Prefab Homes: A Practical Guide to Modern Modular Living
Discover how prefabricated homes—also called prefab or modular houses—are reshaping residential construction. Built in controlled factories and assembled on-site, these homes deliver faster build times, consistent quality, and lower costs. Learn about types, benefits, common myths, pricing, and future trends in prefab housing to decide if it's the right choice for your next home.
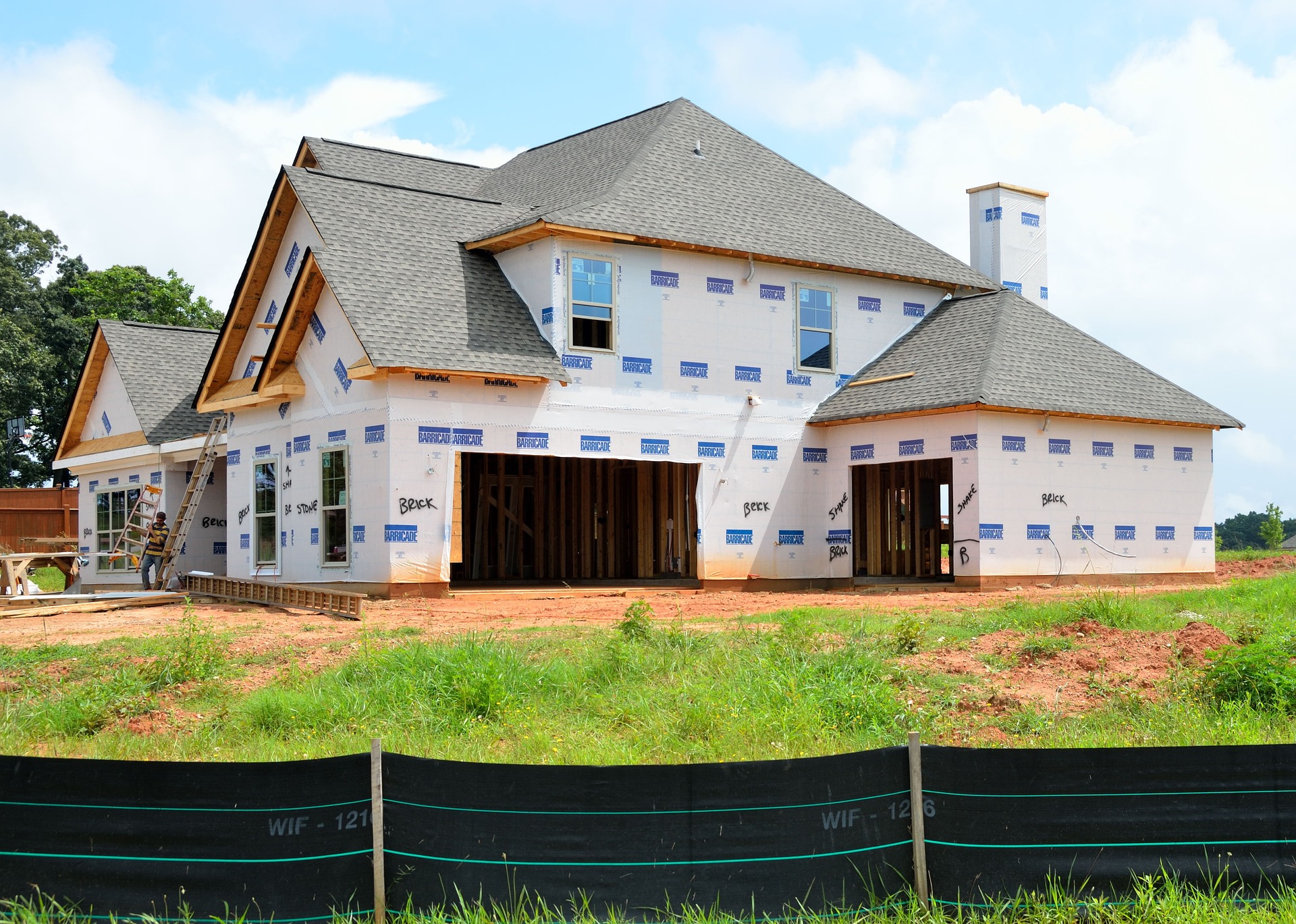

Types of prefabricated homes
Prefabricated housing comes in several distinct forms, each suited to different budgets, building sites, and regulatory environments. Understanding these categories helps buyers match a home type to their needs.
