Psoriasis Treatment: Understanding Your Options for Healthier Skin
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that affects millions of people worldwide, causing red, scaly patches on the skin. While there is no cure for psoriasis, various treatment options can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. In this article, we'll explore the different approaches to psoriasis treatment, from topical creams to advanced medical interventions.
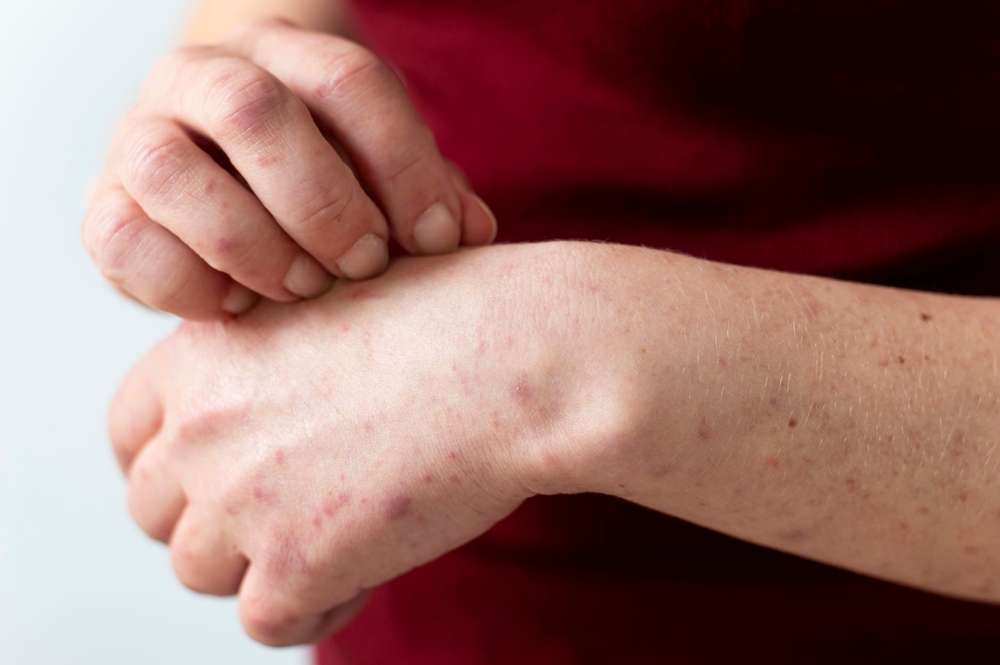
The effects of psoriasis on the skin can vary widely. Symptoms may include red, inflamed patches covered with silvery scales, dry and cracked skin, itching or burning sensations, and thickened or ridged nails. These symptoms can appear anywhere on the body but are most commonly found on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back.
What topical treatments are available for psoriasis?
Topical treatments are often the first line of defense against mild to moderate psoriasis. These medications are applied directly to the affected skin and can help reduce inflammation, slow cell growth, and relieve itching. Some common topical treatments include:
-
Corticosteroids: These anti-inflammatory creams or ointments are available in various strengths and can be effective for short-term use.
-
Vitamin D analogues: Synthetic forms of vitamin D, such as calcipotriene, help slow skin cell growth and remove scales.
-
Retinoids: Topical retinoids, like tazarotene, can help normalize skin cell production and reduce inflammation.
-
Coal tar: This traditional treatment can help slow skin cell growth and reduce scaling, itching, and inflammation.
-
Salicylic acid: Often used in combination with other treatments, salicylic acid helps remove scales and soften plaques.
How do systemic medications work in treating psoriasis?
For more severe cases of psoriasis or when topical treatments are ineffective, systemic medications may be prescribed. These medications work throughout the body to target the underlying causes of psoriasis. Some common systemic treatments include:
-
Methotrexate: This medication suppresses the immune system and can help slow skin cell growth.
-
Cyclosporine: Another immunosuppressant that can be effective for severe psoriasis but is typically used for short periods due to potential side effects.
-
Oral retinoids: Medications like acitretin can help reduce skin cell production and inflammation.
-
Biologics: These newer, targeted drugs work by blocking specific parts of the immune system responsible for psoriasis. Examples include etanercept, adalimumab, and ustekinumab.
What role does phototherapy play in psoriasis management?
Phototherapy, or light therapy, involves exposing the skin to controlled amounts of natural or artificial ultraviolet (UV) light. This treatment can help slow skin cell growth and reduce inflammation. There are several types of phototherapy used for psoriasis:
-
Narrowband UVB: This targeted form of UV light is often considered the most effective type of phototherapy for psoriasis.
-
Broadband UVB: A less focused form of UV light that can be effective for some patients.
-
Psoralen plus UVA (PUVA): This treatment combines UVA light with a light-sensitizing medication called psoralen.
-
Excimer laser: A targeted form of UVB light that can be used to treat specific areas of psoriasis.
How can lifestyle changes and alternative therapies complement psoriasis treatment?
While medical treatments are essential for managing psoriasis, lifestyle changes and alternative therapies can also play a crucial role in symptom management:
-
Stress reduction: Techniques like meditation, yoga, or counseling can help manage stress, a common psoriasis trigger.
-
Dietary changes: Some people find that certain foods worsen their symptoms. Keeping a food diary and working with a nutritionist may help identify triggers.
-
Moisturizing: Regular use of moisturizers can help reduce dryness, itching, and scaling associated with psoriasis.
-
Gentle skincare: Using mild, fragrance-free products and avoiding hot showers can help prevent skin irritation.
-
Alternative therapies: Some people find relief with acupuncture, aloe vera, or fish oil supplements, although scientific evidence for these approaches is limited.
What are the latest advancements in psoriasis treatment?
Ongoing research continues to uncover new treatment options for psoriasis. Some recent advancements include:
-
New biologics: Researchers are developing more targeted biologics that may offer improved efficacy with fewer side effects.
-
JAK inhibitors: These oral medications work by blocking specific enzymes involved in inflammation and are showing promise in clinical trials.
-
Personalized medicine: Advances in genetic testing may help doctors predict which treatments will be most effective for individual patients.
-
Combination therapies: Researchers are exploring how combining different treatments can enhance their effectiveness and reduce side effects.
-
Nanotechnology: This emerging field may lead to more targeted and efficient delivery of psoriasis medications.
Psoriasis treatment has come a long way in recent years, offering hope and improved quality of life for many people living with this chronic condition. By working closely with a dermatologist and exploring various treatment options, individuals with psoriasis can find an approach that works best for their unique needs and circumstances.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.






