How Your Home's Market Value Is Determined
Understand the factors that shape your property's market price and learn practical ways to estimate and lift value. This guide covers location, home features, market trends, and renovation impact, explains valuation approaches like CMA, cost and income methods, and when to use an appraiser or online AVM. Perfect for homeowners, buyers, and investors seeking clear, actionable valuation insight.

How Your Home’s Market Value Is Determined
In a changing real estate market, knowing what your home is worth matters whether you plan to sell, refinance, or simply track your investment. Property value is the result of physical attributes, neighborhood conditions, and prevailing market forces combined with professional valuation techniques. This guide explains the main influences on market price and the most dependable ways to estimate and preserve home value.
Primary Drivers of Property Value
Location tops the list. Properties in desirable neighborhoods—good schools, low crime, convenient shopping and transit—typically command higher prices. Proximity to employment centers, public transportation, and planned infrastructure projects can boost or reduce desirability. Local zoning, floodplain status, and environmental risks also affect marketability.
The home’s physical traits matter next. Square footage, layout, age, structural condition, and the quality of finishes influence how a property compares to nearby listings. Lot size, outdoor amenities, and scenic views can add premiums in many areas. Conversely, deferred maintenance, structural defects, or poorly configured floor plans reduce buyer interest and market value.
Broader economic and market conditions shape what buyers will pay at any given time. Interest rates, local job growth, housing inventory, and national economic trends all play a role. Short-term factors—seasonal demand, sudden buyer surges, or changes to lending standards—can move prices quickly, while long-term trends determine appreciation potential.
Renovations, Upgrades and Maintenance
Not all improvements return the same value. Kitchen and bathroom updates typically offer solid returns because buyers expect modern, functional spaces. Routine upkeep—replacing an aging roof, servicing HVAC systems, and resolving structural issues—prevents depreciation and preserves asking price.
High-end or highly personalized upgrades may appeal to a limited pool of buyers and are less likely to be fully recouped. Strategic enhancements that broaden appeal—neutral finishes, improved energy efficiency (better insulation, modern windows, efficient heating), and general modernization—tend to be safer investments than bespoke luxury additions.
Using Market Analysis to Price a Home
Comparative market analysis (CMA) is a primary tool for residential pricing. A CMA examines recent sales of similar properties nearby and adjusts for differences in size, age, condition, and features to produce a realistic price range. Real estate agents frequently prepare CMAs to advise sellers and buyers.
Beyond comparables, market indicators such as inventory levels, days on market, mortgage rates, and local trends help set expectations. In low-inventory, high-demand markets a seller may fetch a premium compared with an otherwise identical home in a buyer’s market.
| Valuation Method | Description | Best Used For |
|---|---|---|
| Sales Comparison | Uses recent nearby sales of similar homes to estimate current market value | Most typical residential properties |
| Cost Approach | Adds land value to the estimated cost to replace the structure, minus depreciation | New construction or unique, hard-to-compare homes |
| Income Approach | Values property based on expected rental income and operating expenses | Investment, rental, or multi-family properties |
| Online Valuation | Automated models using public records and algorithms for quick estimates | Fast, preliminary estimates or market checks |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Professional Valuation Services
Licensed appraisers provide formal valuations following standardized procedures; their reports are typically required by lenders for mortgages and refinances. Appraisals analyze comparable sales, site characteristics, condition, and any legal or physical constraints.
Real estate agents produce CMAs and offer market-savvy advice about buyer preferences, listing strategies, and timing. Home inspectors don’t set value but identify defects that can materially affect price and negotiation leverage.
Automated valuation models (AVMs) and online tools deliver quick ballpark figures using algorithms and public data. They’re convenient for a rapid check but can miss recent renovations, interior upgrades, or local nuances; treat AVMs as starting points, not definitive valuations.
