How Joint Preservation Techniques Extend Mobility
Joint preservation combines targeted clinical care, surgical options, and rehabilitation to maintain natural joint function and delay major reconstruction. By focusing on early diagnosis, load redistribution, and tissue-sparing techniques, clinicians help patients retain mobility and reduce pain while preserving native joint anatomy for as long as possible.
Joint preservation seeks to keep the native joint functional by combining nonoperative management, biologic treatments, and targeted procedures. The approach prioritizes pain control, improved mechanics, and activity-appropriate rehabilitation to delay or avoid joint replacement. These strategies apply across the hip, knee, spine, and other joints, and they emphasize individualized planning based on imaging, bone health, and patient goals.
rehabilitation
Rehabilitation is the cornerstone of joint preservation. A structured program improves strength, flexibility, and neuromuscular control to reduce abnormal joint loading that accelerates degeneration. Physical therapists guide progressive conditioning, gait training, and activity modification to ease symptoms and restore function. For many patients with early cartilage injury or instability, consistent rehabilitation can postpone surgery, enhance recovery after minimally invasive procedures, and support long-term joint health.
arthroscopy
Arthroscopy enables direct assessment and treatment of intra-articular problems with small incisions, addressing meniscal tears, loose bodies, and focal cartilage lesions. Techniques such as debridement, microfracture, or biologic augmentation are performed arthroscopically to reduce tissue trauma and preserve joint anatomy. Because arthroscopy is tissue-sparing, it often shortens hospital stays and allows earlier mobilization, which supports the rehabilitation plan and can delay larger reconstructive surgery.
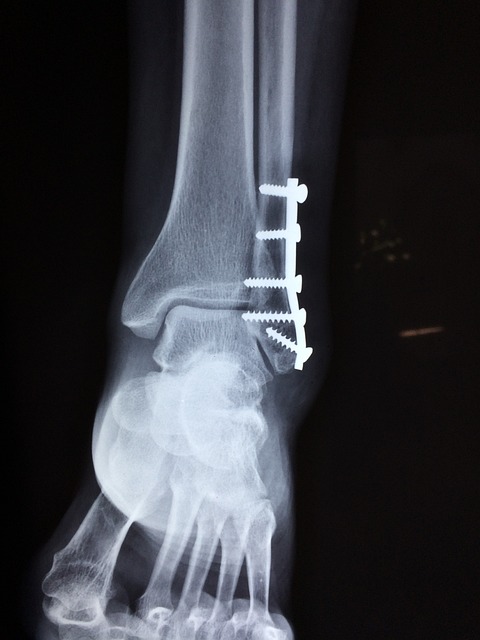
fracture
Proper fracture management is essential to joint preservation after trauma. Restoring joint congruity and stable fixation prevents uneven cartilage loading that leads to post-traumatic arthritis. Internal fixation using plates, screws, or targeted hardware can realign articular surfaces and permit early movement. Where fractures involve periarticular bone, coordinated surgical planning and postoperative rehabilitation improve healing and lower the risk of long-term joint dysfunction.
osteoporosis
Bone quality is a critical consideration in joint-preserving strategies. Osteoporosis increases fracture risk and can compromise fixation used in osteotomies or fracture repair. Assessment of bone density, medical therapies to improve bone health, nutrition optimization, and fall-prevention measures form part of an integrated plan. Strengthening surrounding musculature through rehabilitation also reduces joint loading and supports procedures that depend on reliable bone healing.
imaging
Advanced imaging informs decisions in joint preservation. MRI evaluates cartilage, menisci, ligaments, and early degenerative changes, while CT offers detailed views of bony alignment and complex fracture patterns. Weight-bearing radiographs reveal joint space narrowing and malalignment that may benefit from corrective osteotomy. Accurate imaging helps target interventions—such as realignment, arthroscopy, or biologic therapies—so that treatment preserves function while minimizing unnecessary procedures.
| Provider Name | Services Offered | Key Features/Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Hospital for Special Surgery (HSS) | Joint preservation, arthroscopy, rehabilitation | High-volume programs and research-driven care |
| Mayo Clinic | Orthopedics, fracture care, imaging-guided planning | Multidisciplinary teams and comprehensive diagnostics |
| Cleveland Clinic | Sports medicine, spine care, joint-sparing surgery | Integrated rehabilitation pathways and outcome tracking |
| Johns Hopkins Orthopaedics | Hip and knee preservation, minimally invasive procedures | Emphasis on individualized treatment planning |
| Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital (UK) | Complex reconstruction, osteotomy, trauma care | Specialized centers for conservative and surgical options |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
minimally invasive
Minimally invasive techniques aim to reduce soft-tissue disruption and speed recovery. Procedures labeled minimally invasive include arthroscopic repairs, small-incision osteotomies, and targeted implant insertion when joint-sparing fixation is needed. These approaches can decrease postoperative pain and facilitate earlier rehabilitation, which is important for returning to daily activities or sports. Careful patient selection and imaging-guided planning determine when a minimally invasive strategy is appropriate.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.
Joint preservation blends early diagnosis, rehabilitation, imaging-led planning, and selective surgical techniques to extend mobility and maintain native joint function. Addressing bone health, correcting mechanical contributors, and using tissue-sparing interventions allow many patients to remain active longer while deferring major joint replacement. Ongoing research and multidisciplinary care continue to refine which combinations of therapy best preserve joints across age groups and activity levels.