Monitoring Devices: Understanding Blood Pressure Monitors and Their Impact on Health
Blood pressure is a vital indicator of overall health, and monitoring it regularly can provide invaluable insights into one's cardiovascular well-being. With the advent of technology, blood pressure monitors have become increasingly accessible and user-friendly, allowing individuals to track their health from the comfort of their homes. This article explores the world of blood pressure monitoring devices, focusing on their importance, types, and proper usage.
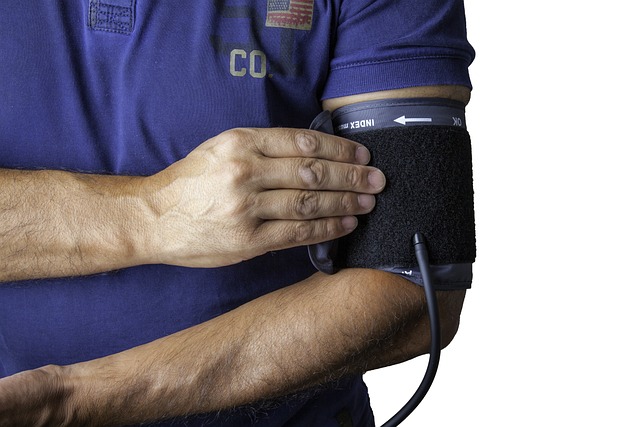
Modern digital blood pressure monitors use oscillometric measurements, detecting vibrations in the arterial wall to determine blood pressure values. This technology has made it possible for individuals to easily measure their blood pressure at home without the need for a stethoscope or specialized training.
Why is regular blood pressure monitoring important for health?
Regular blood pressure monitoring is crucial for maintaining good health and preventing cardiovascular diseases. High blood pressure, or hypertension, is often called the “silent killer” because it typically has no symptoms but can lead to serious health complications if left unchecked. By monitoring blood pressure regularly, individuals can:
-
Detect hypertension early
-
Track the effectiveness of medications and lifestyle changes
-
Identify patterns and triggers that affect blood pressure
-
Provide valuable information to healthcare providers for better treatment decisions
Consistent monitoring empowers individuals to take a proactive approach to their cardiovascular health, potentially preventing or managing conditions such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney problems.
What are the different types of blood pressure monitors available?
There are several types of blood pressure monitors available for home use, each with its own advantages and considerations:
-
Upper arm monitors: These are considered the most accurate and are similar to those used in medical settings. They consist of a cuff that wraps around the upper arm and a digital display unit.
-
Wrist monitors: More compact and portable, wrist monitors are easier to use but may be less accurate if not positioned correctly at heart level during measurement.
-
Finger monitors: While convenient, finger monitors are generally less accurate and not recommended for regular home use.
-
Smartphone-compatible monitors: These devices connect to smartphones via Bluetooth, allowing users to track and analyze their blood pressure data over time using dedicated apps.
When choosing a blood pressure monitor, it’s essential to consider factors such as accuracy, ease of use, cuff size, and any additional features that may be beneficial for individual needs.
How to properly use a blood pressure monitor for accurate readings?
To ensure accurate blood pressure readings, follow these guidelines:
-
Choose the right cuff size: An ill-fitting cuff can lead to inaccurate measurements.
-
Prepare properly: Avoid caffeine, exercise, and smoking for at least 30 minutes before taking a reading.
-
Find a quiet, comfortable location: Sit in a chair with your back supported and feet flat on the floor.
-
Position the cuff correctly: For upper arm monitors, place the cuff directly on the skin, about an inch above the elbow. For wrist monitors, ensure the device is at heart level.
-
Relax and remain still: Take a few deep breaths and avoid talking during the measurement.
-
Take multiple readings: For the most accurate assessment, take two to three readings, one minute apart, and calculate the average.
-
Record results: Keep a log of your readings, including date, time, and any relevant factors that may affect blood pressure.
By following these steps, you can obtain more reliable blood pressure measurements, providing valuable information for you and your healthcare provider.
What features should you look for when choosing a blood pressure monitor?
When selecting a blood pressure monitor, consider the following features to ensure you choose a device that best suits your needs:
-
Accuracy: Look for devices clinically validated by organizations such as the Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation (AAMI) or the British Hypertension Society (BHS).
-
Memory function: Ability to store multiple readings for easy tracking and comparison.
-
Multiple user profiles: Useful for households where more than one person needs to monitor their blood pressure.
-
Large, easy-to-read display: Ensures clear visibility of results, especially for those with vision impairments.
-
Irregular heartbeat detection: Alerts users to potential arrhythmias.
-
Bluetooth connectivity: Allows for easy data transfer to smartphones or computers for long-term tracking.
-
Cuff size options: Ensures proper fit for accurate readings across different arm sizes.
-
Portability: Consider size and battery life if you plan to travel with your monitor.
| Product | Type | Key Features | Price Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Omron Platinum | Upper Arm | Multi-user, smartphone connectivity, TruRead technology | $70 - $100 |
| Withings BPM Connect | Upper Arm | Wi-Fi sync, compact design, FDA-cleared | $90 - $130 |
| iHealth Track | Wrist | Lightweight, large display, 200 reading memory | $30 - $50 |
| A&D Medical UA-767F | Upper Arm | Wide-range cuff, irregular heartbeat detection | $50 - $70 |
| Beurer BC30 | Wrist | Fully automatic, risk indicator, 2x60 memory | $40 - $60 |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
In conclusion, blood pressure monitors are essential medical devices for maintaining cardiovascular health. By understanding the different types available, learning proper usage techniques, and selecting a monitor with suitable features, individuals can take control of their health through regular blood pressure monitoring. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional to interpret your readings and develop an appropriate health management plan.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.




