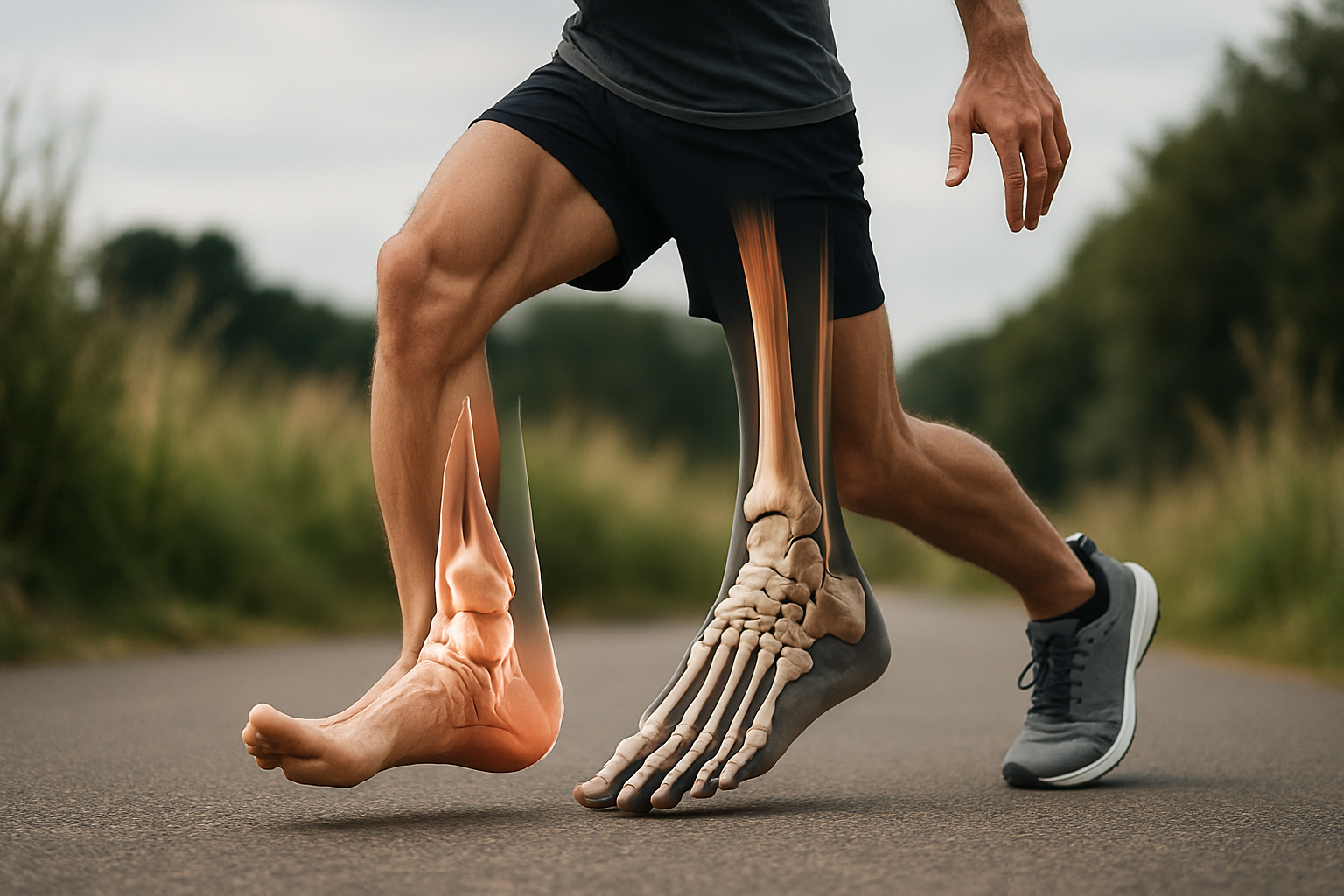
Restoring Movement: A Look at Skeletal Health
The ability to move freely and without pain is fundamental to quality of life. Our skeletal system, encompassing bones, joints, muscles, tendons, and ligaments, forms the intricate framework that enables every step, lift, and gesture. When this system is compromised by injury, disease, or age-related wear, orthopaedic care emerges as a vital medical specialty dedicated to diagnosing, treating, and preventing conditions affecting these crucial structures. This field plays a critical role in helping individuals regain function and reduce discomfort, thereby enhancing their overall well-being and independence.

