Understanding Blood Pressure Monitoring Devices: A Comprehensive Guide
Blood pressure monitoring is a crucial aspect of maintaining good health, and with advancements in medical technology, it has become easier than ever to keep track of this vital sign. From traditional arm cuffs to modern wrist monitors, there's a wide range of devices available for both clinical and home use. This article explores the world of blood pressure monitoring devices, their importance, and how to choose the right one for your needs.
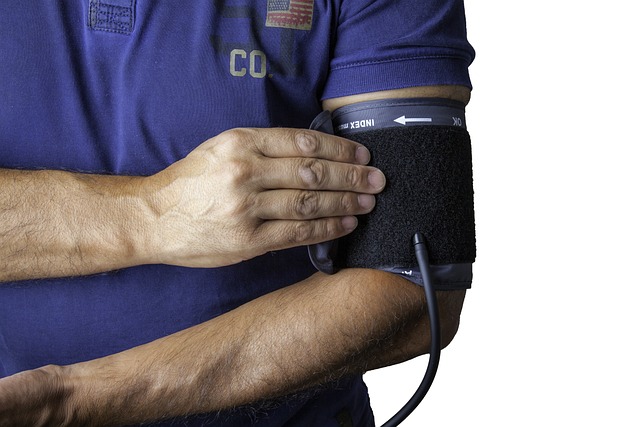
How do different types of blood pressure monitors work?
There are several types of blood pressure monitors available, each with its own mechanism:
-
Manual Sphygmomanometers: These traditional devices use a cuff, a stethoscope, and a mercury or aneroid gauge. A healthcare professional inflates the cuff manually and listens for specific sounds to determine systolic and diastolic pressure.
-
Automatic Arm Monitors: These digital devices automatically inflate the cuff and use oscillometric measurements to determine blood pressure. They’re easy to use and provide quick, accurate readings.
-
Wrist Monitors: These compact devices measure blood pressure at the wrist. While convenient, they require proper positioning for accurate readings.
-
Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitors: These devices are worn for 24 hours and take periodic readings throughout the day and night, providing a comprehensive overview of blood pressure fluctuations.
What features should you look for in a blood pressure monitor?
When choosing a blood pressure monitor, consider the following features:
-
Accuracy: Look for devices that meet international standards for accuracy.
-
Cuff Size: Ensure the cuff fits properly around your upper arm or wrist for accurate readings.
-
Memory Function: Many digital monitors can store multiple readings, allowing you to track trends over time.
-
Multiple User Profiles: Some devices can store separate readings for different users.
-
Connectivity: Advanced monitors can connect to smartphones or computers for easy data tracking and sharing with healthcare providers.
-
Irregular Heartbeat Detection: This feature alerts you to potential heart rhythm abnormalities.
-
Ease of Use: Choose a device with a clear display and simple operation, especially for home use.
Are wrist blood pressure monitors as accurate as arm monitors?
Wrist blood pressure monitors have gained popularity due to their compact size and ease of use. However, their accuracy compared to upper arm monitors has been a subject of debate in the medical community. While wrist monitors can be convenient, they are generally considered less accurate than upper arm monitors for several reasons:
-
Position Sensitivity: Wrist monitors are more sensitive to body position. The wrist must be at heart level for an accurate reading, which can be challenging to maintain consistently.
-
Artery Location: The arteries in the wrist are narrower and closer to the skin surface, potentially affecting the accuracy of readings.
-
User Error: Incorrect placement or wrist flexion can lead to inaccurate measurements.
Despite these potential drawbacks, wrist monitors can be useful for certain individuals, such as those with very large upper arms or those who find arm cuffs uncomfortable. If using a wrist monitor, it’s crucial to follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully and periodically compare readings with those from an upper arm monitor or at a healthcare provider’s office.
How can you ensure accurate blood pressure readings at home?
To get the most accurate blood pressure readings at home:
-
Measure at the same time each day, preferably in the morning and evening.
-
Avoid caffeine, exercise, and smoking for at least 30 minutes before measuring.
-
Sit quietly for 5 minutes before taking a reading.
-
Position yourself correctly: sit with your back straight, feet flat on the floor, and arm supported at heart level.
-
Take multiple readings and record the average.
-
Use a properly sized cuff.
-
Regularly calibrate your device and replace batteries as needed.
-
Compare your home readings with those taken at your healthcare provider’s office to ensure accuracy.
What are the latest innovations in blood pressure monitoring technology?
The field of blood pressure monitoring is continually evolving, with new technologies emerging to make the process more convenient and accurate:
-
Cuffless Monitors: These devices use sensors to measure blood pressure without the need for a traditional inflatable cuff.
-
Smartwatch Integration: Some smartwatches now include blood pressure monitoring capabilities, although their accuracy is still being evaluated.
-
Continuous Monitoring Devices: These wearable sensors can track blood pressure throughout the day without interrupting daily activities.
-
AI-powered Analysis: Advanced algorithms can analyze blood pressure data to predict trends and potential health risks.
-
Telemedicine Integration: Many modern monitors can transmit data directly to healthcare providers, enabling remote monitoring and timely interventions.
In conclusion, blood pressure monitoring devices play a crucial role in preventive healthcare and chronic disease management. Whether you choose an upper arm monitor for home use or opt for a more advanced wearable device, regular monitoring can provide valuable insights into your cardiovascular health. Always consult with your healthcare provider to determine the best monitoring approach for your individual needs and to interpret your blood pressure readings in the context of your overall health.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.




