Rehabilitation strategies for skeletal injuries
Skeletal injuries, ranging from minor fractures to complex bone trauma, require careful management and a structured approach to healing. Effective rehabilitation is crucial not only for the immediate repair of the affected bone but also for restoring full function, strength, and mobility to the injured area. Understanding the journey from initial diagnosis to complete recovery involves a multidisciplinary effort, focusing on various stages of treatment and therapeutic interventions designed to help individuals regain their independence and quality of life after a bone injury.

This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.
Skeletal injuries can significantly impact an individual’s daily life, necessitating a comprehensive understanding of their nature and the subsequent steps required for a successful recovery. The process typically begins with an accurate diagnosis, followed by a tailored treatment plan that evolves as the bone heals. Rehabilitation plays a central role, guiding the injured limb or body part back to its pre-injury state through targeted exercises and therapies. The ultimate goal is to minimize complications, alleviate pain, and ensure a return to normal activities with sustained health and wellness.
Understanding Bone Injury and Diagnosis
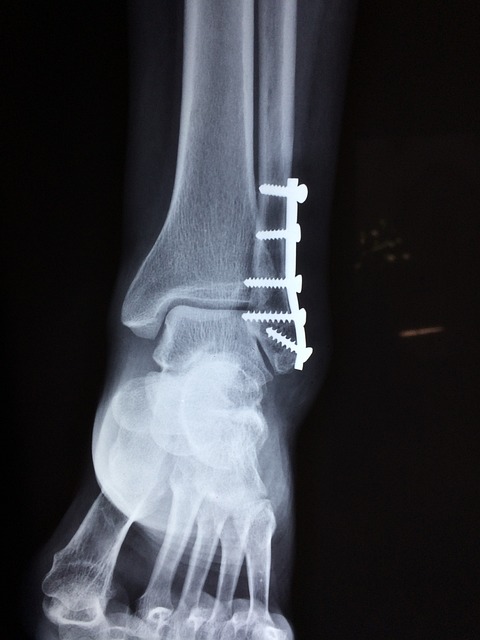
Identifying the exact nature and extent of a bone injury is the foundational step in any treatment plan. A thorough diagnosis often involves physical examination, patient history, and imaging techniques such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans. These diagnostic tools help healthcare professionals pinpoint the type of fracture, its location, and whether surrounding tissues are also affected. Early and accurate diagnosis is critical for determining the most appropriate initial treatment, whether it involves conservative methods or surgical intervention, and setting the stage for effective recovery.
Initial Treatment Approaches: Casting and Splinting
Once a bone injury is diagnosed, initial treatment often focuses on stabilizing the fractured bone to promote proper healing. Non-surgical methods commonly include casting and splinting. A cast, typically made of plaster or fiberglass, provides rigid support, immobilizing the injured area completely to allow the bone fragments to align and fuse. Splints, on the other hand, offer less rigid support and are often used for temporary stabilization, swelling management, or for injuries that require periodic inspection. Both methods are designed to protect the healing bone from further damage and facilitate the natural repair process.
The Role of Orthopedics and Surgery in Repair
For more severe or complex skeletal injuries, orthopedic intervention, which may include surgery, becomes necessary. Orthopedic specialists are trained in the diagnosis and treatment of musculoskeletal conditions, including fractures. Surgical procedures, such as open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) or external fixation, may be performed to realign bone fragments and stabilize them using plates, screws, rods, or pins. These interventions are crucial for restoring the anatomical integrity of the bone, especially in cases where conservative methods are insufficient, ensuring optimal conditions for healing and long-term function.
Comprehensive Rehabilitation and Therapy for Recovery
Rehabilitation is a cornerstone of recovery from skeletal injuries, beginning shortly after initial treatment and continuing until full function is restored. Physical therapy is often central to this process, involving a series of exercises designed to improve range of motion, strength, and flexibility. Occupational therapy may also be introduced to help individuals adapt to daily tasks and improve their ability to perform essential activities. The specific rehabilitation plan is tailored to the individual’s injury, age, and overall health, progressing gradually to challenge the healing bone and surrounding muscles while preventing re-injury. Consistent adherence to the therapy program is vital for achieving the best possible outcome.
Managing Pain and Restoring Mobility
Pain management is an integral part of the recovery process, allowing individuals to participate effectively in rehabilitation. Various strategies, including medication, ice, heat, and gentle exercises, may be employed to control discomfort. As pain subsides and healing progresses, the focus shifts towards restoring mobility. This involves a progressive series of exercises aimed at increasing the range of motion in the affected joint and strengthening the surrounding muscles. Restoring full mobility is essential for regaining independence and returning to routine activities, ensuring that the injured area can support weight and movement without undue strain.
| Provider Name | Services Offered | Key Features/Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Local Physical Therapy Clinics | Personalized exercise programs, manual therapy, pain management | Close to home, individualized care, focus on functional recovery |
| Orthopedic Rehabilitation Centers | Advanced physical therapy, occupational therapy, specialized equipment | Comprehensive programs, expert staff, integration with medical care |
| Hospital-based Therapy Departments | Inpatient and outpatient rehabilitation, post-surgical care | Coordinated care with surgeons, access to hospital resources |
| Sports Medicine Clinics | Injury assessment, rehabilitation for athletes, performance enhancement | Specialized in athletic injuries, focus on return to sport |
| Home Health Physical Therapy | Therapy sessions conducted in the patient’s home | Convenience, tailored to home environment, ideal for limited mobility |
Strategies for Prevention and Long-term Skeletal Wellness
Beyond immediate recovery, adopting strategies for long-term skeletal wellness is crucial in preventing future injuries. This includes maintaining a balanced diet rich in calcium and Vitamin D, engaging in regular weight-bearing exercises to strengthen bones, and taking precautions to avoid falls or accidents. For individuals recovering from a bone injury, understanding the mechanisms of their injury can help them implement specific preventive measures. Regular check-ups with healthcare professionals, especially for those with conditions affecting bone density, also contribute significantly to sustained bone health and overall wellness, reducing the risk of future skeletal trauma.
Recovery from skeletal injuries is a journey that demands patience, consistent effort, and professional guidance. From the initial diagnosis and stabilization to comprehensive rehabilitation and long-term wellness strategies, each phase plays a critical role in restoring function and improving quality of life. By understanding the various aspects of fracture treatment and engaging actively in the recovery process, individuals can achieve optimal healing and regain their independence, ensuring their skeletal health for the future.