Prefabricated Homes Today: Smart, Sustainable Living
Prefabricated (prefab) and modular homes are reshaping residential construction by combining faster build times, better quality control, and sustainable design. Manufactured in controlled factories and assembled onsite, these customizable, energy-efficient homes offer modern amenities and cost advantages for homeowners seeking efficiency, flexibility, and long-term value in their housing decisions.
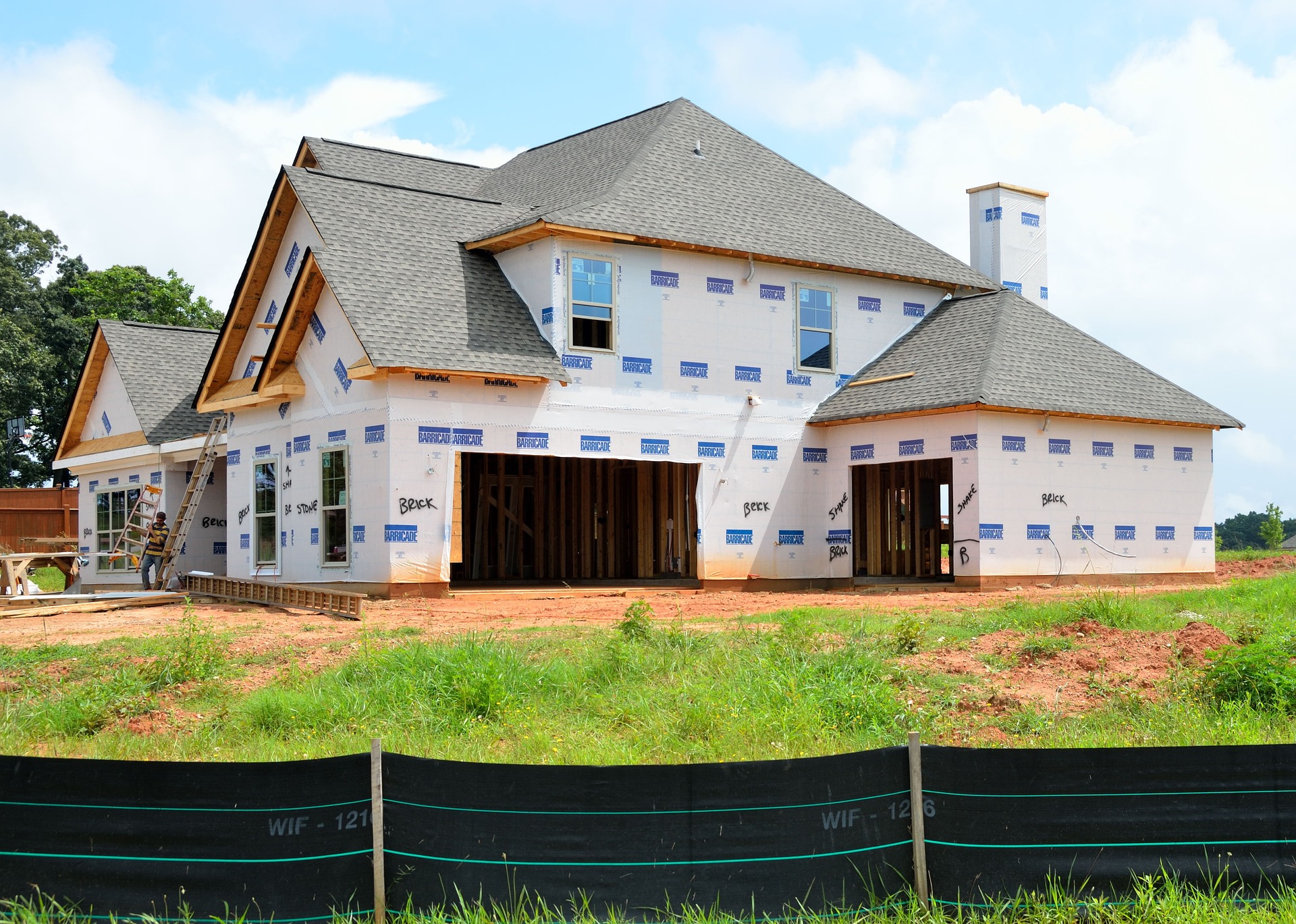

Advantages of Prefabricated Homes
Prefabricated homes, often called prefab or modular homes, deliver a number of practical benefits compared with traditional site-built construction. Because major components are produced in a factory setting, the overall construction timeline is frequently shortened—commonly by about 30 to 50 percent—cutting weeks or months from delivery schedules. Controlled manufacturing environments also enable stricter quality oversight: parts are checked at multiple stages before they leave the facility, reducing the likelihood of on-site mistakes and rework.
