Manufacturing Jobs in the Netherlands: Roles and Career Paths
The manufacturing sector in the Netherlands offers a range of roles across factories, research labs, and supply-chain operations. This article provides general information about manufacturing jobs and career development; it does not list specific job openings or imply immediate availability of vacancies. Use this as a guide to understand typical positions, skills employers seek, and how industry trends may affect your career planning in the Netherlands.
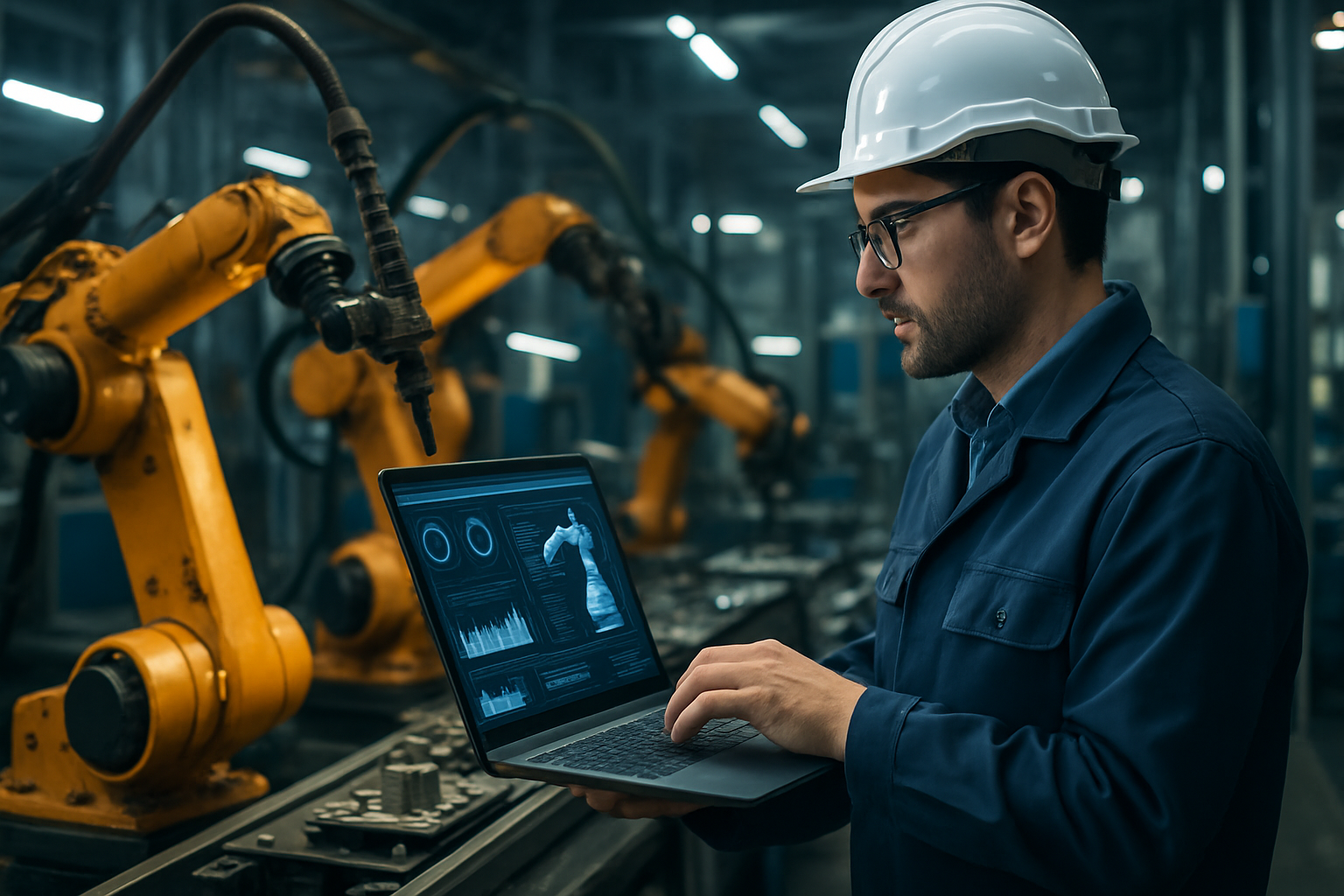

What types of manufacturing roles exist in factories?
Factory roles in manufacturing span entry-level production work to technical and managerial positions. Common positions include production operators, machine technicians, quality control inspectors, and maintenance staff. Skilled roles often require technical training in areas such as CNC operation, electrical systems, or robotics. Many facilities also have roles in logistics, warehouse management, and process improvement. Shift work, safety procedures, and adherence to quality standards are core expectations across most factory roles.
How can I develop a manufacturing career path?
A manufacturing career often starts with vocational training, apprenticeships, or short technical courses and can progress through certifications and on-the-job experience. Early steps include gaining competence in standard operating procedures, safety certifications, and basic machine operation. Mid-career progression may involve specialist training in automation, PLC programming, or quality management (e.g., Six Sigma basics). Leadership roles typically require both technical depth and experience in team supervision, continuous improvement, and project management.
What is the manufacturing industry landscape in the Netherlands?
The Netherlands hosts a diverse manufacturing industry that includes high-tech sectors like electronics and semiconductors, as well as food processing, chemicals, and machinery. The country’s logistics infrastructure and port access support export-oriented production. Industry trends include increased automation, digitalization (Industry 4.0), and an emphasis on sustainability and circular manufacturing. These trends shape demand for technicians skilled in automation, data handling, and energy-efficient processes rather than purely manual roles.
Which skills are important for factory work in the Netherlands?
Foundational skills for factory work include mechanical aptitude, basic electrical knowledge, and adherence to safety standards. Increasingly important are digital literacy, familiarity with PLCs, and the ability to interpret technical drawings and process documentation. Soft skills such as teamwork, problem-solving, and communication in a multilingual environment are valuable in the Netherlands. Language requirements vary by employer; many international firms use English, while Dutch can be advantageous for roles involving local teams or regulatory compliance.
What industry sectors hire for manufacturing positions?
Key sectors hiring manufacturing staff include food and beverage processing, pharmaceuticals, high-tech equipment, automotive components, and chemical production. Each sector has specific regulatory and quality standards — for example, GMP in pharmaceuticals or HACCP in food processing — that shape hiring and training needs. Suppliers and tiered manufacturing networks also create positions in component production, assembly, and testing. Employers range from multinational corporations to regional manufacturers and contract manufacturers serving multiple industries.
How can training and certifications support a manufacturing career?
Formal vocational education, apprenticeships, and industry certifications strengthen candidacies for manufacturing roles. In the Netherlands and internationally recognized paths, technical diplomas (MBO level in the Dutch system), electrical/mechanical apprentice certificates, and specialized credentials in automation or quality control are common. Short courses in health and safety, forklift operation, or PLC programming provide practical advantages. For long-term progression, consider continuous learning in areas like predictive maintenance, robotics, and data-driven process optimization.
Conclusion
Manufacturing jobs in the Netherlands encompass a broad array of roles across factory floors and supporting functions in supply chains and engineering. Career growth typically combines practical experience, targeted training, and adaptability to evolving industry trends such as automation and sustainability. This overview is informational and does not represent specific job listings; for current vacancies, consult official job boards, company career pages, or local services in your area.