Pilates for Rehabilitation and Overall Fitness
Pilates is a movement system that emphasizes controlled movement, breath, alignment, and core strength. Originating in the early 20th century, it has evolved into mat-based and equipment-assisted methods used by people with a range of goals—from improving posture and mobility to supporting recovery after injury. This article outlines how pilates connects with physical therapy, rehabilitation, exercise programming, and broader fitness goals.

This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.
How does pilates support physical therapy?
Pilates complements physical therapy by focusing on controlled, low-impact movements that target deep stabilizing muscles, particularly the core and pelvic floor. Physical therapists often borrow pilates principles—breath coordination, neutral spine, and precise repetition—to help patients regain movement quality, reduce compensatory patterns, and restore functional mobility. For people with chronic low back pain or postural issues, pilates-style exercises can be integrated into a therapeutic plan to address movement deficits identified during clinical assessment.
Beyond isolated muscle strengthening, pilates trains motor control and body awareness, which therapists use to progress patients safely through stages of rehabilitation. Collaboration between a pilates instructor and a licensed physical therapist can ensure exercises match clinical goals and precautions, especially after surgery or acute injuries.
Can pilates aid rehabilitation after injury?
Pilates can be adapted for rehabilitation by scaling intensity and complexity to the person’s recovery stage. Early rehabilitation typically emphasizes gentle mobilization, pain management, and reactivation of inhibited muscles; pilates offers many low-load options (mat work, small accessory tools) suitable for this phase. As healing progresses, exercises can advance to improve endurance, balance, and functional strength relevant to daily tasks or sport-specific activities.
Safety depends on individualized assessment—factors such as the type of injury, healing timeline, and medical restrictions determine which pilates exercises are appropriate. Working with clinicians who understand both rehabilitation protocols and pilates progressions helps reduce risk and ensures that exercises support tissue healing and return-to-activity goals.
What pilates exercises focus on core and overall exercise benefits?
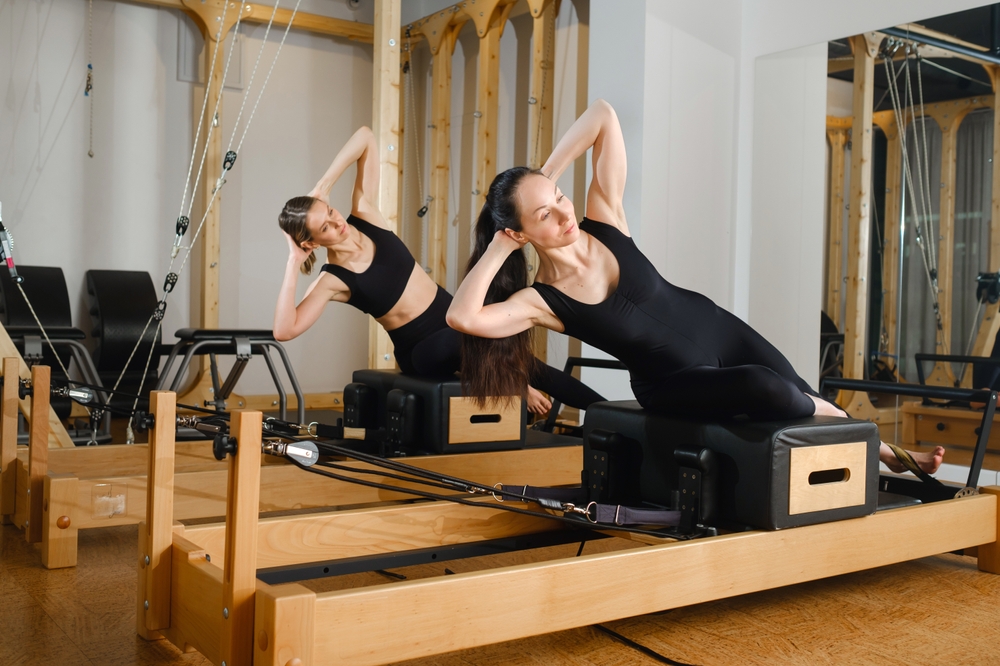
Classic pilates exercises that target core stability include the pelvic tilt, dead bug variations, bridging, and controlled rolling patterns. Equipment such as the reformer and Cadillac adds options for graded resistance and assisted movement, allowing practitioners to challenge balance and coordination while maintaining control. Regular practice improves spinal alignment, breath mechanics, joint mobility, and muscular endurance—components that contribute to better daily movement and reduced injury risk.
As an exercise modality, pilates emphasizes quality over quantity: shorter sessions with mindful repetition often yield improved motor control and posture. For fitness seekers, combining pilates with aerobic and strength training can create a balanced program that supports cardiovascular health, muscular strength, and flexibility without excessive joint loading.
How to include pilates in your exercise routine?
Begin by matching pilates intensity and format to your current fitness and any medical considerations. Beginners benefit from guided classes or private sessions that teach foundational breathing, pelvic and scapular stabilization, and safe movement patterns. Frequency of two to three sessions per week can build noticeable improvements in posture and control; home mat routines and short daily mobility sessions reinforce those gains.
Progress by increasing complexity (adding equipment or unstable surfaces), integrating pilates sequences with functional strength exercises, or working on movement skills—lunges, squats, and overhead reaching—with pilates-based alignment cues. Tracking progress through movement tests (balance, single-leg stance, controlled squat depth) helps tailor exercise progression while reducing the chance of overuse.
Where to find pilates and local services for fitness and rehabilitation?
Pilates is available through various providers: independent pilates studios, rehabilitation clinics that offer clinical pilates, community fitness centers with certified instructors, and online programs. When seeking services in your area, consider credentials (certifications in pilates and relevant healthcare licenses), experience with rehabilitation or clinical populations, and whether the provider communicates modifications for injuries or medical conditions. Clinics that integrate physical therapy and pilates-style sessions may be a good option for those needing rehabilitation oversight.
Ask prospective providers about assessment procedures, class size, equipment availability (reformer, Cadillac, small props), and how they coordinate with referring healthcare professionals. For remote or hybrid options, look for instructors who offer individualized feedback and clear progressions to maintain safety outside supervised sessions.
Pilates offers a scalable approach that can fit preventive fitness, adjunctive rehabilitation, and long-term movement maintenance. Its emphasis on control, posture, and breath makes it a practical complement to other exercise modalities and to clinical programs focused on restoring function.
In summary, pilates can support physical therapy and rehabilitation when adapted to individual needs and used alongside appropriate clinical guidance. It provides specific exercise tools for core stability, movement quality, and postural improvement while also serving broader fitness aims when combined with aerobic and strength training. Consider professional assessment to ensure exercises are safe and aligned with your health and performance goals.