Understanding Dentures: Restore Your Smile & Confidence
Discover a comprehensive guide to dentures — removable dental appliances that replace missing teeth and supporting gums. Learn about complete, partial, immediate, implant-supported, overdenture, and invisible options, what to expect during treatment, maintenance tips, and cost estimates to help you choose the right solution for comfort, function, and appearance. Get clear, practical information on care, longevity, and financing so you can make a confident decision about restoring your smile.
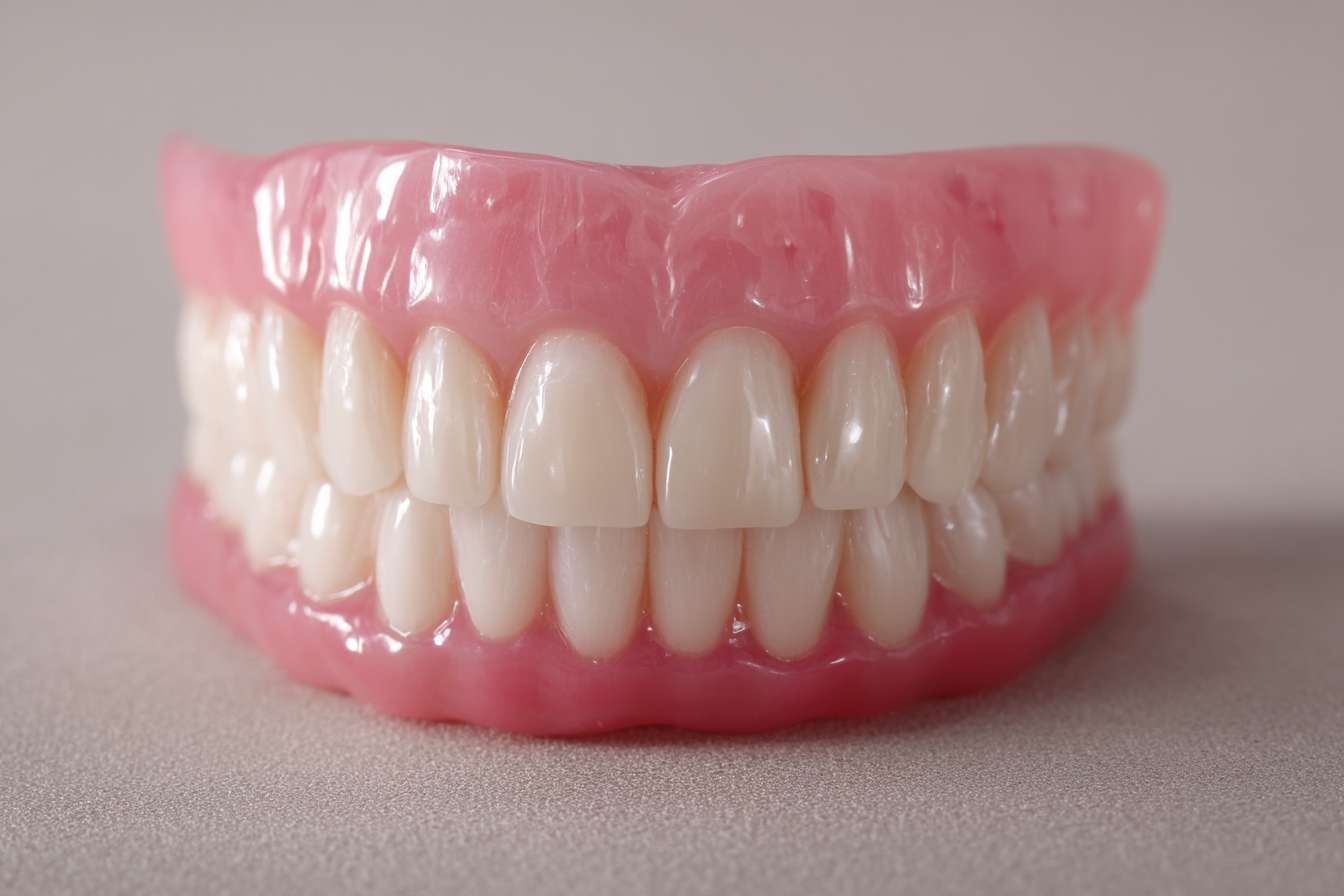
Introduction: Dentures are removable dental appliances created to replace missing teeth and the surrounding gum tissue. For many people, dentures restore chewing ability, improve speech, support facial contours, and increase self-esteem. This guide walks through the main denture varieties, highlights modern alternatives, explains the fitting process, offers care recommendations, and provides typical cost estimates so you can choose the best solution for your needs.
