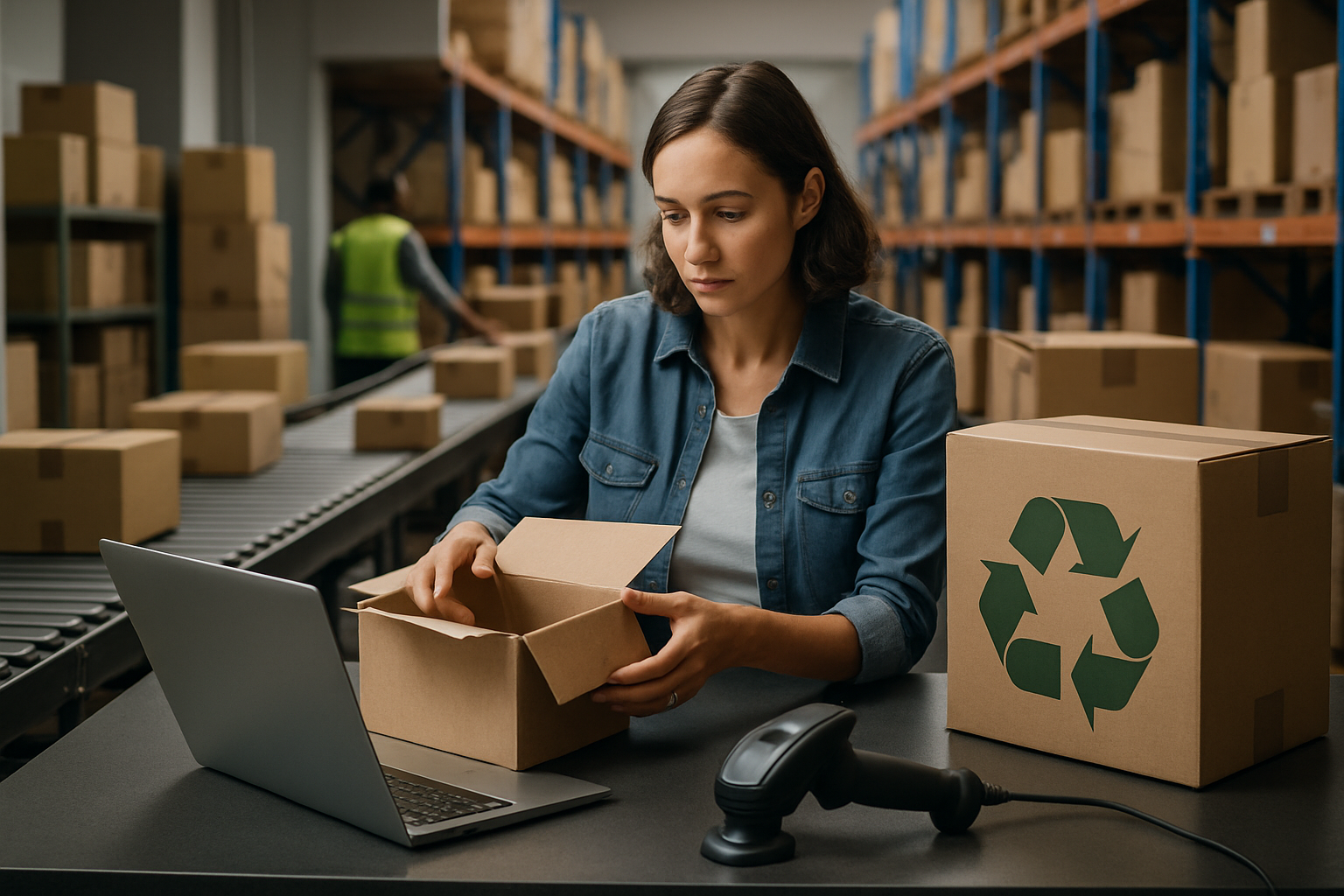
Packing Jobs: Essential Work in Manufacturing and Distribution
Packing jobs play a crucial role in the manufacturing and distribution industries, ensuring products are safely prepared for transport and delivery to customers. These positions are vital components of the supply chain, requiring attention to detail, efficiency, and physical stamina. Whether in a factory setting or a distribution center, packing workers contribute significantly to the smooth operation of businesses across various sectors.

