Hearing Clinics: What to Expect and How They Help
Hearing clinics provide targeted care for people experiencing hearing difficulties, from initial screening to long-term support. They bring together trained audiologists, diagnostic equipment, and hearing aid technology to identify the type and degree of hearing loss and recommend suitable interventions. This article explains typical clinic services, how sound is evaluated, and what to expect when seeking care. This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.
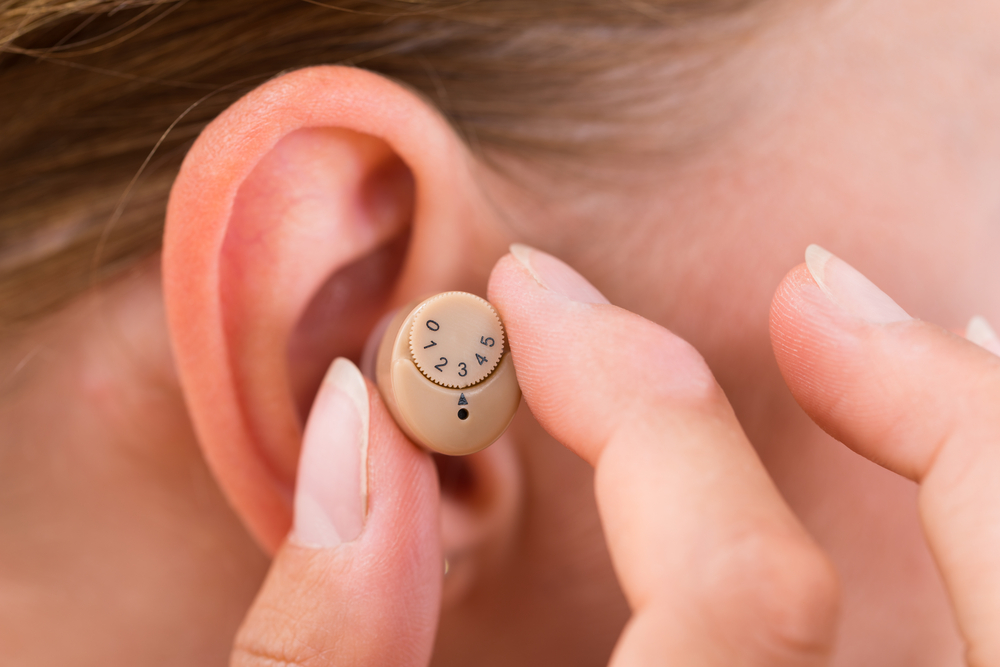

What does an audiologist do at a hearing clinic?
An audiologist is a licensed specialist who evaluates hearing and balance, interprets diagnostic test results, and recommends appropriate treatments. In a hearing clinic an audiologist will take a medical and noise-exposure history, perform pure-tone and speech audiometry to measure hearing thresholds and speech understanding, and run middle-ear and balance tests if needed. They explain findings in plain language, discuss options such as hearing aids or assistive devices, and provide counseling on communication strategies and hearing protection.
How do hearing aids improve your sound?
Hearing aids amplify and process sound to make speech and environmental noises clearer for people with hearing loss. Modern devices go beyond simple amplification: they selectively boost frequencies where loss occurs, reduce background noise, and adjust gain based on listening situations. In a clinic, an audiologist programs and fine-tunes hearing aids to match your audiogram and personal preferences, then verifies performance with real-ear measurements or speech tests so the amplified sound is both effective and comfortable.
What technology do clinics use?
Clinics use a range of diagnostic and fitting technologies to assess hearing and optimize treatments. Diagnostic tools include calibrated audiometers, tympanometers for middle-ear function, and otoacoustic emissions for cochlear screening. For fittings, clinicians rely on software platforms from hearing aid manufacturers to program devices, as well as probe-microphone systems to measure how a hearing aid delivers sound in the ear. Tele-audiology and remote fine-tuning are growing, letting clinicians support patients between visits using secure smartphone apps and cloud services.
How are hearing loss evaluations conducted?
A full hearing evaluation usually combines subjective and objective measures. Subjective tests, like pure-tone and speech audiometry, ask the patient to respond to tones and words to map hearing thresholds and speech understanding. Objective tests—such as tympanometry and otoacoustic emissions—do not require behavioral responses and help identify middle-ear or cochlear issues. Results are interpreted to classify the type (conductive, sensorineural, mixed) and severity of hearing loss, which guides recommendations for hearing aids, medical referral, or other interventions.
| Provider Name | Services Offered | Key Features/Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Amplifon | Hearing assessments, hearing aids, follow-up care | Global network of clinics, branded and multiple manufacturers, professional fittings |
| Specsavers Hearing | Hearing tests, hearing aid supply, repairs | Integrated with optical services in many locations, community-based clinics |
| Miracle-Ear | Hearing evaluations, hearing aids, accessories | Wide retail footprint in the US, in-person fittings and ongoing support |
| Beltone | Hearing tests, hearing aid fitting, tinnitus support | Clinic network and local audiologists, personalized counseling |
| Audika | Diagnostic testing, hearing aids, rehabilitation | International clinics focused on audiology-led care and aftercare |
Finding local services for hearing aids and care
When choosing a clinic in your area, look for credentialed audiologists, clear testing protocols, and aftercare options. Important practical considerations include whether the clinic offers in-person programming and follow-up, trials or demo periods for hearing aids, repair and maintenance services, and accessibility of appointments. Reading clinic websites and verified patient reviews can help, but direct questions about experience with your specific type of hearing loss, manufacturer options, and warranty coverage are best asked during an initial consultation.
What ongoing support should I expect after fitting?
Good clinics provide a schedule of follow-up visits to fine-tune hearing aids and assess progress. Early follow-up usually occurs within a few weeks after the first fitting to adjust settings and address comfort or sound-quality concerns. Clinics may offer hearing rehabilitation, communication strategies training, tinnitus management, and periodic hearing checks as hearing can change over time. Many clinics provide hearing aid maintenance, battery or charger support, and software updates to improve performance as technology advances.
Conclusion
Hearing clinics combine clinical expertise, diagnostic testing, and hearing aid technology to help people manage hearing loss and improve communication. Understanding the roles of audiologists, the types of tests used, and the technology available can make clinic visits more productive. When selecting care, prioritize qualified clinicians, clear follow-up plans, and a clinic that offers personalized fittings and long-term support to match your evolving hearing needs.