Scalp Psoriasis Relief: Effective Treatments & Care
Scalp psoriasis affects millions and causes red, scaly patches, itching, and flaking that can harm scalp and hair health. Discover proven treatments—from medicated shampoos and topical therapies to phototherapy and systemic options—plus practical care tips and lifestyle changes to reduce flare-ups and improve scalp comfort. Learn how to manage symptoms and when to consult a dermatologist for a personalized plan.
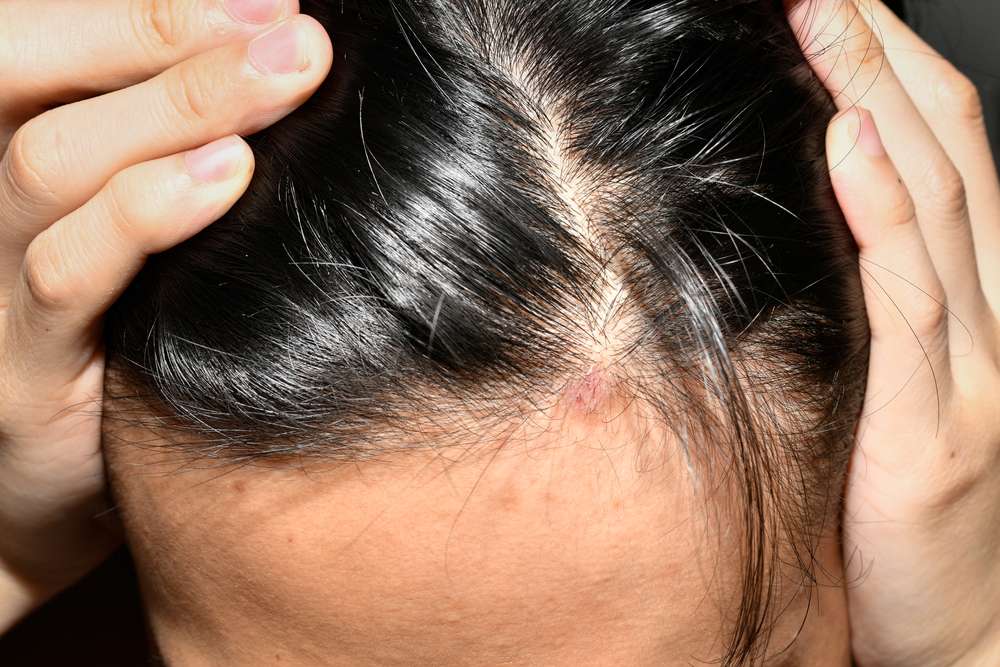
Scalp psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that produces raised, red patches and silvery scales on the scalp. While it cannot be cured, many treatments and daily-care strategies can significantly reduce itching, flaking, and discomfort and help preserve hair health. Understanding triggers, treatment choices, and practical management techniques lets you take control and reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups.
What triggers scalp psoriasis?
Several factors can increase the likelihood of developing scalp psoriasis or provoke flare-ups. Genetics play a large role: having a family history of psoriasis raises your risk. Psychological stress is another common trigger—periods of high stress often precede flares. Environmental conditions such as cold weather, dry air, or exposure to certain medications can worsen symptoms. Finally, injuries or trauma to the scalp, including cuts, insect bites, or harsh chemical treatments, can precipitate psoriatic lesions through a phenomenon called the Koebner response. Recognizing and addressing these triggers is an important step in prevention and long-term control.
How scalp psoriasis affects hair
Although scalp psoriasis itself doesn’t directly destroy hair follicles, the inflammation, scale buildup, and mechanical trauma from scratching can lead to temporary hair thinning or shedding. Common hair-related consequences include:
- Dry, brittle hair due to disrupted oil distribution across the scalp.
- Increased hair shedding from inflammation and excessive manipulation.
- Difficulties styling when flakes and plaques are visible, which can affect self-confidence.
Most hair loss related to psoriasis is reversible once inflammation is controlled and the scalp environment improves. Gentle care and targeted treatments can help hair recovery.
