Project Management Software for Productivity and Collaboration
Project management software centralizes planning, tracking, and communication so teams can complete work with clearer priorities and fewer bottlenecks. These tools combine task organization, timelines, resource allocation, and reporting into a single environment that adapts to different methodologies—from Kanban boards to Gantt charts—helping teams maintain focus on outcomes rather than scattered documents.
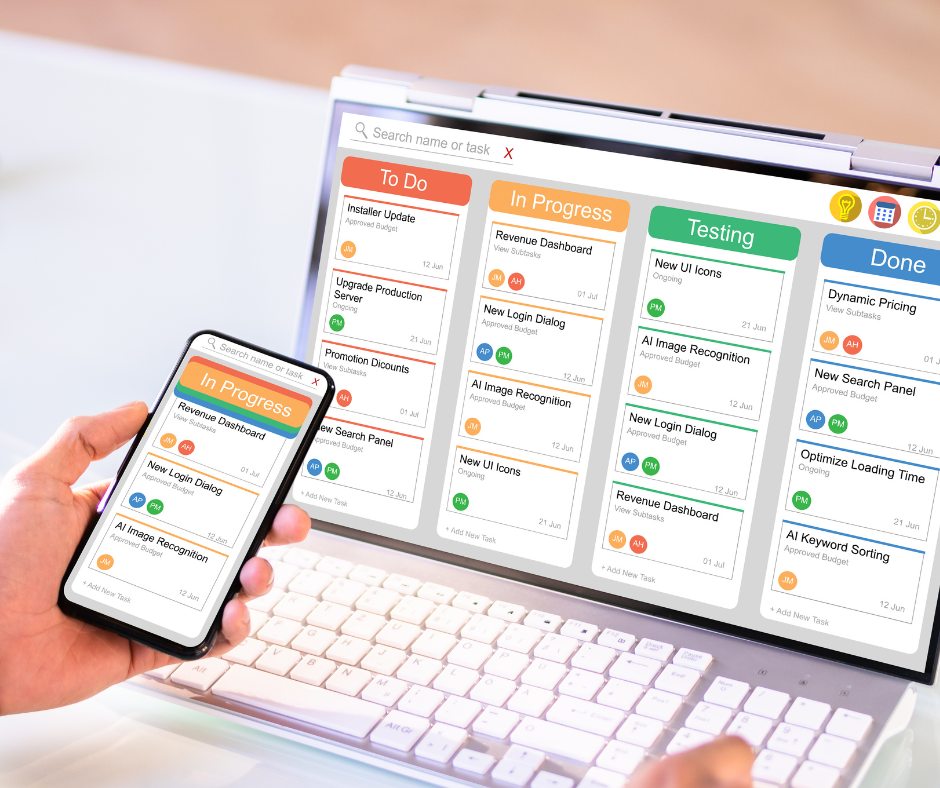
How project management organizes work
Project management breaks complex initiatives into manageable tasks, assigns ownership, and sets deadlines. A formal project structure clarifies scope, dependencies, milestones, and deliverables. When teams use a consistent framework, it becomes easier to estimate effort, balance workloads, and identify risks early. This organization supports better decision-making because stakeholders can view project status, outstanding issues, and upcoming work in one place, which reduces duplicate efforts and untracked commitments.
What software features support teams
Software for project management typically offers task lists, boards, timelines, file attachments, and reporting dashboards. Integration with email, calendars, and messaging platforms helps keep context in one place; APIs enable custom connections to CRM or accounting systems. Role-based permissions and audit logs improve governance for regulated projects. Selecting tools that match team size and workflow—whether lightweight task-tracking or enterprise portfolio management—reduces friction and improves adoption by aligning feature sets with real needs.
How productivity improves with PM tools
Productivity gains from project management software come from clearer priorities, fewer interruptions, and automated routine work. Centralized task views let individuals focus on what matters next, while shared timelines align cross-functional teams on delivery dates. Built-in time tracking and resource views help managers spot overloads and reassign work before deadlines slip. Productivity is also supported by templates and reusable processes that reduce setup time for recurring projects, allowing teams to start delivering faster without reinventing workflows.
How collaboration is enabled across teams
Collaboration features in project management software consolidate conversations, document versions, and decisions alongside tasks. Comment threads attached to tasks keep context intact instead of scattering feedback across email. Shared boards and real-time updates make status visible to everyone, which reduces meetings and clarifies expectations. For distributed teams, mobile access and timezone-aware scheduling help maintain continuity. When evaluating collaboration needs, consider how easily external partners or clients can be included and what controls are available for sharing information.
Where automation fits into workflows
Automation in project management handles repetitive steps—like assigning reviewers, moving tasks between stages, or creating subtasks when a trigger occurs—so teams spend less time on coordination. Common automation patterns include recurring task creation, status-based notifications, and integration-triggered updates (for example, creating a task when a support ticket is opened). Automations should be designed to reduce manual handoffs and enforce process consistency while remaining transparent so teams understand why items change state. Carefully scoped automations reduce errors and free capacity for higher-value work.
Adoption, integrations, and local services to consider
Successful adoption depends on training, leadership support, and integration with existing systems. Look for software that supports single sign-on (SSO), common data formats, and standard integrations with tools your teams already use—messaging, file storage, calendars, and CRM. If you need implementation help, consider local services or consultants in your area who can assess workflows, configure the system, and create templates that reflect your processes. Pilot programs with a representative team can reveal gaps before broad rollout and help build best practices for governance, naming conventions, and data hygiene.
Conclusion
Project management software is a practical toolset that helps teams plan, coordinate, and deliver work with greater clarity. By combining structured task management, collaboration spaces, productivity features, and automation, these platforms reduce friction and make project outcomes more predictable. The right approach balances functionality with user adoption: select tools that match your workflows, integrate with existing systems, and are supported by clear processes and training so teams can focus on delivering results rather than managing complexity.




