Welding Jobs: Essential Safety Gear for Welders
Welding is a critical skill in many industries, from construction to manufacturing. As a welder, your safety is paramount. This article explores the essential safety gear every welder should use to protect themselves on the job, focusing on helmets, gloves, and steel-toed boots.
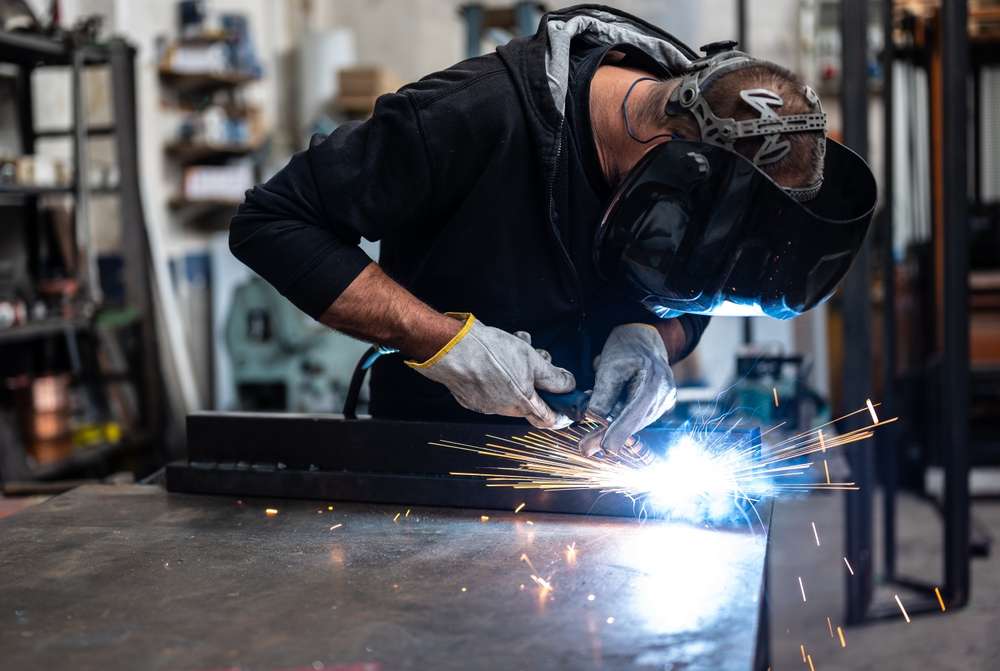

How do welding helmets protect welders?
Welding helmets are arguably the most recognizable piece of safety gear for welders. These helmets serve multiple crucial functions:
-
Eye protection: The helmet’s lens shields the welder’s eyes from the intense ultraviolet and infrared radiation produced during welding, which can cause severe eye damage or even blindness.
-
Face protection: The helmet covers the entire face, protecting against flying sparks, debris, and molten metal splatter.
-
Respiratory protection: Some advanced helmets incorporate respirators to filter out harmful fumes and particles.
Modern welding helmets often feature auto-darkening technology, which automatically adjusts the lens shade when an arc is struck, allowing for more comfortable and efficient work.
What types of gloves are best for welding?
Welding gloves are essential for protecting a welder’s hands from heat, sparks, and sharp edges. The best gloves for welding jobs depend on the specific type of welding being performed:
-
MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding: Typically requires lighter, more flexible gloves made of deerskin or cowhide leather.
-
TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding: Calls for thinner gloves that offer more dexterity, often made from goatskin or sheepskin leather.
-
Stick welding: Demands heavy-duty gloves, usually made from thick cowhide leather, to withstand high heat and spatter.
Regardless of the type, all welding gloves should be heat-resistant, durable, and provide adequate protection without sacrificing too much manual dexterity.
Why are steel-toed boots important for welders?
Steel-toed boots are a crucial component of a welder’s safety gear for several reasons:
-
Impact protection: The steel toe cap protects the feet from heavy falling objects, which is common in welding environments.
-
Heat resistance: Quality welding boots are made from materials that can withstand high temperatures and protect against hot metal splatter.
-
Electrical hazard protection: Many steel-toed boots designed for welding also offer protection against electrical hazards, which is essential when working with welding equipment.
-
Slip resistance: Welding often involves working on slippery surfaces, so boots with good traction are vital for preventing accidents.
When choosing steel-toed boots for welding, look for those that meet or exceed ASTM F2413-18 standards for protective footwear.
How often should welding safety gear be replaced?
The longevity of welding safety gear depends on factors such as frequency of use, type of welding performed, and the quality of the equipment. However, general guidelines for replacement include:
-
Welding helmets: Replace the lens as soon as it becomes scratched or pitted. The helmet itself should be replaced if it shows signs of cracking or significant wear.
-
Gloves: Replace when they develop holes, thin spots, or when they no longer provide adequate protection against heat.
-
Steel-toed boots: Replace when the steel toe becomes exposed, the sole wears down significantly, or the boot loses its ability to protect against electrical hazards.
-
Other PPE: Items like flame-resistant clothing should be replaced when they show signs of wear, holes, or when they no longer fit properly.
Regular inspection of all safety gear is crucial to ensure it continues to provide adequate protection.
What are the consequences of not using proper welding safety gear?
Failing to use proper welding safety gear can lead to severe consequences, both immediate and long-term:
-
Eye injuries: From temporary flash burn to permanent blindness.
-
Burns: Ranging from minor to severe, potentially requiring hospitalization.
-
Respiratory issues: Inhalation of welding fumes can lead to short-term illness or long-term lung damage.
-
Cuts and lacerations: Particularly to hands and feet if not properly protected.
-
Hearing loss: Long-term exposure to high noise levels without proper ear protection can result in permanent hearing damage.
-
Electrical shock: Improper protection can lead to severe electrical injuries or even fatalities.
By consistently using appropriate safety gear, welders can significantly reduce their risk of injury and ensure a long, healthy career in the field.
In conclusion, welding jobs require a strong commitment to safety, with proper gear being the first line of defense against workplace hazards. Helmets, gloves, and steel-toed boots form the core of a welder’s protective equipment, each playing a vital role in safeguarding against the unique risks associated with welding. By investing in high-quality safety gear and maintaining it properly, welders can protect their health, enhance their job performance, and contribute to a safer work environment for everyone.