Scalp Psoriasis: Effective Treatments and Care Guide
Scalp psoriasis causes itchy, red, scaly patches that can be physically and emotionally taxing. This guide explains how dermatologists diagnose the condition and outlines topical, systemic, and in-office therapies, practical hair-care tips, product costs, and lifestyle changes to help manage symptoms and improve comfort.
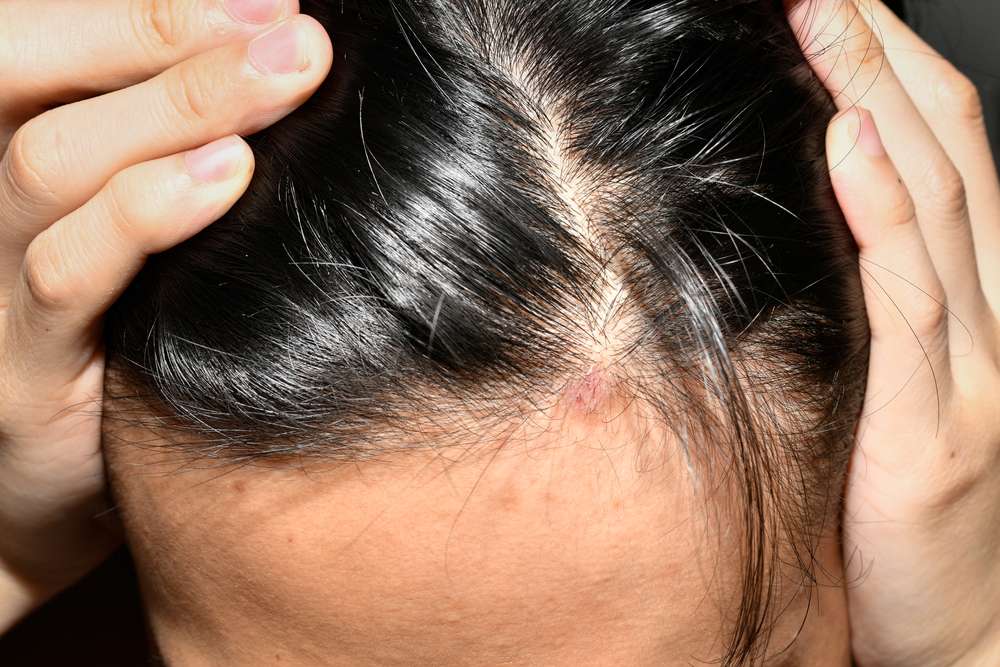
Scalp psoriasis is a long-term autoimmune condition that produces flaky, inflamed patches on the scalp. Although there is no permanent cure, a combination of medical therapies, targeted hair-care routines, and lifestyle adjustments can control symptoms and reduce flare-ups. This guide explains how clinicians approach diagnosis and treatment, summarizes available options, and offers practical steps to support ongoing care.
How dermatologists diagnose and approach treatment
A dermatologist usually identifies scalp psoriasis by examining the scalp and reviewing your medical history, including family history, symptom patterns, and any triggers. In most cases a visual inspection suffices, but if the diagnosis is unclear, a skin biopsy or additional testing may be requested. The provider will assess severity, the extent of scalp involvement, hairline or body spread, and how previous therapies performed.
Treatment plans are tailored to the individual and often combine topical therapies, in-office procedures, and, for more severe disease, systemic medications. Office-based options include prescription topical formulations, phototherapy (UV treatment), and specialized scalp therapies applied under medical supervision. The dermatologist will weigh potential benefits, side effects, convenience, and cost when recommending a regimen.
Treatment options: topical, systemic, and in-office
Topical treatments are commonly the first-line approach for mild to moderate scalp disease and may be used alongside other therapies for more extensive cases.
- Medicated shampoos: Shampoos with salicylic acid or coal tar help remove scales and reduce inflammation. They’re often used several times per week.
- Corticosteroid solutions and foams: Prescription steroid preparations applied directly to affected areas reduce redness and itch and can be formulated as lotions, solutions, foams, or gels for easier application under hair.
- Vitamin D analogues: Topical agents such as calcipotriene (a vitamin D derivative) help slow skin cell growth and are frequently combined with steroids.
- Topical retinoids: These can normalize skin cell production but may be irritating for some people and are used as directed by a clinician.
Systemic therapies are considered when scalp psoriasis is severe, widespread, or unresponsive to topical care:
- Oral medications: Immunosuppressive oral drugs can control inflammation systemically but require monitoring for side effects.
- Biologic injections: Targeted biologic therapies block specific immune pathways and have dramatically improved outcomes for many people with moderate to severe psoriasis.
- Light therapy: Phototherapy (narrowband UVB or targeted UV devices) exposes affected areas to controlled ultraviolet light to slow abnormal skin cell turnover. Some phototherapy options are performed in clinic.
Practical hair-care tips for people with scalp psoriasis
Consistent, gentle hair care helps treatments work better and reduces irritation:
- Choose mild, fragrance-free shampoos and products to minimize irritation.
- Avoid very hot water when washing; lukewarm water is gentler on inflamed skin.
- Use a soft touch when brushing or combing—harsh scrubbing can aggravate lesions.
- Apply prescribed treatments directly to the scalp as directed, parting hair to reach affected areas.
- Maintain a regular washing schedule that removes scales without stripping natural oils; daily washing is not necessary for everyone.
- Consider shorter hair or styles that make it easier to apply topical medicines and keep the scalp accessible for treatment.
Common products and their relative effectiveness
| Treatment Type | Active Ingredients | Typical Cost Range |
|---|---|---|
| Medicated Shampoo | Coal tar, Salicylic acid | $10–30 |
| Prescription Topicals | Corticosteroids, Vitamin D analogues, Retinoids | $30–100 |
| Biologics | Targeted immunologic agents | $1,000–3,000/month |
| Light Therapy | Narrowband UV / Targeted UV devices | $50–300/session |
Prices and cost estimates are approximate and may change over time. Independent research and consultation with providers are recommended before making financial decisions.
Lifestyle strategies to support treatment and reduce flares
Medical therapy is often most effective when paired with lifestyle measures that address common triggers and improve overall skin health:
- Stress management: Techniques such as mindfulness, exercise, and adequate sleep can reduce stress-related flare-ups.
- Anti-inflammatory diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and omega-3 fatty acids may help reduce systemic inflammation.
- Regular scalp moisturizing: Using emollients or prescribed leave-on products can keep the scalp from becoming overly dry and cracked.
- Avoid known triggers: Smoking, excessive alcohol, certain medications, or skin injuries (Koebner phenomenon) can worsen psoriasis in some people.
- Sun protection: Limited, controlled sun exposure may be helpful, but protect the scalp from sunburn and follow your clinician’s guidance about UV exposure.
Putting it all together
Managing scalp psoriasis usually requires patience and routine. Many people achieve substantial symptom reduction by combining physician-guided medical treatments with thoughtful hair care and lifestyle changes. Regular follow-up with a dermatologist helps adjust therapies as needed, monitor side effects, and optimize results.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.




