Power Banks: How They Work and How to Choose One
Portable power banks are compact external batteries that let you recharge mobile devices when a wall charger isn't available. They vary in capacity, output power, size and safety features, and are used across daily commuting, travel, and field work. Understanding how they store and deliver energy helps you match a power bank to your devices and usage patterns.
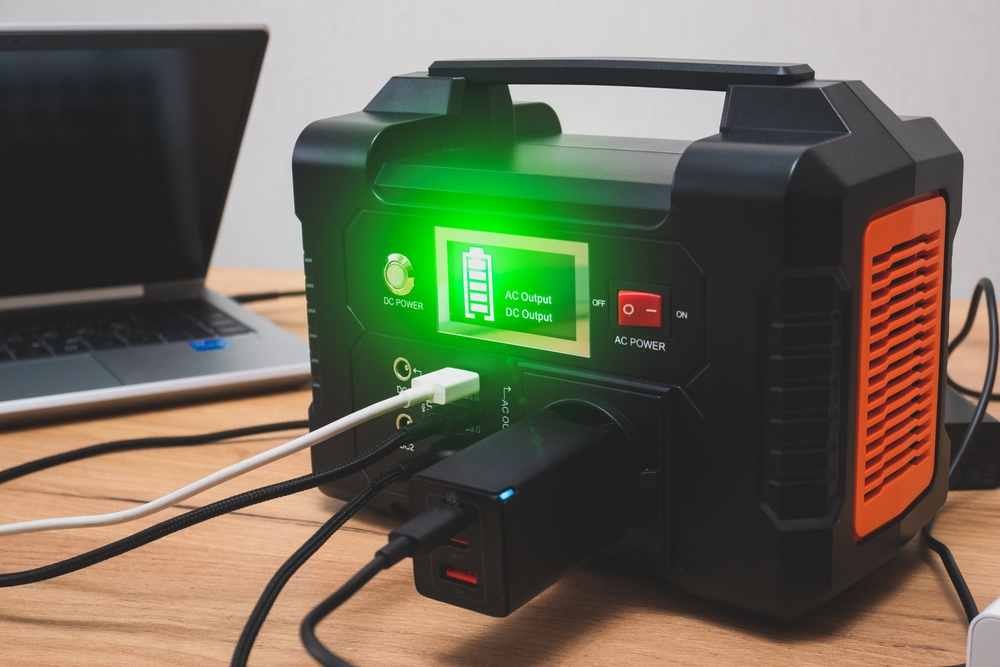

What is a power bank and how does it help mobile devices?
A power bank is an external battery pack that stores electrical energy and provides it via USB or other outputs to charge mobile devices such as smartphones, tablets, and small electronics. Most power banks contain lithium-ion or lithium-polymer cells, voltage regulation circuits, and at least one output port. For everyday users, they offer convenience and portability: you can recharge a mobile device away from a charger or local services, extending uptime for calls, navigation, and apps.
How does the battery inside a power bank work?
The battery cells in a power bank store energy chemically and release it as electrical current when a device draws power. Lithium-based cells are common because of high energy density and relatively low weight. Internal circuitry handles charge/discharge control, step-up/step-down conversion, and protection against overcurrent, overvoltage, and short circuits. Capacity is rated in milliamp-hours (mAh), which indicates stored charge but does not translate linearly to the number of full charges for a device due to conversion losses and voltage differences.
What should you know about charger compatibility and output?
Not all power banks charge devices the same way. Output specifications—voltage and current—determine how quickly a charger can refill a mobile device. Typical USB-A outputs provide 5V at 1A–2.4A; modern power banks often include USB-C ports with Power Delivery (PD) for higher voltages and faster charging. Matching the power bank’s output to your device’s charging protocol improves efficiency and safety. Also consider input specs: faster input allows the power bank itself to recharge more quickly from a wall adapter.
How to choose by capacity, ports, and electronics safety features
Pick capacity based on the devices you use and how many recharges you need. A modern smartphone with a 3,000–5,000 mAh battery might require a 10,000 mAh power bank for two full charges, accounting for efficiency losses. Look for multiple ports if you plan to charge several devices. Check for electronics safety features such as overcharge protection, temperature monitoring, and certified components; reputable manufacturers provide circuit protection and comply with safety standards. Weight and size are trade-offs: higher capacity usually means heavier units.
What are practical considerations for everyday use and travel?
Consider form factor, airline regulations, and how you carry a power bank. Airlines and local services restrict lithium battery capacity for checked luggage; smaller units are generally permitted in carry-on. For travel, prioritize compactness, fast charging, and a durable exterior. If you use power banks for work or field operations with sensitive electronics, choose models with stable output and lower ripple to prevent possible interference. Store power banks at moderate temperatures and avoid exposing them to moisture or impact to preserve battery life.
Conclusion
Power banks are a practical accessory that bridge the gap between fixed chargers and mobile device needs, offering flexibility for commuting, travel, and remote work. Understanding capacity ratings, battery type, output compatibility and essential electronics safety features enables informed choices. Match a power bank to your device’s charging protocol and typical usage patterns to balance capacity, size and charging speed while observing manufacturer guidance and transport regulations.