Hair Loss Explained: Causes, Prevention, Treatments
Hair loss affects people of all ages and genders, from early thinning to clear balding patterns. Learn how to spot the first signs, recognize receding hairline patterns, choose gentle care tools, and compare treatments like minoxidil, finasteride, PRP, and transplants. This guide offers practical prevention tips and treatment overviews to help you make informed choices about managing thinning hair and restoring confidence.
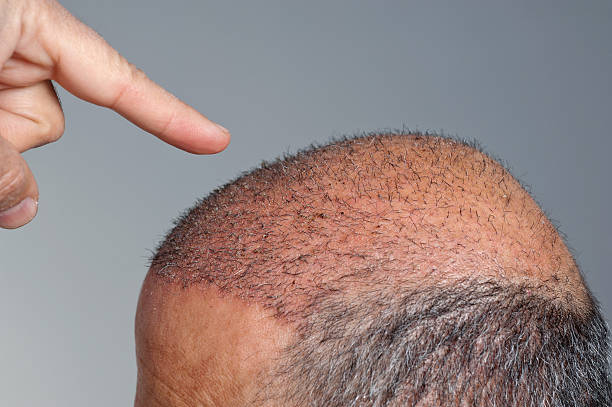
How to Spot Early Thinning
Early-stage hair thinning is often first noticed during everyday routines. You might find more strands in your brush, see your part widening, or notice increased scalp visibility under certain lighting. Women may detect a decrease in ponytail thickness, while men might see hair retreating at the temples. Taking regular photos from the same angles and consulting a healthcare professional can help you monitor changes objectively and decide if intervention is needed.
Recognizing Receding Hairline and Loss Patterns
Hairline recession follows recognizable trends. In male pattern hair loss, thinning often begins at the temples and evolves into an M-shaped hairline, potentially spreading to the crown. Female hair loss tends to present as overall thinning across the top of the head with the frontal hairline largely preserved. Knowing these patterns helps you and your clinician choose targeted strategies, since treatments can differ by pattern and progression.
Choosing Tools and Techniques for Fragile Hair
When hair is fragile or thinning, the right grooming tools and habits make a big difference. Use brushes with soft, flexible bristles that glide through hair without snagging. Wide-toothed combs minimize pulling when detangling; avoid rigid plastic-bristled brushes that can cause breakage and scalp irritation. Reduce mechanical stress by patting hair dry instead of rubbing, using low-heat styling settings, and limiting tight hairstyles that pull at the roots.
Treatment Options: Overview and Effectiveness
Below is a concise comparison of common medical and procedural treatments, including average cost ranges and reported success rates. These figures are estimates and may vary by region, provider, and individual circumstances.
| Treatment Type | Average Cost Range | Success Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Minoxidil | $15-45/month | 40-60% |
| Finasteride | $20-75/month | 66-85% |
| PRP Therapy | $500-2500/session | 60-70% |
| Hair Transplant | $4,000-15,000 | 85-95% |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Topical minoxidil is accessible and can slow thinning or stimulate regrowth for many users. Oral finasteride is effective particularly for male pattern hair loss but requires prescription and monitoring for side effects. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) uses concentrated growth factors from the patient to encourage follicle health and can be useful as part of a multi-modal plan. Surgical hair transplantation offers the most durable and immediate density increase but involves higher costs and recovery time. Success depends on factors such as age, the extent of hair loss, donor hair quality, and adherence to post-procedure care.
Prevention and Daily Maintenance
Preventing unnecessary hair loss involves consistent, gentle care and attention to overall health. Key strategies include:
- Scalp hygiene and care: keep the scalp clean and avoid harsh chemicals that damage follicles.
- Nutrition: ensure adequate protein, iron, zinc, vitamin D, and B vitamins—nutrients that support the hair growth cycle.
- Gentle styling: limit heat tools, chemical treatments, and tight hairstyles that exert chronic tension on hair.
- Stress and sleep: chronic stress and poor sleep patterns can disrupt hair growth cycles; stress management and restorative sleep help maintain normal hair renewal.
- Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol intake: both can negatively impact circulation and nutrient delivery to hair follicles.
Consistent scalp massages may improve blood flow, and appropriate over-the-counter or prescription therapies can be introduced early to preserve existing hair.
Combining Treatments and Setting Expectations
Effective hair loss management is often multimodal. A common approach combines topical agents (like minoxidil), oral medications (where appropriate), lifestyle adjustments, and procedures such as PRP or transplantation for more advanced cases. Results take time; medical treatments typically require several months before visible improvement, and surgical results evolve over a year or more. Tracking progress with photographs, symptom logs, and follow-up visits helps refine a long-term plan.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.
Hair loss can be emotionally difficult, but understanding causes, early warning signs, and the range of treatments lets you make informed decisions. With a tailored plan and realistic expectations, many people successfully slow progression, restore density, or achieve satisfying cosmetic outcomes. Regular consultations with a clinician will ensure your strategy adapts as your needs change.