-
Inspecting products for quality before packing
-
Selecting appropriate packaging materials based on product specifications
-
Operating packaging machinery or using hand-packing techniques
-
Labeling packages with relevant information such as product codes or shipping details
-
Stacking packed items on pallets for efficient storage and transport
Factory packing jobs often require workers to maintain a fast pace while ensuring accuracy and adherence to safety standards. The specific duties may vary depending on the type of products being manufactured and the company’s packaging requirements.
How do packing jobs differ in distribution centers?
While similar in many aspects, packing jobs in distribution centers can differ from those in factories. Distribution center packers typically handle a wider variety of products that have already been manufactured. Their primary responsibilities include:
-
Receiving and sorting incoming products
-
Picking items from inventory based on customer orders
-
Assembling multi-item packages or gift sets
-
Customizing packaging for special promotions or seasonal offerings
-
Preparing packages for shipping, including weighing and applying postage
Distribution center packing jobs often involve more variety in day-to-day tasks compared to factory positions. Workers may need to adapt quickly to different types of products and packaging requirements throughout their shift.
What skills and qualifications are needed for packaging worker positions?
While many packing jobs do not require extensive formal education, certain skills and qualifications can make candidates more competitive:
-
Physical stamina: The ability to stand for long periods and lift moderate weights is essential.
-
Attention to detail: Ensuring accurate packing and labeling is crucial for customer satisfaction.
-
Basic math skills: Workers often need to count items and perform simple calculations.
-
Time management: Meeting production quotas while maintaining quality is important.
-
Teamwork: Many packing jobs involve collaborating with others on assembly lines or in warehouse settings.
-
Safety awareness: Understanding and following proper safety procedures is critical in manufacturing environments.
Some employers may prefer candidates with a high school diploma or equivalent, while others provide on-the-job training for entry-level positions. Familiarity with inventory management systems or specific packaging equipment can be advantageous for more advanced roles.
How does technology impact modern packing jobs?
Technology has significantly transformed packing jobs in recent years, introducing new tools and processes to improve efficiency and accuracy:
-
Automated packaging machines: Many factories now use advanced equipment to streamline packaging processes, requiring workers to operate and monitor these machines.
-
Barcode scanners and RFID technology: These tools help track inventory and ensure correct items are packed for each order.
-
Digital packing lists: Electronic systems have largely replaced paper-based methods, allowing for real-time updates and reduced errors.
-
Ergonomic equipment: Improved workstation designs and lifting aids help reduce physical strain on workers.
As technology continues to evolve, packing job responsibilities may shift towards more oversight and quality control roles, with workers managing automated systems rather than performing all tasks manually.
What are the career prospects for those in packaging manufacturing jobs?
Packing jobs can serve as entry points into the manufacturing and logistics industries, offering opportunities for career advancement:
-
Supervisory roles: Experienced packers may progress to team leader or shift supervisor positions.
-
Quality control: Some workers transition into quality assurance roles, leveraging their product knowledge.
-
Logistics coordination: Understanding of packing processes can lead to opportunities in inventory management or shipping coordination.
-
Machine operation: Packers may advance to operating more complex packaging machinery.
-
Training and development: Experienced workers often become trainers for new employees.
Additionally, skills gained in packing jobs, such as attention to detail and efficiency, are transferable to various other industries, providing a solid foundation for diverse career paths.
What is the typical work environment for packaging factory workers?
The work environment for packaging factory workers can vary depending on the specific industry and facility, but generally includes the following characteristics:
-
Fast-paced atmosphere: Production lines often operate at high speeds to meet demand.
-
Shift work: Many factories run multiple shifts, including nights and weekends.
-
Climate-controlled settings: Most indoor facilities maintain comfortable temperatures, though some may be cooler for food products.
-
Safety measures: Proper protective equipment and adherence to safety protocols are typically required.
-
Teamwork-oriented: Collaboration with colleagues is often essential for smooth operations.
-
Repetitive tasks: The nature of packing work can involve repeating similar actions throughout the shift.
While the work can be physically demanding, many companies prioritize employee well-being by implementing ergonomic workstations and regular break schedules to prevent fatigue and injury.
In conclusion, packing jobs remain an integral part of the manufacturing and distribution sectors, offering stable employment opportunities with potential for growth. As industries continue to evolve, these roles adapt to incorporate new technologies and processes, ensuring their ongoing importance in the global supply chain.