Eco Houses: Designing Sustainable, Energy-Efficient Homes
Eco houses combine smart design, efficient systems, and renewable sources to reduce environmental impact while improving comfort and resilience. These homes prioritize materials, construction methods, and technologies that lower energy use and emissions over the building’s life. Whether retrofitting an existing house or building new, the principles of renewable energy integration, durable building envelopes, and thoughtful layout can create living spaces that are healthier, less expensive to operate, and aligned with net zero goals. This article explains core strategies and practical considerations for creating an eco house that performs well today and adapts for tomorrow.
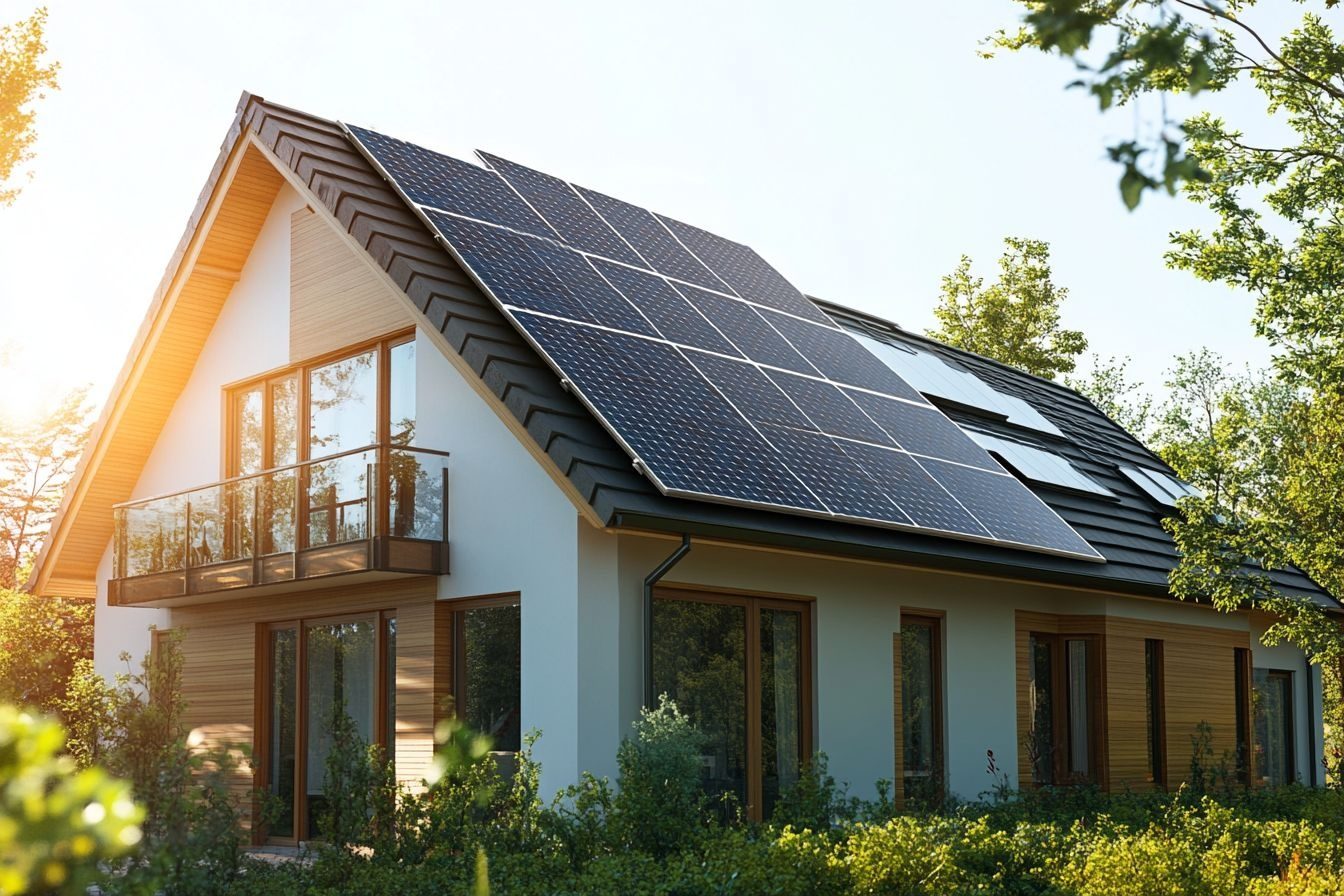

What is renewable energy for homes?