This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.
Beyond the initial discomfort, issues within the musculoskeletal system can significantly impact daily activities and long-term health. Orthopaedic care spans a broad spectrum, from non-surgical interventions like physical therapy and medication to complex surgical procedures designed to repair, reconstruct, or replace damaged components. Understanding the various aspects of skeletal health and the available treatment pathways is essential for anyone experiencing difficulties with their movement.
Understanding the Musculoskeletal System: Joints, Bones, and Soft Tissues
The human musculoskeletal system is a complex network that provides structure, support, and the capacity for movement. It comprises bones, which form the body’s rigid framework; joints, where bones meet and allow articulation; and muscles, which contract to produce force. Complementing these are soft tissues such as tendons, connecting muscles to bones, and ligaments, which link bones to other bones, providing stability. Cartilage acts as a smooth, elastic tissue cushioning the ends of bones within joints, reducing friction and absorbing shock. Together, these components ensure skeletal health and facilitate everyday movement.
Common Conditions Affecting Mobility and Function
Various conditions can compromise the integrity and function of the musculoskeletal system. Fractures, or broken bones, can result from trauma or underlying conditions that weaken bone density. Arthritis, characterized by inflammation of the joints, includes conditions like osteoarthritis, which involves the breakdown of cartilage, and rheumatoid arthritis, an autoimmune disorder. Injury to soft tissues, such as tendon tears or ligament sprains, are also common. Specific areas like the spine, knee, hip, and shoulder are frequently affected by degenerative conditions or injuries, leading to pain and reduced mobility.
Approaches to Orthopaedic Care and Movement Restoration
Orthopaedic treatment is not exclusively surgical; it often begins with conservative methods. These can include physical therapy, medication, injections, and lifestyle modifications aimed at managing symptoms and improving function. When non-surgical options prove insufficient or a condition requires direct structural intervention, orthopaedic surgery may be considered. Procedures range from arthroscopy for minimally invasive joint repair to total joint replacement for severely damaged hips or knees. The overarching goal is always to restore movement, alleviate pain, and enhance the patient’s quality of life.
The Role of Rehabilitation in Recovery
Whether an individual undergoes surgery or pursues conservative treatment, rehabilitation is a cornerstone of effective orthopaedic care. Physical therapy plays a critical role in recovery, focusing on strengthening muscles around affected joints, improving flexibility, and restoring range of movement. Occupational therapy may also be involved to help individuals adapt daily tasks. Adhering to a prescribed rehabilitation program is essential for optimizing outcomes, preventing re-injury, and achieving the fullest possible return to normal function and mobility.
Considering Orthopaedic Procedures: Cost Insights
The financial aspect of orthopaedic procedures can vary significantly, influenced by factors such as the complexity of the surgery, the type of facility (hospital vs. outpatient center), geographic location, and insurance coverage. Patients should consult with their healthcare providers and insurance companies to understand potential costs, including surgeon fees, anesthesia, facility charges, and post-operative care.
| Product/Service | Provider | Cost Estimation (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Knee Arthroscopy | Hospital/Clinic | $5,000 - $15,000 |
| Hip Replacement | Hospital/Clinic | $20,000 - $60,000 |
| Shoulder Repair (Rotator Cuff) | Hospital/Clinic | $10,000 - $30,000 |
| Spinal Fusion | Hospital/Clinic | $50,000 - $150,000 |
| Fracture Repair (Simple) | Hospital/Clinic | $2,000 - $10,000 |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Maintaining healthy skeletal health is a lifelong endeavor, crucial for sustained mobility and an active lifestyle. Orthopaedic care offers pathways to alleviate pain, correct structural issues, and restore function for many individuals. By understanding the intricate nature of our joints, bones, and muscles, and the comprehensive care available, individuals can make informed decisions about their health and work towards a future of improved movement and well-being.