Prefab Homes: The Modern Housing Revolution
Prefabricated (prefab) and modular homes are reshaping residential construction by moving much of the build process into controlled factories. Faster to assemble, more energy-efficient, and often more affordable than traditional builds, prefab homes offer sustainable, customizable solutions for today’s housing needs. Discover how this approach cuts waste, shortens timelines, and supports renewable integration for modern living.
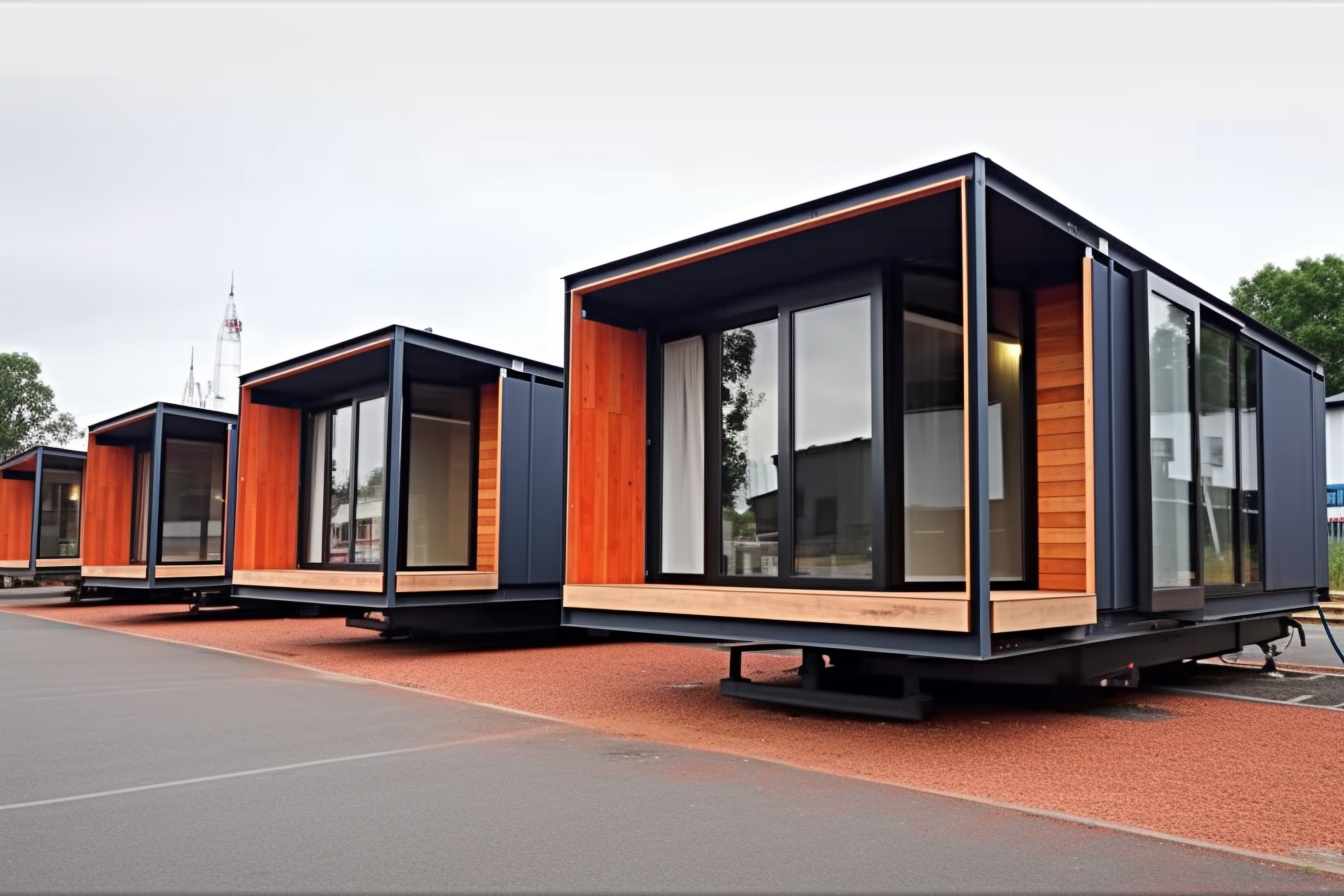

Prefabricated homes are changing how we think about building houses. Instead of constructing every element on-site, many components are designed digitally, manufactured in a factory, and then transported for final assembly. This streamlined approach reduces delays, improves quality control, and offers compelling advantages for homeowners and builders alike.