Protecting and Monitoring Your Home’s Value
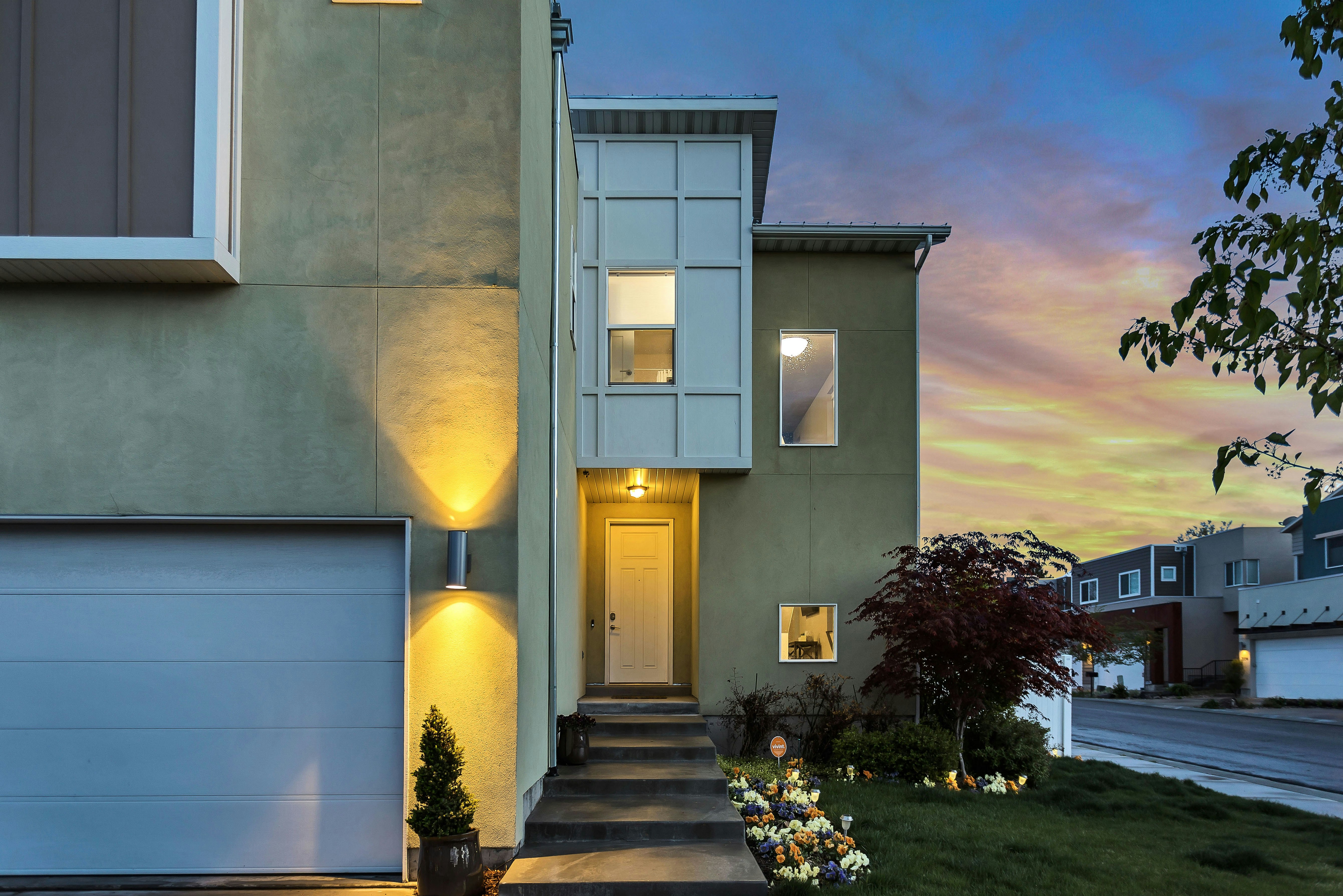
Consistent maintenance is the backbone of value preservation. Keep records for major systems, document renovations with receipts and photos, and address small issues before they escalate into costly repairs. Curb appeal matters: fresh paint, tidy landscaping, and good exterior lighting positively shape buyer perception.
Stay informed about neighborhood developments and municipal plans—new transit, school changes, or zoning updates can alter desirability. Consider periodic professional assessments such as an appraisal or a CMA every few years to monitor equity and inform refinancing or sale decisions.
Putting It All Together
Estimating a home’s worth requires layering several perspectives: evaluate location and physical features, account for broader market conditions, and select the valuation method aligned to your objective. Thoughtful, well-targeted improvements and disciplined upkeep protect and can increase value, while professionals provide the most reliable, actionable estimates. Combined, these steps let homeowners, buyers, and investors make confident, data-driven property decisions.