The Power of Generators: Understanding Your Energy Options
In today's world, reliable power is essential for both homes and businesses. Power generators play a crucial role in ensuring continuous electricity supply, especially during outages or in remote locations. This article explores various types of power generators, their applications, and the growing importance of renewable energy sources in power generation.
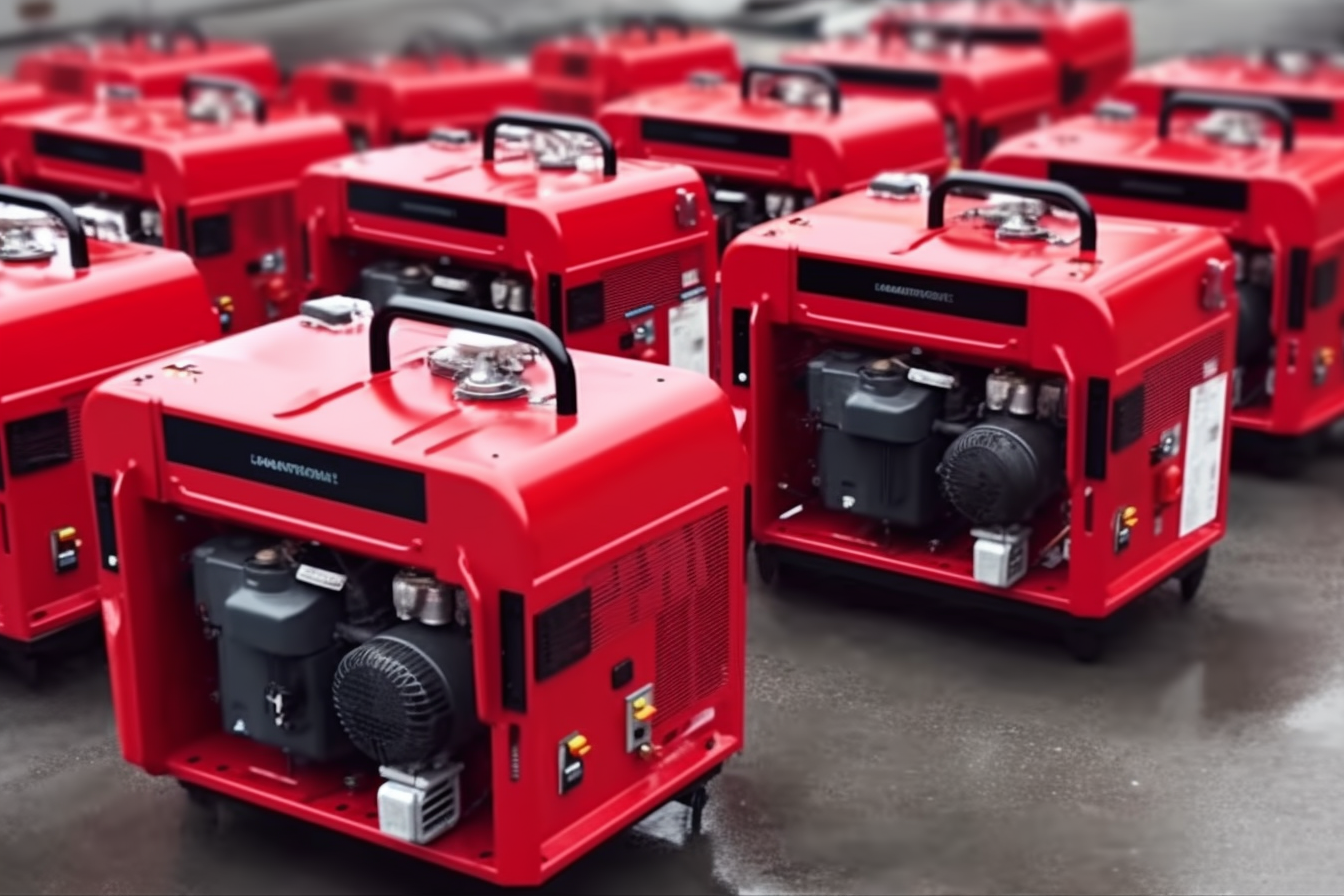

The primary components of a power generator include an engine, an alternator, a fuel system, a voltage regulator, and a cooling and exhaust system. The engine provides the mechanical energy, while the alternator converts it into electrical energy. The type of fuel used and the size of the generator determine its power output and efficiency.
