Packing Jobs: Opportunities in Factory and Manufacturing Settings
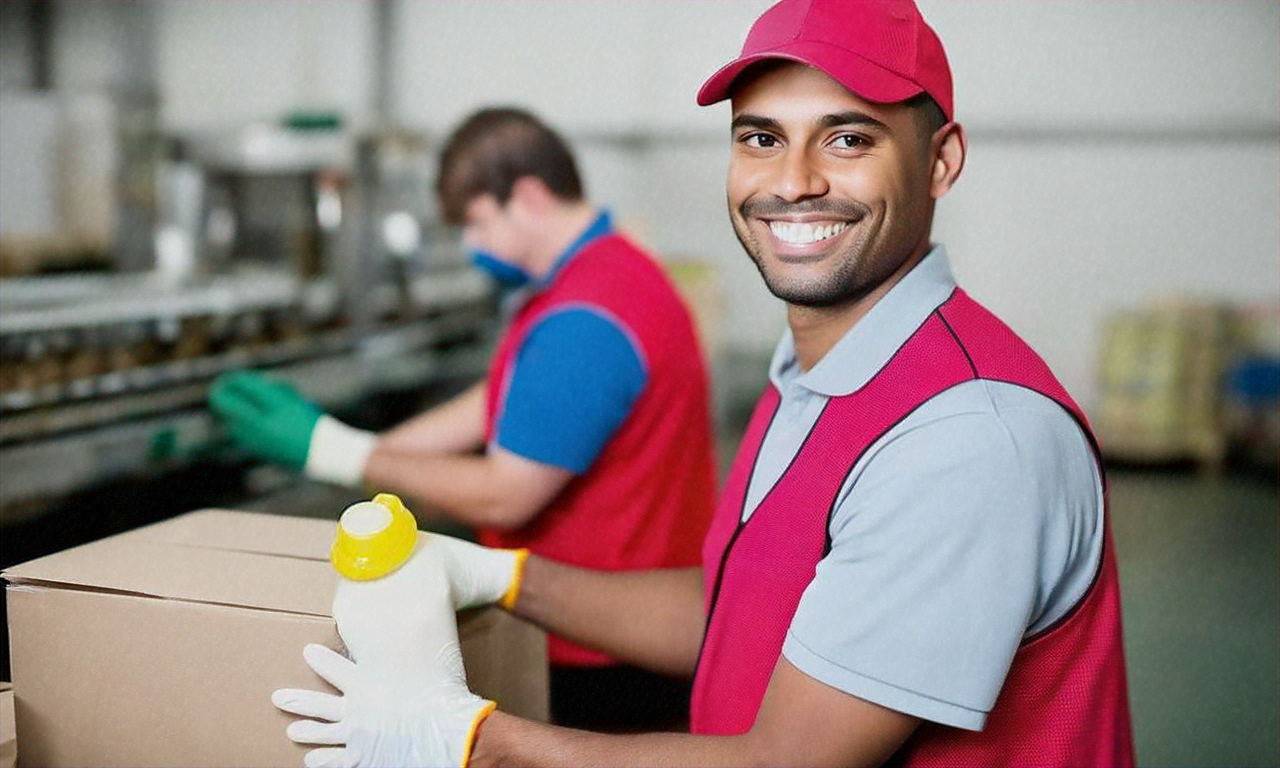
Packing jobs play a crucial role in the manufacturing and distribution sectors, serving as an essential link between production and delivery to customers. These positions involve carefully preparing, organizing, and securing products for shipping or storage, ensuring they reach their destination in perfect condition. Packing jobs are found in various industries, from food processing to electronics manufacturing, offering diverse opportunities for workers with different skill sets and experience levels.

