Rhinoplasty Uncovered: Art and Science of Nose Surgery
Rhinoplasty, often called a nose job, blends cosmetic refinement with functional repair. This guide explains how rhinoplasty is performed, the differences between open and closed approaches, recovery expectations, risks to consider, and factors that influence cost. Learn what to expect from consultation to recovery and how to choose a qualified surgeon.
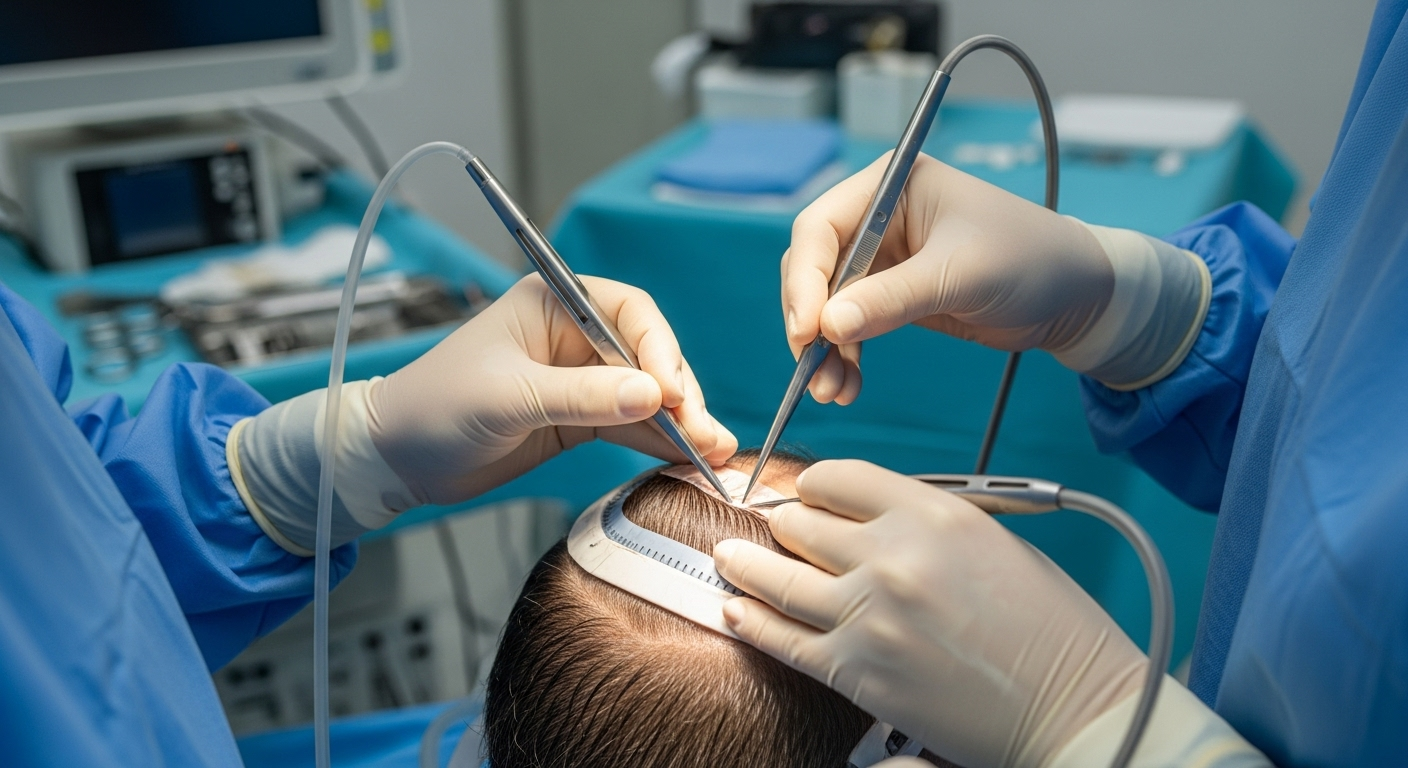
Rhinoplasty can change how you look and breathe. Whether performed for cosmetic reasons or to correct structural problems, nasal surgery is a complex procedure that combines careful surgical technique with an eye for proportion and balance. Many patients report increased confidence and improved nasal function after the operation, but successful outcomes depend on realistic goals, skilled surgeons, and a clear understanding of the process.