What are the advantages of diesel generators?
Diesel generators are among the most popular types of power generators due to their reliability and efficiency. They offer several advantages:
-
Fuel efficiency: Diesel engines are more efficient than gasoline engines, providing more power per unit of fuel consumed.
-
Durability: Diesel generators are built to last and can operate for extended periods without requiring frequent maintenance.
-
Lower operating costs: Although diesel fuel may be more expensive initially, the overall operating costs are often lower due to better fuel efficiency.
-
High power output: Diesel generators can produce significant amounts of power, making them suitable for large-scale industrial applications and backup power for critical facilities.
-
Longevity: With proper maintenance, diesel generators can have a lifespan of 20,000 to 30,000 hours of use.
How is renewable energy changing the power generation landscape?
Renewable energy sources are transforming the power generation sector by offering cleaner, sustainable alternatives to traditional fossil fuel-based generators. The most common forms of renewable energy for power generation include:
-
Solar energy: Solar panels convert sunlight directly into electricity through photovoltaic cells.
-
Wind energy: Wind turbines harness the kinetic energy of wind to generate electricity.
-
Hydroelectric power: Dams and water turbines generate electricity from the flow of water.
-
Geothermal energy: Heat from the earth’s core is used to produce steam and drive turbines.
-
Biomass: Organic matter is burned or converted into biofuels to generate electricity.
The adoption of renewable energy sources helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions, decreases dependence on finite fossil fuels, and can lead to long-term cost savings for consumers and businesses.
What are the benefits of solar panels for power generation?
Solar panels have become increasingly popular for both residential and commercial power generation. Here are some key benefits:
-
Clean energy: Solar power produces no direct emissions, making it environmentally friendly.
-
Low operating costs: Once installed, solar panels have minimal maintenance requirements and no fuel costs.
-
Energy independence: Solar power can reduce reliance on the grid and provide energy security.
-
Scalability: Solar systems can be easily expanded to meet growing energy needs.
-
Long lifespan: Quality solar panels can last 25-30 years with proper maintenance.
-
Government incentives: Many countries offer tax credits or rebates for solar installations, making them more affordable.
How do wind turbines contribute to power generation?
Wind turbines are another significant player in renewable energy power generation. They offer several advantages:
-
Zero emissions: Wind power produces no pollutants during operation.
-
Land-efficient: Wind farms can coexist with other land uses, such as agriculture.
-
Cost-effective: Wind energy is one of the lowest-priced renewable energy technologies available.
-
Job creation: The wind energy sector creates numerous jobs in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance.
-
Domestic energy production: Wind power reduces dependence on imported fuels.
-
Technological advancements: Ongoing research is improving turbine efficiency and reducing costs.
What factors should be considered when choosing a power generator?
Selecting the right power generator depends on various factors:
-
Power requirements: Determine the total wattage needed to run essential appliances or equipment.
-
Fuel type: Consider availability, cost, and environmental impact of different fuel options.
-
Portability: Decide whether a stationary or portable generator is more suitable for your needs.
-
Noise levels: Some generators can be quite loud, which may be a concern in residential areas.
-
Runtime and fuel efficiency: Look for generators that can operate for extended periods on a single tank of fuel.
-
Maintenance requirements: Consider the long-term costs and effort required for upkeep.
-
Environmental regulations: Ensure the generator complies with local emissions standards.
-
Budget: Balance initial costs with long-term operating expenses when making a decision.
-
Backup power needs: Determine if the generator will be used for emergency backup or regular power supply.
-
Renewable energy integration: Consider how the generator might work alongside renewable energy sources in a hybrid system.
In conclusion, power generators play a vital role in ensuring reliable electricity supply across various applications. While traditional diesel generators remain popular for their efficiency and reliability, the growing adoption of renewable energy sources like solar panels and wind turbines is reshaping the power generation landscape. As technology advances and environmental concerns increase, the future of power generation is likely to see a greater integration of renewable sources with traditional backup systems, providing cleaner, more sustainable energy solutions for homes and businesses alike.