Asthma Treatment: Effective Strategies for Managing Symptoms and Improving Quality of Life
Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It causes inflammation and narrowing of the airways, leading to breathing difficulties, coughing, and wheezing. While there is no cure for asthma, various treatment options are available to manage symptoms effectively and improve the quality of life for those affected. This article explores the most common and effective asthma treatments, their benefits, and how they can be integrated into a comprehensive management plan.
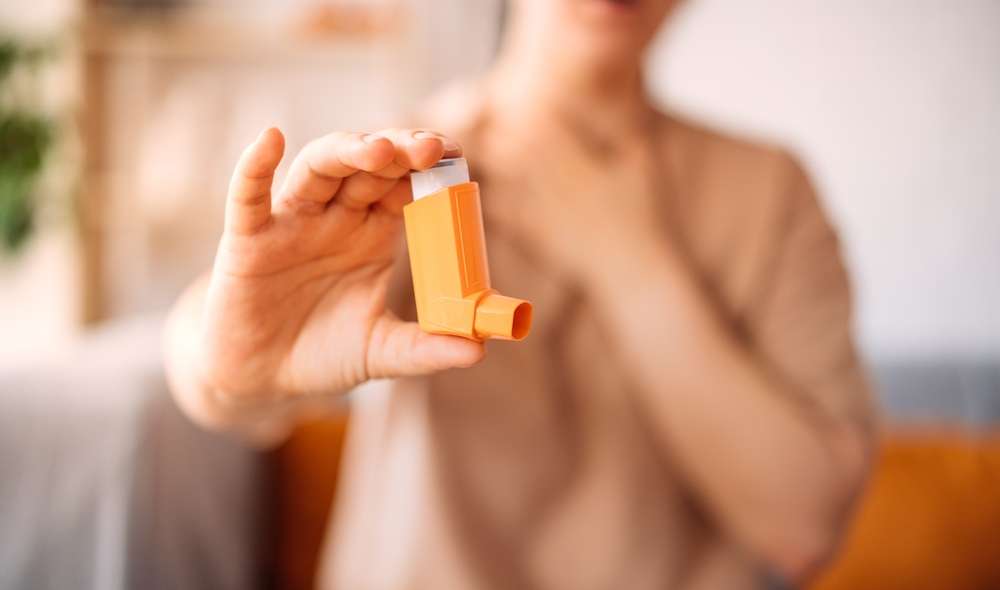

How do inhaled medications help manage asthma?
Inhaled medications are the cornerstone of asthma treatment, delivering medicine directly to the lungs where it’s needed most. There are two main types of inhaled medications: controllers and relievers. Controller medications, such as inhaled corticosteroids, are used daily to reduce airway inflammation and prevent symptoms. Reliever medications, like short-acting beta-agonists, provide quick relief during asthma attacks by relaxing the muscles around the airways. Proper inhaler technique is crucial for the effectiveness of these medications, and healthcare providers often demonstrate the correct usage to ensure optimal benefit.
What role do oral medications play in asthma management?
While inhaled medications are the primary treatment for most people with asthma, oral medications can play an important role in managing more severe cases or specific types of asthma. Leukotriene modifiers, for example, are oral medications that help prevent asthma symptoms by blocking the action of certain inflammatory substances in the body. Oral corticosteroids may be prescribed for short periods during severe asthma exacerbations to quickly reduce inflammation. In some cases, biologics - a newer class of medications that target specific pathways in the immune system - may be recommended for patients with severe, persistent asthma that doesn’t respond well to standard treatments.
How can lifestyle changes and trigger avoidance improve asthma control?
Identifying and avoiding asthma triggers is a crucial aspect of managing the condition. Common triggers include allergens (such as pollen, dust mites, and pet dander), irritants (like smoke and strong odors), respiratory infections, and physical activity. Creating an asthma-friendly environment at home by reducing dust, controlling humidity, and using air purifiers can significantly improve symptoms. Regular exercise, when done safely and with proper precautions, can actually improve lung function and overall health for many people with asthma. Working with a healthcare provider to develop an asthma action plan that outlines steps for daily management and how to handle worsening symptoms is also an essential part of effective asthma control.
What are some emerging treatments for asthma?
Research in asthma treatment is ongoing, with several promising approaches on the horizon. Bronchial thermoplasty is a relatively new procedure that uses heat to reduce the amount of smooth muscle in the airways, potentially decreasing their ability to constrict. While not suitable for all patients, it may offer hope for those with severe, persistent asthma. Additionally, personalized medicine approaches are becoming more prevalent, with treatments tailored to an individual’s specific type of asthma based on genetic and biological markers. These targeted therapies aim to provide more effective treatment with fewer side effects.
How is the effectiveness of asthma treatment monitored?
Regular monitoring is essential to ensure that asthma treatment is effective and to make necessary adjustments. This typically involves tracking symptoms, measuring lung function through spirometry or peak flow meters, and assessing overall quality of life. Patients are often encouraged to keep an asthma diary to record symptoms, medication use, and potential triggers. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider allow for review of the treatment plan and discussion of any concerns or changes in symptoms. Proper education about self-management techniques, including how to recognize and respond to worsening symptoms, is also a crucial component of effective asthma care.
Asthma treatment has come a long way in recent years, offering a range of options to help individuals manage their condition effectively. From inhaled medications and oral treatments to lifestyle modifications and emerging therapies, the goal is to provide personalized care that allows people with asthma to lead full, active lives. By working closely with healthcare providers and adhering to treatment plans, many individuals with asthma can achieve good symptom control and maintain optimal lung function. As research continues, the future holds promise for even more targeted and effective treatments, bringing hope to those affected by this chronic respiratory condition.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.