraction, or FUE, retrieves individual follicular units directly from the donor area using tiny punches.
Each technique has advantages. FUT can yield many grafts in a single session, which may be beneficial for extensive balding. FUE leaves minimal linear scarring and often has a faster initial recovery. The best choice depends on your hair loss pattern, the density of donor hair, personal preferences about scarring and recovery, and the surgeon’s recommendation.
Who makes a good candidate?
Not everyone with hair loss should undergo transplantation. Suitable candidates typically include:
- Men and women with androgenetic alopecia or pattern hair loss
- People whose hair loss has stabilized rather than progressing rapidly
- Individuals with adequate donor hair to cover the thinning zones
- Those in generally good health without conditions that impede wound healing
- Candidates who have realistic expectations about outcomes and maintenance
Patients with diffuse hair thinning that affects the donor area, certain autoimmune hair disorders, or insufficient donor follicles may not be ideal candidates. A thorough consultation and scalp evaluation by a qualified hair transplant surgeon will determine suitability.
Benefits and potential downsides
Hair transplantation can offer several meaningful benefits:
- Natural-looking results when grafts are placed with proper angulation and density
- A long-term solution because transplanted hairs are usually resistant to future loss
- Enhanced self-confidence and improved appearance
- Reduced visible scarring with FUE and well-hidden linear scars with FUT
- Customizable treatment plans tailored to individual hair loss patterns
However, there are risks and limitations to consider:
- Possible infection or bleeding at donor or recipient sites
- Scarring, especially a linear scar with FUT
- Unnatural appearance if the procedure is performed without artistic placement
- Shock loss, where existing hairs temporarily shed after surgery
- Multiple sessions may be required to achieve desired density
- Non-transplanted hair can continue to thin, potentially necessitating future treatments
Preparing for surgery
A well-planned preoperative routine improves outcomes. Common preparation steps include:
- Consulting with a board-certified hair transplant surgeon to set realistic goals
- Following specific pre-op instructions, which may include stopping certain medications and supplements
- Avoiding alcohol and nicotine for a period before and after surgery to support healing
- Arranging transportation on the day of the procedure
- Washing hair thoroughly the night before or the morning of surgery
- Wearing comfortable, loose clothing and preparing your home with any prescribed medications and recovery supplies
What to expect during and after the procedure
Most hair transplants are done under local anesthesia and can take several hours depending on graft numbers. You may experience mild discomfort during the procedure, but most patients tolerate it well.
After surgery, anticipate a recovery process that typically involves:
- Swelling, redness, and tenderness around treated areas for several days
- Small scabs around implanted follicles that will flake off naturally
- Detailed aftercare instructions from your surgeon on washing, topical care, and activity restrictions
- Many patients returning to work within about a week, while avoiding vigorous exercise for several weeks
- Transplanted hairs often shed initially; new growth commonly starts around 3 to 4 months
- Gradual maturation of transplanted hair, with full visible results usually evident between 12 and 18 months
Typical costs and what influences price
| Technique | Average Cost Range | Factors Affecting Cost |
|---|---|---|
| FUE | $4,000 - $15,000 | Number of grafts, surgeon experience, clinic location |
| FUT | $4,000 - $10,000 | Size of strip removed, procedure complexity, surgeon expertise |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Many clinics offer financing plans or staged treatments to spread cost. The final price depends on graft count, technique, the surgeon’s reputation, and the region where the clinic operates.
Making an informed decision
A hair transplant can be transformative, but success relies on selecting an experienced surgeon, having realistic expectations, and following pre- and post-operative instructions. Consider seeking multiple consultations, reviewing before-and-after photos, and asking about the surgeon’s complication rates and graft survival statistics.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.