-
Modular homes are constructed in multiple sections or “modules” at a factory, transported to the site, and permanently joined on a foundation. Because modules are assembled indoors under controlled conditions, finish quality and dimensional accuracy tend to be high, and designs can be highly customizable.
-
Manufactured homes (historically called mobile homes) are factory-built on a permanent chassis, which allows them to be moved if necessary. Today’s manufactured homes often include modern finishes and energy-conscious features, and they remain a cost-effective route to homeownership where zoning allows.
-
Panel-built homes use pre-fabricated wall, floor, and roof panels that are produced offsite and assembled much like a kit on the construction site. This approach reduces on-site labor and offers flexibility in layout while maintaining the efficiencies of factory production.
Each approach offers a different balance of customization, transport logistics, and suitability for local building codes, so it’s important to weigh site conditions, financing options, and regulatory requirements when choosing a type.
Advantages of choosing a prefabricated home
Prefabricated construction provides several compelling benefits over traditional site-built houses. Working in a factory environment enables tighter quality control and standardized processes, which often translate into fewer defects and more consistent finishes.
Energy performance is another advantage. Prefab homes commonly use up-to-date insulation, airtight building techniques, and modern materials, which can lower heating and cooling costs. Because components are cut precisely in controlled environments, material waste is typically reduced—making prefab homes a more sustainable building choice.
Speed is also a practical benefit: weather delays and on-site scheduling conflicts are minimized, so projects frequently finish faster than equivalent site-built homes. Faster completion can reduce financing and holding costs, and enable homeowners to move in sooner.
Clearing up common misconceptions
Many potential buyers worry that prefabricated homes are inherently inferior in quality or design. This is an outdated notion. Contemporary prefab houses must comply with applicable building codes and standards, and reputable manufacturers often exceed those minimums.
Customization is readily achievable. Modular and panel systems can accommodate varied floor plans, finishes, and architectural styles. Durability is likewise comparable: many modern prefab homes use robust materials and construction techniques that match or exceed the longevity of site-built homes when properly maintained.
Another myth is that prefab equals cheap-looking. In reality, finishes, fixtures, and architectural detailing are increasingly indistinguishable from traditional construction, and high-end prefabricated options exist for buyers seeking premium materials and bespoke design.
Cost considerations and market comparison
Overall, prefabricated homes generally cost less than equivalent site-built houses, largely because factory efficiencies and reduced on-site labor lower overhead. Typical savings are often in the 10–25% range, though actual costs vary by region, design complexity, site preparation needs, and local permitting requirements.
Below is a practical comparison of common prefab home types, their typical price ranges, core features, and average construction timelines.
| Home Type | Average Cost Range | Key Features | Construction Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Modular | $180,000–$360,000 | Highly customizable layouts, installed on permanent foundation | 3–4 months |
| Manufactured | $50,000–$150,000 | Built on a chassis for mobility, faster installation | 2–3 months |
| Panel-Built | $150,000–$300,000 | Efficient thermal performance, flexible design | 2–3 months |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
When budgeting, include site work (grading, foundation, utilities), local permitting fees, transport costs for modules or panels, and interior finishes. Financing options can differ: manufactured homes often use different loan products than modular or site-built homes, so consult lenders familiar with prefab financing.
The future of prefabricated housing
The prefab sector is evolving rapidly as technology, design, and sustainability priorities converge. Smart home systems are being integrated during factory assembly, making connectivity and automation easier and more affordable. Manufacturers are also increasingly adopting low-impact materials and greener production methods to reduce lifecycle environmental footprints.
Innovations such as advanced manufacturing techniques, prefabricated mass timber, and improved logistics are helping lower costs and expand architectural possibilities. As urbanization and housing affordability pressures grow, prefab housing offers scalable solutions for faster, more predictable construction.
For buyers, the growing variety and quality of prefabricated options mean more choices—whether seeking an affordable starter home, a highly customized modular build, or a sustainably designed panel residence. With careful planning, attention to local regulations, and clear budgets, prefabricated homes can deliver excellent value, performance, and living comfort for modern homeowners.
Final considerations
If you’re exploring prefab as an option, start by researching reputable manufacturers, visiting model homes when possible, and getting multiple estimates that include site prep and delivery. Verify code compliance, warranty coverage, and after-sales support. Prefabrication isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution, but for many buyers it represents a smart, efficient alternative to conventional construction—combining speed, quality, and cost-effectiveness in a rapidly advancing marketplace.