Prefabricated Homes Guide: Modern, Efficient Building
Discover how prefabricated homes combine fast construction, eco-friendly materials, and contemporary design. This guide explores factory-built options—modular, panelized, mobile, and custom prefab—highlighting benefits like reduced waste, energy efficiency, shorter build times, and realistic cost expectations for prospective homeowners.
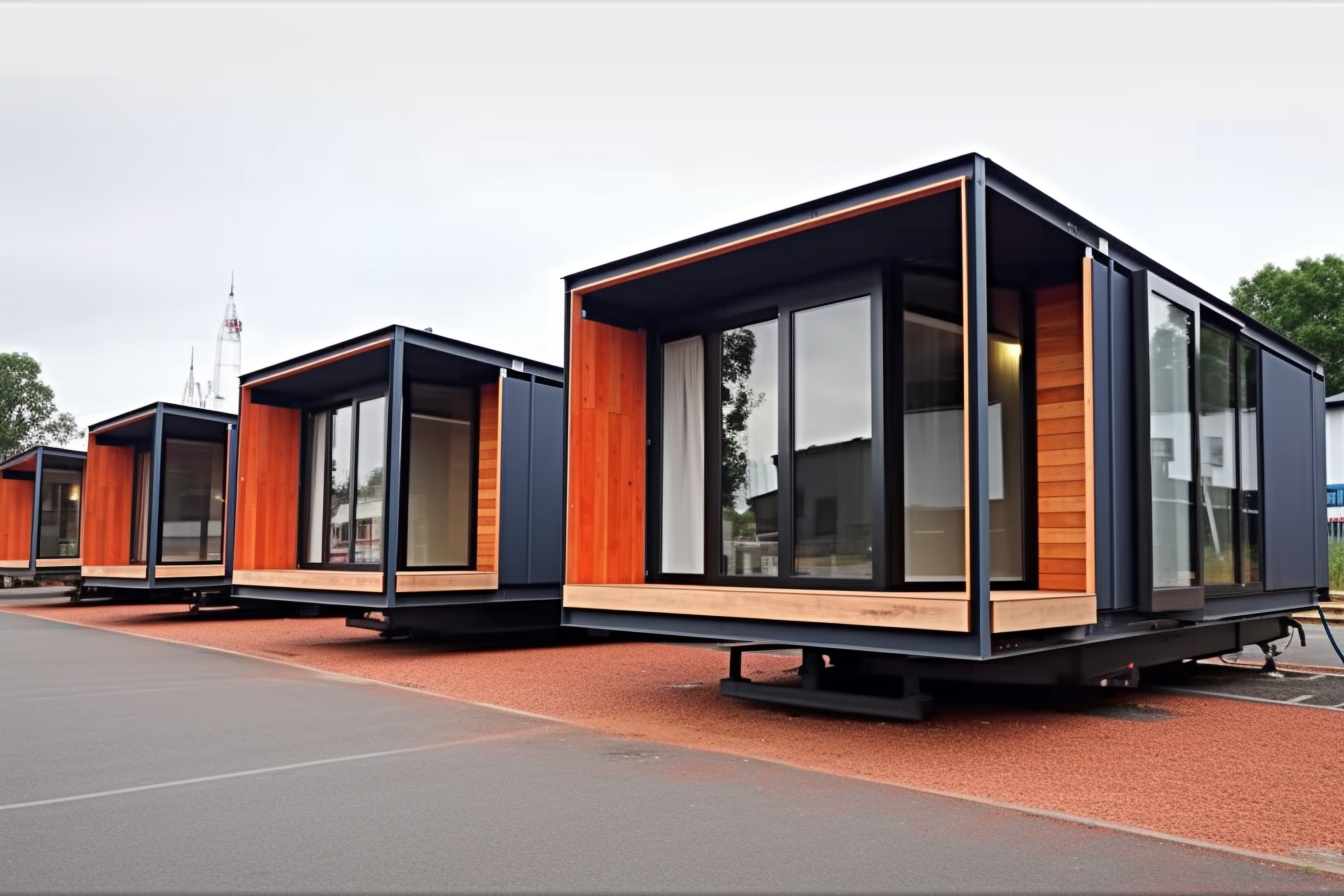

Types of prefabricated homes
Prefabricated dwellings come in several forms to suit different budgets, lifestyles, and site conditions. Modular homes are assembled from multiple factory-built sections (modules) that are joined on-site to form a finished residence. Panelized systems deliver pre-manufactured walls, floors, and roof panels to the property for rapid on-site assembly. Mobile homes are built atop a chassis and designed for relocation, though they are often treated as a distinct housing category. Finally, custom prefab solutions let buyers work with manufacturers to create one-off designs without sacrificing the efficiencies of factory production.