Renewable energy refers to electricity or heat derived from naturally replenished sources such as sunlight, wind, and geothermal heat. In residential settings, renewable energy typically means rooftop solar, small wind turbines in suitable locations, and heat pumps that leverage ambient heat. Integrating renewable energy reduces reliance on fossil fuels, cuts utility bills over time, and supports local grid decarbonization when paired with smart controls and battery storage. When planning, consider local services for permitting, incentives, and installer reputations—these vary by region and affect feasibility and payback.
How do solar panels fit into eco houses?
Solar panels are the most common onsite renewable energy source for eco houses. Photovoltaic modules convert sunlight into electricity for immediate use, and excess can charge batteries or feed the grid. Key considerations include roof orientation and pitch, shading, inverter type, and system size relative to household demand. Solar paired with battery storage improves resilience during outages and helps shift consumption to reduce grid peaks. Regular cleaning and periodic inspections keep panels efficient. Combining solar panels with energy-efficient appliances and smart energy management maximizes the environmental and financial benefits.
Can modular construction speed sustainable builds?
Modular construction uses prefabricated components built in controlled factory settings and assembled onsite. This approach often reduces waste, improves quality control, and shortens construction schedules—advantages for eco houses aiming to minimize embodied energy and on-site disruption. Modular methods can incorporate high-performance insulation, airtight assemblies, and pre-installed mechanical systems that are optimized for energy efficiency. Design flexibility allows for scalable net zero-ready packages. When evaluating modular options, review manufacturers’ sustainability claims, material sourcing, and how well modules integrate with local services for foundations and finishing work.
What does net zero mean for your house?
A net zero home produces as much energy over a year as it consumes, typically through a mix of onsite generation (often solar panels) and aggressive reductions in energy demand. Achieving net zero requires a holistic strategy: a well-sealed, highly insulated envelope; energy-efficient heating, cooling, and hot water systems; high-performance windows; and renewable generation sized to match expected loads. Passive design—orientation, daylighting, and natural ventilation—reduces mechanical needs. Monitoring and behavioral adjustments also matter. Net zero can be applied to operational energy; lowering embodied carbon in materials is a related but separate goal that many eco house projects now address.
How to make an eco house energy efficient?
Energy-efficient homes focus on reducing demand before adding generation. Start with a continuous insulation layer, airtight construction, and thermal-bridge-free details. Upgrade to efficient HVAC systems such as air-source heat pumps, install heat-recovery ventilation for indoor air quality, and choose LED lighting and ENERGY STAR-rated appliances. Smart thermostats and whole-home energy monitoring help optimize use patterns. Water-saving fixtures and efficient hot water delivery reduce both energy and water footprints. Consider lifecycle impacts of materials—durability and low-maintenance finishes often lead to better long-term sustainability. Work with local services experienced in energy-efficient builds to ensure design and execution align.
Conclusion
Eco houses blend practical design choices with modern technology to reduce emissions, lower operating costs, and enhance occupant comfort. Focusing first on reducing demand—through insulation, airtightness, and efficient systems—makes renewable energy like solar panels more effective and affordable. Modular construction can accelerate and tidy the building process while supporting sustainability targets. Whether pursuing net zero or simply improving efficiency, coordinated planning with experienced local services, attention to materials, and an emphasis on long-term performance will yield the best results for homeowners and the environment.