How prefabrication works
Most prefab projects begin with detailed designs created in computer-aided design (CAD) software. These digital plans guide precision manufacturing in an off-site facility, where walls, floors, roof sections, and interior modules are produced under controlled conditions. Once components are completed, they are shipped to the property and assembled on a prepared foundation. The factory environment allows for tighter tolerances and consistent finishes that can be difficult to achieve with fully on-site construction.
Benefits of choosing a prefab home
Speed is one of the most noticeable benefits. Because much of the work happens indoors, projects are less vulnerable to weather interruptions and seasonal slowdowns, which often extend timelines for traditional builds. With parallel workflows—site preparation happening while modules are built—completion times can be dramatically shortened.
Prefab construction also tends to generate less material waste. Factories can optimize cuts and recycle leftovers more effectively than on-site crews, which supports sustainable building practices. Consistency in manufacturing reduces the likelihood of construction errors and rework, supporting predictable quality across multiple units.
Energy performance is another strength. Factory-built components fit more precisely, enabling better air sealing and effective insulation installation. Many manufacturers go further by offering high-performance windows, efficient HVAC systems, and smart controls. Some prefab homes are even engineered to meet rigorous energy standards such as Passive House, and modular designs are well-suited to integrating renewable systems like rooftop solar during production.
Cost advantages often come from shortened construction periods and reduced on-site labor. While the base price per square foot can be similar to conventional construction, minimizing delays and unexpected expenses can make the overall investment more predictable and sometimes cheaper. The controlled production process helps guard against the budget overruns that frequently occur with traditional projects.
Prefab versus traditional construction
Traditional building typically assembles the entire structure on-site, which gives broad flexibility for in-the-moment design changes but introduces greater exposure to weather, fluctuating material availability, and scheduling conflicts. Prefab shifts much of the work to a factory, providing a more controlled workflow and better repeatable quality.
Customization is no longer a major limitation for prefab homes. Many manufacturers provide modular design libraries and finish options that allow buyers to personalize layouts, facades, and interiors. While on-site custom modifications are easier with stick-built homes, the gap is narrowing as prefab firms expand their design offerings.
For regions with short building seasons or harsh climates, prefab’s reduced on-site time and weather immunity can be especially advantageous. Likewise, developers building multiple units can benefit from factory efficiencies and consistent quality across projects.
Energy efficiency and sustainability
The precise construction practices used in prefab production help minimize thermal bridging and air leakage, yielding better long-term energy performance. Manufacturers can install high-grade insulation and test assemblies for airtightness before shipment. Factory integration of energy-saving technologies—high-efficiency windows, LED lighting, energy-star appliances, and home automation—further reduces operating costs.
Modular construction also simplifies the incorporation of renewables. Solar panels, battery systems, or pre-plumbed infrastructure for future green upgrades can be installed during manufacturing, streamlining final on-site hookups and lowering installation complexity.
Costs and what to expect
Below is a general pricing guide for prefabricated homes. Actual costs vary by region, manufacturer, finishes, and additional site expenses.
| Home Type | Size (sq ft) | Average Cost Range |
|---|---|---|
| Small Prefab | 400 - 1,000 | $80,000 - $200,000 |
| Medium Prefab | 1,000 - 2,000 | $180,000 - $360,000 |
| Large Prefab | 2,000+ | $300,000 - $500,000+ |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Keep in mind the figures above usually cover the manufactured dwelling itself and may exclude important additional costs: land purchase, site preparation (grading, foundation work), utility hookups, transportation of modules, local permits, and any special foundation or access requirements. Accurately budgeting a prefab project requires factoring in these site-specific expenses.
Future outlook for prefab housing
The prefab sector is poised for continued growth as technology and materials evolve. Advances in digital design, robotic fabrication, and new sustainable materials will expand both the aesthetic possibilities and performance of factory-built homes. Urban density pressures and the need for affordable housing are likely to encourage modular solutions that can be produced quickly and repeatedly.
Environmental concerns also favor prefab methods: less waste, lower on-site disturbance, and better integration of energy-efficient systems align with broader sustainability goals. As manufacturers broaden customization options and mainstream acceptance grows, prefabricated homes are likely to become a familiar and respected alternative to conventional building.
Final thoughts
Prefabricated homes offer a practical, modern option for people seeking efficiency, quality, and sustainability in residential construction. By combining digital design, factory precision, and thoughtful integration of energy systems, prefab builds reduce uncertainty while expanding accessible housing choices. For homeowners and developers looking for predictable timelines, improved performance, and greener outcomes, modular and prefab solutions deserve serious consideration.