Each approach has distinct advantages. Modular construction offers high consistency and quick assembly, panelized buildings provide flexibility in design while simplifying on-site labor, mobile homes emphasize affordability and mobility, and custom prefab blends tailored aesthetics with controlled manufacturing.
Why choose a prefab home?
There are compelling reasons why homeowners and builders are increasingly turning to prefab methods. Producing components inside a factory reduces exposure to weather delays and enables tighter quality control. That controlled environment typically leads to less material waste and fewer defects than traditional stick-built construction.
Speed is another major benefit: factory fabrication and on-site work can proceed in parallel, often cutting total project timelines by as much as half compared with conventional builds. Many prefab homes also incorporate energy-saving features—better insulation, efficient windows, and modern HVAC integrations—that lower utility bills and reduce a home’s carbon footprint. When sustainability matters, prefab construction makes it easier to use responsibly sourced or recycled materials and to optimize building systems for long-term performance.
Cost considerations and pricing overview
Costs for prefabricated houses vary widely based on size, finish level, site conditions, transportation, and local labor. A common per-square-foot estimate for many prefab projects ranges from about $100 to $200, but customization, high-end finishes, or complicated sites can push total prices higher.
Below is a practical pricing snapshot to help you compare typical options and scale expectations:
| Home Type | Base Price Range | Average Size Range |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Modular | $100,000–$200,000 | 1,000–2,000 sq ft |
| Custom Modular | $200,000–$500,000 | 2,000–3,500 sq ft |
| Luxury Prefab | $500,000+ | 3,000+ sq ft |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on available market information and may change over time. Independent research and vendor quotes are recommended before making financial decisions.
Beyond the sticker price, remember to budget for land acquisition, site preparation, foundation work, utility connections, permits, and transport or crane costs. Some manufacturers provide turnkey packages that include on-site installation, while others supply a ready-to-assemble shell that requires additional contractor work.
Meeting codes and navigating regulations
Prefabricated structures must comply with the same building codes and safety standards that govern traditional construction. Factory-built sections typically undergo their own quality inspections during production and must satisfy transportation regulations when moved to the site. Once on-location, local permitting and inspection processes apply to foundations, utility hookups, and final assembly.
Regulatory requirements can differ regionally, so early coordination with local building departments and your prefab manufacturer is crucial. This helps avoid costly redesigns, delays in approvals, or problems during inspection. Some jurisdictions have streamlined processes for modular buildings, while others treat mobile and modular homes under separate rules—confirm classifications and permit needs upfront.
Design flexibility and customization options
Modern prefabrication doesn’t mean sacrificing design. Many manufacturers offer extensive customization of floor plans, interior layouts, and exterior finishes. Buyers can select materials, fixtures, cabinetry, and energy systems to match personal tastes. Some firms provide architectural consultations to adapt standard modules or panels into unique designs, blending factory precision with individualized aesthetics.
Prefab also supports a range of architectural styles—from minimalist, contemporary boxes to craftsman or traditional facades—by varying cladding, rooflines, and window arrangements. Interior customization can include open-plan living areas, built-in storage solutions, upgraded kitchens and bathrooms, and smart home integrations.
Practical considerations for buyers
When evaluating prefab options, consider these practical factors:
- Manufacturer reputation and warranty coverage: Ask for references, production photos, and warranty terms.
- Site access and logistics: Verify that roads, bridges, and property access can accommodate transport and cranes.
- Foundation and site prep: Confirm soil conditions, grading needs, and drainage plans.
- Timeline expectations: Understand which parts of the project proceed concurrently and which are sequential.
- Financing and appraisal: Some lenders and appraisers treat prefab homes differently—seek lenders experienced with factory-built housing.
Conclusion
Prefabricated housing offers a compelling alternative to traditional construction for those seeking faster schedules, reduced waste, and improved quality control. With options ranging from affordable mobile units to high-end custom modular residences, prefab methods can suit many lifestyles and budgets. Careful planning—covering costs, codes, site logistics, and design preferences—ensures that a factory-built home delivers the combination of efficiency and personalization many buyers want.