Guide to Recliner Chairs: Types, Features, and Buying Tips
Recliner chairs are a common choice for living rooms, home offices, and specialized seating areas because they combine comfort with adjustable support. Choosing the right recliner involves understanding different frame types, control mechanisms, upholstery materials, and space considerations. This guide explains the main options, how mechanisms work, what to look for in materials and accessibility, and provides a cost comparison to help with purchasing decisions.
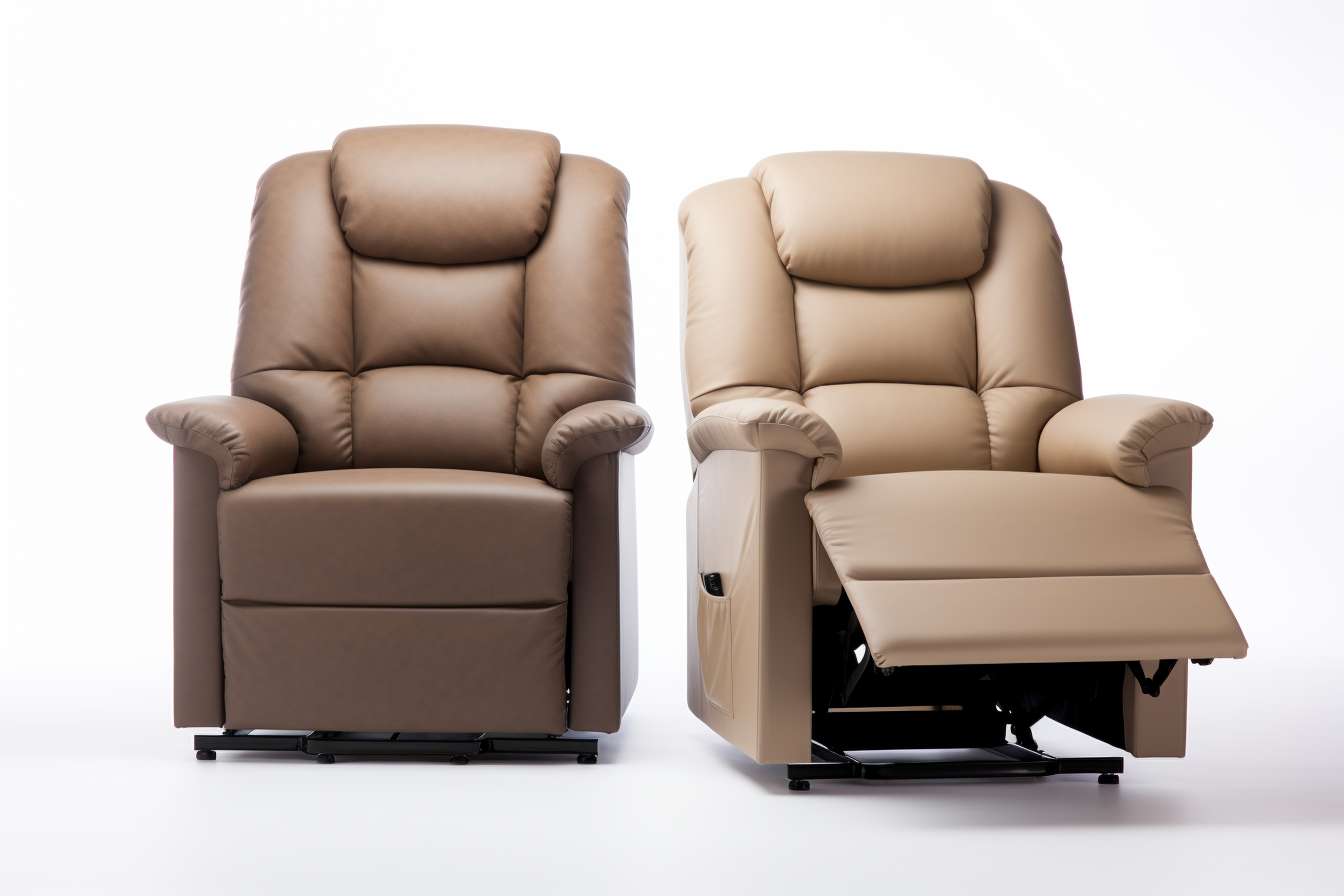

What are the main types of recliner chairs?
Recliner chairs are available in several configurations to suit different needs. Manual recliners use a lever or push-back action and are typically simpler and lighter. Power recliners use an electric motor to adjust position and can include memory presets and USB ports. Lift recliners include a lifting mechanism to assist people with mobility limitations. Glider or swivel recliners add motion for relaxation without fully reclining. Knowing the type helps match the chair to intended use, room layout, and mobility needs.
How do recliner mechanisms differ?
Mechanisms vary in complexity and maintenance requirements. Push-back or chaise-style recliners shift the user’s weight back to extend the footrest without external controls. Lever-operated recliners use a visible handle to change positions. Power mechanisms are more convenient for precise adjustments and often feature quieter motors and multiple stages of tilt. Lift mechanisms use linear actuators to raise the seat for standing assistance. Consider mechanism durability, warranty coverage, and available repair or local services when selecting a model.
What materials and features matter when buying?
Upholstery and internal build quality influence comfort and longevity. Common upholstery options include leather, bonded leather, polyester blends, and microfiber—each with different cleaning and wear characteristics. High-resilience foam or pocketed coil seats tend to hold shape longer than low-density foam. Additional features to evaluate include removable covers for cleaning, head and lumbar support adjustments, built-in storage or cup holders, and compatibility with room dimensions. For households with children or pets, stain-resistant fabrics and sturdy finishes are practical choices.
What maintenance and accessibility considerations apply?
Routine maintenance extends a recliner’s service life: tighten screws, check for noisy mechanisms, clean upholstery according to manufacturer recommendations, and keep electronics dry. For households requiring accessibility, evaluate seat height, armrest width, and lift-function power. Some power recliners have battery backup or hand control options that are easier for users with limited hand dexterity. When professional setup or repairs are needed, look for local services that offer delivery, assembly, and authorized parts to preserve warranties.
How much do recliner chairs cost and comparison?
Below is a general comparison of common recliner options from recognizable providers, with broad cost estimates to illustrate typical price bands.
| Product/Service | Provider | Cost Estimation |
|---|---|---|
| Power recliner (mid-range) | La‑Z‑Boy | $600–$1,500 |
| Manual recliner (entry-level) | Ashley Furniture | $200–$700 |
| Budget recliner (online brands) | Wayfair / Multiple brands | $150–$600 |
| Home décor recliner (retailer lines) | Home Depot / Home Decorators | $200–$800 |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
The ranges above reflect typical market tiers: budget models under $400, mid-range between $400–$900, and higher-end or custom options exceeding $1,000. Additional costs to consider include delivery and assembly fees, extended warranties, and optional features like power articulations or upgraded upholstery. In many regions, local services can offer installation or refurbishment at an extra charge; comparing provider policies on returns and parts availability can affect total ownership cost.
Conclusion
Selecting a recliner chair is a balance between comfort, mechanism type, materials, and budget. Identify how you will use the chair—daily relaxation, mobility assistance, or occasional seating—then prioritize mechanisms and upholstery that match those needs. Check warranty and repair support from providers and consider local services for delivery and assembly. With an understanding of types, features, and estimated costs, you can make a more informed choice that fits both space and lifestyle.