Effective treatment options
Managing scalp psoriasis often requires combining approaches tailored to how severe and extensive the condition is. Work with a dermatologist to design a plan suited to your needs. Main treatment categories include:
-
Topical corticosteroids: Steroid creams, ointments, foams, and medicated shampoos reduce inflammation and slow the rapid turnover of skin cells. They are commonly used for localized flares.
-
Salicylic acid: Often included in medicated shampoos or topical formulations, salicylic acid softens and helps remove thick scales so other medications can penetrate more effectively.
-
Coal tar: Available in shampoos, ointments, and gels, coal tar helps slow skin cell growth and soothe scaling and itching. It may be preferred by some for long-term scalp control.
-
Phototherapy: Controlled ultraviolet (UV) light exposure—administered in clinics or via specialized home units—can reduce inflammation and abnormal cell proliferation in resistant cases.
-
Systemic medications: For moderate to severe disease or when psoriasis affects other body areas, oral or injectable drugs that modulate the immune system (including biologics) can offer substantial improvement.
-
Complementary and natural approaches: Some individuals report relief from aloe vera, tea tree oil, or diluted apple cider vinegar. Evidence varies, so discuss any home remedies with your clinician before use.
Managing flaking and itching day-to-day
Comfort and preventing further irritation are central to daily management. Practical strategies include:
- Use a gentle medicated shampoo: Products containing coal tar or salicylic acid help control scale. Rotate products and follow package or physician guidance for frequency.
- Keep the scalp moisturized: Apply fragrance-free, hypoallergenic moisturizers or emollients to reduce dryness and cracking.
- Avoid scratching: Scratching can aggravate lesions and increase risk of secondary infection. Instead, lightly massage the scalp with fingertips or a soft brush to loosen flakes.
- Try cold compresses: Applying a cool, damp cloth can temporarily relieve itching and inflammation.
- Reduce stress: Techniques like meditation, deep breathing, or yoga may help lower the frequency of stress-related flares.
- Watch your diet: Although evidence is mixed, some people notice improvement when they limit alcohol, caffeine, and processed foods and emphasize anti-inflammatory choices like fruits, vegetables, and omega-3–rich foods.
Consistency with a gentle routine is key—abrupt changes or harsh treatments often worsen symptoms.
Lifestyle steps that help long-term control
Small, sustainable changes can reduce flare frequency and support overall skin health:
- Prioritize stress management through hobbies, therapy, or relaxation practices.
- Modify your diet if you notice links between specific foods and flares; consider consulting a dietitian for personalized advice.
- Practice gentle hair care: use lukewarm water, avoid aggressive brushing, and steer clear of harsh chemical treatments or tight hairstyles that stress the scalp.
- Use a humidifier in dry climates or during winter to prevent excessive scalp dryness.
- Quit smoking: Tobacco use is associated with worse psoriasis outcomes and may reduce treatment efficacy.
- Maintain regular exercise to help reduce systemic inflammation and improve well-being.
Quick comparison of common treatments
| Treatment | How it helps | Notes/Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Topical corticosteroids | Reduces inflammation and itching | Effective for flares; use under physician guidance to avoid side effects |
| Salicylic acid | Softens and helps remove scales | Often paired with other therapies for better absorption |
| Coal tar | Slows cell growth and soothes scaling | May be messy and has a distinct odor; long-term use discussed with doctor |
| Phototherapy | Slows skin cell turnover via UV light | Requires clinic visits or specialized home units; effective for persistent cases |
| Systemic meds/biologics | Targets immune response for moderate-severe disease | Prescribed and monitored by specialists; potential systemic side effects |
Costs vary by treatment type, location, and insurance coverage. Consult your healthcare provider and insurer for accurate pricing information.
Final thoughts
While scalp psoriasis can be persistent, many people achieve substantial relief by combining medical treatments with thoughtful daily care and lifestyle adjustments. Early intervention, consistent scalp maintenance, and a partnership with a dermatologist will help you find the most effective and sustainable approach for your situation.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.