-
Wrapping items in protective materials such as bubble wrap or foam
-
Placing products securely in appropriate packaging
-
Labeling packages with relevant information, including shipping details and product specifications
-
Operating packaging machinery, such as shrink-wrap machines or box sealers
-
Maintaining a clean and organized work area
-
Following safety protocols and adhering to company guidelines
These responsibilities may vary depending on the specific industry and the type of products being packaged. Some packing jobs may require additional skills, such as operating forklifts or using specialized packaging equipment.
What qualifications are needed for packing jobs in factories?
While many packing jobs are entry-level positions that don’t require extensive qualifications, there are some common requirements and desirable skills:
-
High school diploma or equivalent (often preferred but not always mandatory)
-
Physical stamina and ability to stand for long periods
-
Manual dexterity and hand-eye coordination
-
Basic math skills for counting and measuring
-
Attention to detail and quality control
-
Ability to work in a fast-paced environment
-
Team player mentality and good communication skills
-
Flexibility to work different shifts, including nights and weekends
-
Knowledge of safety procedures and willingness to follow them strictly
Some employers may require additional certifications, such as forklift operation or hazardous materials handling, depending on the specific job requirements and industry standards.
How does the manufacturing sector impact packing job opportunities?
The manufacturing sector plays a significant role in creating packing job opportunities. As factories produce goods, there is a constant need for workers to package these items for distribution. The health of the manufacturing industry directly affects the availability of packing jobs:
-
Economic growth: When the economy is strong, manufacturing output typically increases, leading to more packing positions.
-
Automation: While some packing tasks have been automated, many still require human judgment and dexterity, maintaining job opportunities.
-
Industry diversification: Different manufacturing sectors (e.g., food, electronics, pharmaceuticals) create varied packing jobs with unique requirements.
-
Seasonal demand: Some industries experience peak seasons, creating temporary packing job opportunities.
-
E-commerce growth: The rise of online shopping has increased the demand for efficient packaging solutions, potentially leading to more packing jobs in fulfillment centers.
Understanding these factors can help job seekers identify potential opportunities and trends in the packing job market within the manufacturing sector.
What are the working conditions like for packing workers?
Working conditions for packing jobs can vary depending on the specific industry and employer, but there are some common characteristics:
-
Physical demands: Packing often involves standing for long periods, lifting moderately heavy objects, and performing repetitive motions.
-
Work environment: Most packing jobs are in warehouse or factory settings, which can be noisy and may have temperature fluctuations.
-
Shift work: Many manufacturing facilities operate around the clock, requiring packing workers to work various shifts, including nights and weekends.
-
Safety measures: Proper safety equipment, such as gloves, safety glasses, and steel-toed boots, is often required and provided by employers.
-
Teamwork: Packing jobs frequently involve working alongside others on assembly lines or in coordinated groups.
-
Productivity targets: Many packing positions have set quotas or productivity goals that workers are expected to meet.
-
Technology integration: Increasingly, packing jobs may involve using computerized systems or operating packaging machinery.
While the work can be physically demanding, many employers strive to create safe and comfortable working environments for their packing staff.
What are the career advancement opportunities in packing and manufacturing?
Packing jobs can serve as a starting point for long-term careers in manufacturing and logistics. There are several potential paths for advancement:
-
Team leader or supervisor roles, overseeing packing operations
-
Quality control positions, ensuring packaging meets standards
-
Logistics coordinator roles, managing inventory and shipments
-
Machine operator positions, running advanced packaging equipment
-
Warehouse management opportunities
-
Supply chain management careers
-
Production planning and scheduling roles
-
Safety coordinator positions, focusing on workplace safety practices
Advancement often requires a combination of experience, demonstrated skills, and sometimes additional education or certifications. Many companies offer on-the-job training and development programs to help employees progress in their careers.
In conclusion, packing jobs offer valuable opportunities in the manufacturing sector, providing essential services in the production and distribution chain. While these positions can be physically demanding, they often serve as entry points into broader careers in manufacturing, logistics, and supply chain management. As the manufacturing industry continues to evolve, packing jobs remain a crucial component, adapting to new technologies and changing consumer demands.