Energy performance is another strong selling point. Many prefab homes are built using efficient insulation, high-performance windows, and integrated systems that reduce energy use and utility bills. Manufacturers increasingly select sustainable or recycled materials, helping to lower embodied carbon and waste during construction. For homeowners interested in longevity and lower operating costs, prefab options can offer a compelling combination of durability and environmental responsibility.
Design Options and Customization
Modular construction today spans a wide range of architectural styles—from minimalist modern boxes to more traditional pitched-roof designs. Buyers can often choose layouts, finishes, fixtures, and exterior cladding to suit personal taste. Options run the gamut from compact, budget-friendly starter homes to large, multi-story residences with premium features such as integrated smart-home systems, solar-ready roofs, and energy-efficient HVAC packages.
This flexibility extends beyond aesthetics. Many manufacturers provide customizable floor plans that can be adapted for growing families, home offices, or multi-generational living. Because modules are designed in advance, architects and designers can optimize each square foot for functionality, creating efficient circulation and storage solutions that maximize usable space.
Cost Considerations and Market Snapshot
One of the main attractions of prefabricated homes is their potential for cost savings. Factory production can reduce labor overhead, waste, and weather-related delays that often inflate site-built budgets. However, final costs vary widely depending on size, level of customization, site preparation needs, foundation work, local permitting fees, and transportation to the build site.
Below is a general pricing guide to illustrate typical base price ranges by home size. These figures are estimates to help readers understand relative costs and are not a substitute for detailed quotes from manufacturers or builders.
| Home Type | Average Size (sq ft) | Base Price Range |
|---|---|---|
| Small Modular | 600-1,200 | $60,000-$120,000 |
| Medium Modular | 1,200-2,000 | $120,000-$200,000 |
| Large Modular | 2,000-3,000+ | $200,000-$400,000 |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Building Codes, Quality, and Durability
Contrary to outdated perceptions, modern prefab homes must meet or often exceed the same building codes and inspection requirements as site-built residences. Components typically undergo multiple quality-control checks during manufacturing and are inspected again after on-site assembly. Many manufacturers also offer warranties comparable to traditional homebuilders, providing buyers with additional assurance.
Modular units can be engineered to handle local climate demands, including high winds, heavy snow, or seismic activity, depending on regional standards and design choices. The factory process reduces exposure to weather during construction, which can help prevent moisture-related problems that sometimes affect stick-built homes.
Emerging Trends and Industry Innovations
The prefab housing sector is evolving rapidly as new technologies and materials enter the market. Sustainable materials and low-carbon construction methods are increasingly common, while energy-generating and energy-saving systems—like rooftop solar, battery storage, and advanced HVAC—are being integrated at the factory stage. Smart-home technology is another growth area, with manufacturers offering built-in connectivity for lighting, climate control, and security.
Design innovation is focused on making smaller footprints more livable. Solutions such as multi-functional furniture, open-plan layouts, and clever storage design make compact prefab homes feel larger and more functional. In urban contexts facing housing shortages, prefab construction offers a faster route to increasing supply while limiting site disruption.
Is a Prefab Home Right for You?
Prefab homes are an attractive choice for a broad range of buyers: first-time homeowners seeking affordability, eco-conscious buyers prioritizing efficiency, and anyone who values shorter construction timelines. Before committing, prospective buyers should obtain multiple quotes, verify local zoning and permitting requirements, and consider site-specific costs like foundation work and utility hookups.
As manufacturing processes, design tools, and material choices continue to improve, prefabricated homes are likely to become an even more mainstream solution for modern housing needs. For homeowners prioritizing quality, speed, and sustainability, prefab construction presents a versatile and increasingly sophisticated alternative to traditional building methods.