Medical Assistant Training: Start Your Healthcare Career
Explore medical assistant training to gain hands-on clinical skills, administrative knowledge, and patient communication techniques. Learn program lengths, certification routes, estimated costs, in-demand skills employers want, and how to choose an accredited program to launch a rewarding healthcare career.
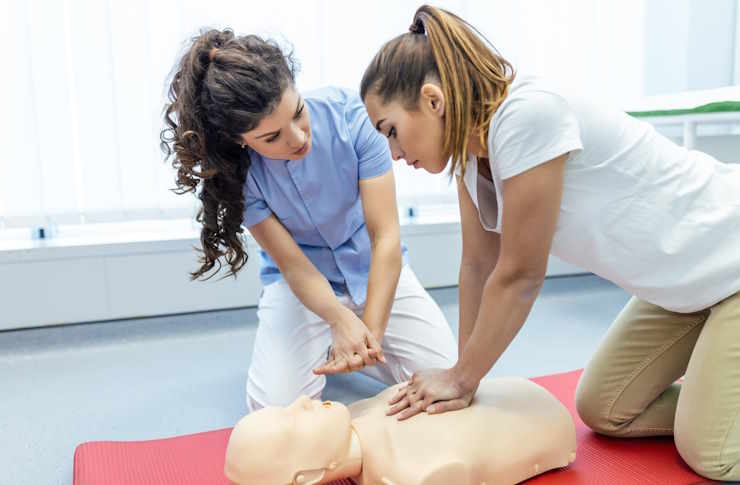
Medical assistant training prepares you for a versatile, patient-focused role that blends clinical tasks with administrative duties. Whether you want a fast route into healthcare or a stepping stone to further clinical study, understanding program length, costs, accreditation, and the skills employers seek will help you choose the best path.
How long does medical assistant training take?
Program durations vary by credential and delivery format. Certificate or diploma programs typically finish within six to twelve months and are designed for rapid entry into the workforce. Associate degree tracks usually take about two years and include broader general-education coursework. Some schools offer accelerated tracks that combine classroom lessons and clinical rotations into a condensed 6- to 8-month schedule; these are demanding and often require full-time study. No matter the option, prioritize programs that mix theoretical instruction with supervised clinical experience so you graduate with both knowledge and practical competence.
What are the job prospects for medical assistants?
Job outlook for medical assistants is strong and growing faster than the average for all occupations, driven by factors such as an aging population, emphasis on preventive care, and expansion of outpatient services. Graduates find work in many settings: physician offices, hospital outpatient departments, urgent care clinics, specialty practices, and community health centers. With on-the-job training and certification, many new medical assistants secure steady positions quickly. Those who seek advancement can move into specialty clinical tasks, lead administrative roles, or pursue additional healthcare credentials.
Which skills separate successful medical assistants from the rest?
Top-performing medical assistants combine technical ability with interpersonal strengths. Essential clinical skills include basic phlebotomy, measuring and recording vital signs, preparing patients for examinations, assisting with minor procedures, and navigating electronic health record systems. Equally important are soft skills: clear communication, empathy, attention to detail, time management, and the capacity to remain composed in busy or stressful environments. Flexibility and teamwork are crucial too, since medical assistants coordinate care with nurses, physicians, and office staff and frequently interact with patients from diverse backgrounds.
How to choose the right training program
Selecting a program means evaluating more than price and convenience. Look for accreditation from recognized organizations such as the Commission on Accreditation of Allied Health Education Programs (CAAHEP) or the Accrediting Bureau of Health Education Schools (ABHES). Accredited programs are more likely to meet industry standards and can influence eligibility for certification exams. Review the curriculum to make sure it covers administrative topics like medical billing, coding, and scheduling as well as clinical competencies such as infection control and clinical procedures. Consider faculty experience, the availability of supervised clinical externships, and career services like job-placement support. If certification is part of your plan, choose a program that prepares students for credentials such as the Certified Medical Assistant (CMA) offered by the American Association of Medical Assistants (AAMA).
What does medical assistant training cost?
Tuition and fees vary depending on program type, the institution, geographic location, and whether training is in-person or online. Use the table below to compare typical ranges and budget accordingly.
| Program Type | Typical Provider | Estimated Cost Range |
|---|---|---|
| Certificate or Diploma | Community college or vocational school | $1,200 - $10,000 |
| Associate Degree | Public university or community college | $8,000 - $25,000 |
| Vocational Program | Private career school | $3,000 - $15,000 |
| Online Program | Accredited online institution | $4,000 - $20,000 |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
When comparing programs, factor in additional expenses such as textbooks, uniforms, supplies, background checks, immunizations, and certification exam fees. Many schools offer financial aid, scholarships, or payment plans; contact admissions or financial aid offices to explore funding options and get a clear estimate of total costs.
Certification and continuing education
While some states and employers do not legally require medical assistant certification, many hiring managers prefer or require it. Earning a credential like the CMA can strengthen your resume, signal competence, and sometimes lead to higher pay. Certification typically involves graduating from an accredited program and passing a standardized exam. After initial certification, continuing education sustains credentials and keeps you up to date with best practices, new procedures, and regulatory changes.
Final considerations and next steps
Medical assistant training offers a relatively quick path into healthcare with a balance of clinical and administrative responsibilities. When deciding, weigh program length, accreditation, curriculum balance, clinical training opportunities, and school support services. Reflect on your career goals: do you want to enter the workforce quickly, or use this role as a springboard to nursing or other healthcare professions? With solid training, strong communication and organizational skills, and a willingness to learn, medical assistants can build stable and meaningful careers in a field with growing demand.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.