Why people choose rhinoplasty
People seek rhinoplasty for a range of reasons: to refine the nasal profile, correct a bump or asymmetry, narrow the nasal tip, improve breathing, or repair damage from injury. Some pursue purely aesthetic changes, while others need reconstruction for medical reasons such as a deviated septum. In many cases, rhinoplasty addresses both appearance and function simultaneously.
Surgical approaches and how the operation is done
Rhinoplasty is usually performed under general anesthesia and typically lasts between one and three hours, depending on the complexity of the changes. Surgeons use two primary approaches:
-
Open rhinoplasty: A small incision is made across the columella (the tissue between the nostrils), which provides the surgeon wide exposure of the nasal framework. This method is favored for more extensive reshaping because it allows precise visualization and manipulation of bone, cartilage, and soft tissue.
-
Closed (endonasal) rhinoplasty: All incisions are placed inside the nostrils, leaving no visible external scars. This technique can be appropriate for less complicated procedures and may reduce postoperative swelling and shorten recovery time.
During the procedure, the surgeon sculpts bone and cartilage to achieve the desired contour and may reposition or trim structures to improve airflow. In cases where additional support or volume is needed, grafts—often harvested from the septum, ear, or rib—are used to reinforce or reshape areas of the nose.
Possible risks and complications
As with any surgery, rhinoplasty carries risks. Short-term effects commonly include swelling, bruising, and mild discomfort. More significant, although uncommon, complications can include:
- Infection
- Excessive bleeding
- Adverse reaction to anesthesia
- Dissatisfaction with cosmetic result
- Persistent breathing problems
- Septal perforation (a hole in the nasal septum)
- Altered skin sensation or numbness
Selecting a board-certified plastic surgeon or an experienced facial plastic surgeon and having a comprehensive preoperative consultation reduces the chance of complications. Open communication about expectations and potential outcomes is essential to achieving a satisfactory result.
Recovery timeline and what to expect
Recovery from rhinoplasty requires patience and adherence to postoperative instructions. A protective splint or cast is typically worn for about one week to support the new nasal shape. Initial swelling and bruising are most pronounced in the first few days to weeks; visible swelling generally subsides over two to three months, but subtle refinements may continue for up to a year as tissues settle and scar tissue softens.
Most people can return to routine non-strenuous activities, work, or school within one to two weeks. However, patients should avoid heavy lifting, bending over, and contact sports for several weeks to months, depending on the surgeon’s guidance, to prevent trauma to the healing nose.
Cost and factors that influence pricing
The price of rhinoplasty varies widely based on the surgeon’s experience, geographic location, facility fees, the complexity of the procedure, and whether it includes functional repairs. In the United States, typical total costs often fall within a broad range.
| Provider Type | Average Cost Range | Factors Influencing Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Board-Certified Plastic Surgeon | $8,000 - $15,000 | Experience, reputation, location |
| Facial Plastic Surgeon | $7,000 - $12,000 | Specialization in facial procedures |
| General Plastic Surgeon | $5,000 - $10,000 | May offer lower rates but less specialization |
| Teaching Hospital | $4,000 - $8,000 | Reduced rates when residents perform surgery under supervision |
These figures typically include the surgeon’s fee, anesthesia, facility costs, and follow-up visits. Additional expenses—such as prescription medications, splints, special garments, or revision procedures—may not be included. Prices can change over time; independent research and a detailed discussion of fees during your consultation are recommended.
Many practices provide financing plans or payment options to help spread the cost. During the initial visit, ask for a full cost breakdown and confirm what services are covered.
Choosing a surgeon and preparing for surgery
Selecting a qualified, board-certified surgeon with extensive rhinoplasty experience is one of the most important steps. Review before-and-after photos, request patient references when available, and ensure the surgeon performs a thorough evaluation that includes both aesthetic goals and functional assessment (e.g., breathing tests, nasal endoscopy if necessary).
Prepare for surgery by following preoperative instructions: stop certain medications or supplements that increase bleeding risk, arrange for someone to drive you home, and plan for time off work and assistance during the early recovery period.
Rhinoplasty can be life-changing, offering both visual and functional benefits when performed by a skilled professional. Understanding the surgical options, potential risks, recovery expectations, and financial considerations helps you make an informed choice and approach the procedure with realistic expectations.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.