Types of Dentures: Dentures come in several styles to address different levels of tooth loss and patient preferences:
-
Complete dentures: These full-arch prostheses replace all teeth in the upper or lower jaw. They rest on the gums and commonly rely on suction and, if necessary, denture adhesives for retention.
-
Partial dentures: Used when some natural teeth remain, partials fill gaps left by missing teeth. They attach to existing teeth with clasps or precision attachments and restore chewing and aesthetics without full extraction.
-
Immediate dentures: Made ahead of time and placed right after tooth extraction, immediate dentures prevent a period without teeth while healing occurs. Because the gums and bone change after extractions, relining or adjustments are often required as tissues heal.
-
Implant-supported dentures: These dentures are anchored to dental implants embedded in the jaw. Implant retention greatly improves stability, reduces shifting, and usually enhances biting strength and comfort compared with conventional dentures.
-
Overdentures: Overdentures fit over preserved tooth roots or implants. By keeping roots or using implants as anchors, overdentures increase retention and help preserve jawbone volume.
Comparing Traditional and Invisible Dentures: Traditional dentures are generally made from acrylic resin and, in the case of partials, may include metal frameworks or clasps. They are removable and have been a reliable tooth-replacement method for decades, though some wearers report sensation of bulkiness or visible metal components.
Invisible dentures emphasize discreet appearance and comfort. Constructed from flexible or gum-colored materials, they blend with the natural gum line and often eliminate obvious metal clasps. The flexible design can reduce pressure points and slipping for some patients, creating a more natural look and feel.
What to Expect During the Denture Process: Receiving dentures usually involves several appointments to achieve fit, function, and aesthetics:
-
Consultation: Your dentist reviews your oral health, medical history, and goals, then outlines suitable denture options, including whether implants could be beneficial.
-
Impressions and measurements: Accurate molds and measurements of your mouth are taken so technicians can fabricate dentures tailored to your anatomy.
-
Wax try-ins or mock-ups: Provisional models allow you and your dentist to check tooth position, bite, color, and overall appearance. Adjustments are made at this stage before finalizing the appliance.
-
Delivery and fitting: The completed dentures are inserted and evaluated for comfort, speech, and chewing. Necessary adjustments are performed to relieve sore spots and improve function.
-
Follow-up care: Additional visits are common to fine-tune fit and address any areas of irritation as you adapt to the prosthesis.
Caring for Your Dentures: Proper maintenance preserves denture lifespan and protects oral tissues:
- Clean dentures daily using a soft-bristled brush and a non-abrasive denture cleaner to remove plaque and food debris.
- Rinse dentures after eating to clear particles and reduce odor.
- When handling, work over a towel or a basin of water to prevent damage if you drop them.
- Soak dentures overnight in water or a designated soaking solution to keep acrylic hydrated and maintain shape.
- Continue regular dental appointments for oral exams and professional care; dentists can check fit and recommend relining as gums and bone change over time.
Typical Costs and Financial Considerations: Prices depend on denture type, materials, and location. Typical ranges are:
- Complete dentures (upper and lower): $1,000 - $3,000
- Partial dentures: $700 - $1,800
- Implant-supported dentures: $7,000 - $90,000
- Invisible dentures: $2,000 - $4,000
These figures are general estimates and can vary. Conventional dentures are usually less costly initially but often need relines or replacement every 5 to 10 years. Implant-based solutions have higher upfront costs but may provide greater longevity and long-term value.
Insurance and Payment Options: Coverage for dentures varies by insurer and plan. Many dental insurance policies cover a portion of denture treatment, but benefits differ, so verify specifics with your carrier. Dental offices commonly offer financing plans or third-party payment options to help spread costs. Discuss all available payment arrangements and expected out-of-pocket expenses with your dentist before starting treatment.
Conclusion: Dentures remain a flexible and effective approach to replacing missing teeth, offering choices from traditional full and partial plates to implant-retained and discreet invisible options. Understanding the available types, the fitting sequence, maintenance needs, and cost expectations will help you select the best option for comfort, chewing ability, and appearance. Consult your dentist to determine which denture solution aligns with your oral health and budget.
Disclaimer: This article provides general information and is not a substitute for professional dental advice. For individualized recommendations and treatment planning, consult a licensed dental professional.




