Managing Scalp Psoriasis: Symptoms, Triggers & Treatments
Scalp psoriasis affects millions and shows up as red, itchy, scaly patches that can disrupt daily life. This guide explains common symptoms, what may trigger flare-ups, diagnostic steps, and the most effective treatment options—from medicated shampoos and topical therapies to phototherapy and systemic drugs—plus practical lifestyle strategies to reduce symptoms and improve scalp health. Learn how to recognize problems early and when to seek a dermatologist.
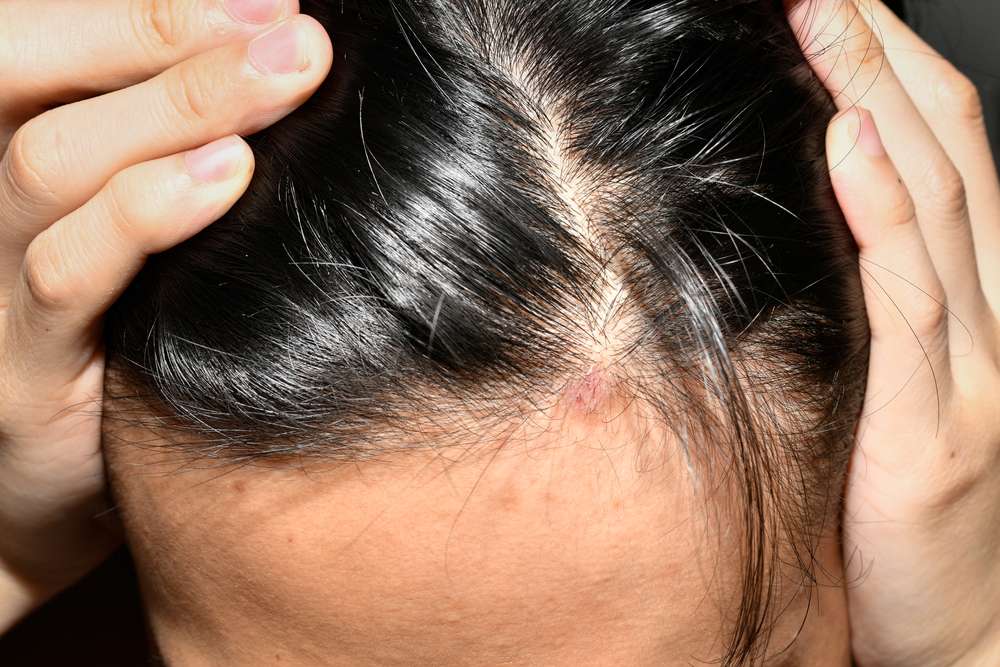
Scalp psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that commonly causes red, inflamed patches covered with silvery scales. While it can range from mild flaking to thick, crusted plaques across the scalp, understanding the signs and how to manage them helps many people reduce discomfort and maintain healthy hair and skin.
Recognizing the symptoms
The most typical signs of scalp psoriasis include:
- Red, well-defined patches on the scalp
- Thick, silvery or white scales (plaques)
- Persistent itching and a burning or stinging sensation
- Dry, cracked skin that can bleed if scratched
- Temporary hair thinning or loss in severe, persistent cases
Symptoms vary from person to person: some experience light flaking similar to dandruff, while others have extensive plaques that spread beyond the hairline to the forehead, neck, or behind the ears. Symptoms often cycle through flare-ups and remissions.
How doctors diagnose it and common triggers
A dermatologist usually diagnoses scalp psoriasis through a visual exam of the affected skin. If the diagnosis is uncertain, a small skin biopsy may be performed to rule out other scalp conditions such as seborrheic dermatitis or fungal infections.
Although the precise cause of psoriasis remains unclear, it involves an accelerated immune-driven skin cell lifecycle. Several factors can provoke or worsen flare-ups:
- Emotional stress
- Skin trauma or infections
- Cold, dry weather
- Certain medications (for example, beta-blockers or lithium)
- Heavy alcohol use and smoking
- Hormonal changes
Identifying personal triggers and minimizing exposure to them is an important part of long-term symptom control.
Treatment options and how they work
Treatment selection depends on how extensive and severe the scalp involvement is. Many people benefit from a combination of approaches tailored by their clinician.
- Topical corticosteroids: These anti-inflammatory creams, gels, foams, or solutions reduce redness and itching and are commonly used for short-term flare control.
- Vitamin D analogues: Synthetic vitamin D compounds help slow the rapid skin cell growth seen in psoriasis and are often combined with corticosteroids.
- Salicylic acid: This keratolytic helps loosen and remove thick scales, improving penetration of other topical treatments.
- Coal tar preparations: Available in shampoos or ointments, coal tar can reduce scaling and slow skin cell turnover, though it may have a strong odor and can stain.
- Medicated shampoos: Shampoos containing ingredients like ketoconazole, tar, salicylic acid, or zinc pyrithione can help manage symptoms and are frequently used alongside topical therapies.
- Phototherapy: Targeted ultraviolet (UV) light treatment administered in a clinic can slow skin cell production and reduce inflammation for some patients.
- Systemic medications: For moderate to severe cases, oral or injectable systemic drugs—including biologics that target specific immune pathways—may be prescribed to control widespread disease.
Working with a dermatologist ensures the safest and most effective combination of treatments for your situation.
When to see a dermatologist
See a healthcare professional if over-the-counter options aren’t helping, or if you experience any of the following:
- Intense itching or pain that interferes with daily life
- Large areas of scalp affected by redness or scaling
- Signs of infection, such as warmth, swelling, or pus
- Noticeable hair loss
- Sleep disruption caused by symptoms
Early medical evaluation can prevent worsening and help you access more effective prescription therapies.
| Treatment | Typical Setting | Estimated Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Topical treatments (steroids, vitamin D) | Pharmacy/Prescription | Varies widely |
| Medicated shampoos | OTC/Prescription | $10–$50 |
| Phototherapy | Clinic sessions | $100–$300 per session |
| Systemic medications (including biologics) | Specialist care | $500–$5,000/month |
Cost estimates are approximate and can vary by location, insurance coverage, and provider. Consult your healthcare provider or insurer for exact pricing.
Lifestyle steps to reduce flare-ups
Medical treatments are often most effective when combined with practical daily measures:
- Manage stress through exercise, meditation, or counseling, since stress frequently triggers flares.
- Use lukewarm water and mild, fragrance-free cleansers; avoid vigorously scrubbing the scalp.
- Moisturize the scalp with recommended emollients to reduce dryness and scaling.
- Identify and avoid personal dietary or environmental triggers; some people report benefit from anti-inflammatory diets.
- Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption, both linked to increased psoriasis severity.
- If sun exposure helps, keep it moderate and discuss safe practices with your doctor to reduce skin cancer risk.
Bottom line
Scalp psoriasis can be uncomfortable and sometimes embarrassing, but many people achieve good symptom control with the right mix of topical therapies, medicated shampoos, lifestyle changes, and, when necessary, medical treatments like phototherapy or systemic drugs. If symptoms persist or worsen, consult a dermatologist to create a tailored treatment plan.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.




