Power Generators: Understanding Your Options for Reliable Backup Energy
When the lights go out unexpectedly, a power generator can be your lifeline to essential electricity. Whether you're preparing for emergencies, planning an off-grid adventure, or seeking a reliable backup for your home or business, understanding the different types of power generators is crucial. This article will explore various generator options, their features, and how to choose the right one for your needs.

What are the benefits of a portable generator?
Portable generators offer flexibility and convenience for a variety of situations. These compact units are ideal for camping trips, tailgating events, or providing temporary power during outages. Key advantages include:
-
Mobility: Easy to transport and set up wherever needed
-
Versatility: Can power multiple devices simultaneously
-
Affordability: Generally less expensive than permanent standby generators
-
Fuel options: Available in gasoline, propane, or dual-fuel models
However, portable generators typically have lower power output and shorter run times compared to larger stationary models. They also require manual setup and refueling, which can be inconvenient during extended outages.
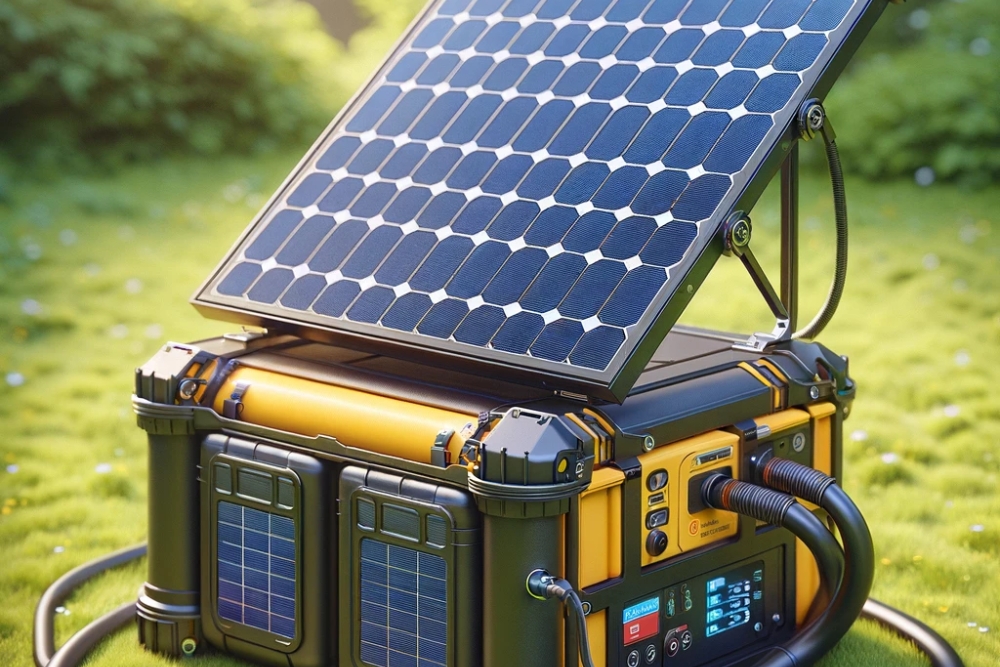
How do solar generators compare to traditional fuel-powered options?
Solar generators are gaining popularity as a clean, quiet alternative to fuel-powered generators. These systems use solar panels to capture sunlight and convert it into electrical energy, which is then stored in a battery for later use. Advantages of solar generators include:
-
Renewable energy: No fuel costs or emissions
-
Silent operation: Ideal for camping or noise-sensitive areas
-
Low maintenance: No engine parts to service
-
Indoor use: Safe to operate inside due to lack of fumes
The main drawbacks of solar generators are their higher upfront cost and dependence on sunlight for recharging. They also generally have lower power output compared to fuel-powered generators, making them better suited for smaller applications or as a supplement to other power sources.
What factors should you consider when choosing a power generator?
Selecting the right generator depends on your specific needs and circumstances. Consider these factors:
-
Power requirements: Calculate the total wattage of devices you need to run simultaneously
-
Fuel type: Gasoline, diesel, propane, or solar based on availability and preferences
-
Portability: Decide between stationary or mobile options
-
Noise level: Consider local regulations and personal comfort
-
Run time: Determine how long you need continuous power
-
Start-up method: Electric start vs. pull-start for convenience
-
Safety features: Look for overload protection, low-oil shutoff, and GFCI outlets
-
Budget: Balance upfront costs with long-term operational expenses
How do different types of generators compare in features and pricing?
When evaluating generator options, it’s helpful to compare features and costs across different types. Here’s a comparison of common generator categories:
| Generator Type | Power Output | Fuel Source | Portability | Estimated Price Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Portable Gasoline | 1,000-10,000W | Gasoline | High | $300-$2,000 |
| Portable Propane | 1,000-8,000W | Propane | High | $400-$2,500 |
| Portable Dual Fuel | 2,000-12,000W | Gasoline/Propane | High | $500-$3,000 |
| Solar Generator | 500-3,000W | Solar/Battery | Moderate | $500-$5,000 |
| Standby Generator | 7,000-20,000W+ | Natural Gas/Propane | None | $3,000-$15,000+ |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
How can you ensure safe and efficient operation of your power generator?
Proper use and maintenance of your generator are essential for safety and longevity:
-
Read the manual thoroughly before operation
-
Place the generator outdoors in a well-ventilated area
-
Use appropriate extension cords rated for the load
-
Never backfeed power into your home’s electrical system
-
Perform regular maintenance, including oil changes and air filter replacements
-
Store fuel properly and use fuel stabilizers for long-term storage
-
Test your generator regularly to ensure it’s ready when needed
-
Install carbon monoxide detectors in your home as an added safety measure
By understanding the different types of power generators available and considering your specific needs, you can make an informed decision to ensure reliable backup power when you need it most. Whether you opt for a portable generator for occasional use or invest in a solar generator for sustainable energy, proper selection and maintenance will help keep the lights on during unexpected outages or off-grid adventures.