Scalp Psoriasis: Causes, Care, and Best Treatments
Scalp psoriasis causes red, itchy, flaky patches that affect millions worldwide. This comprehensive guide explains common triggers, symptoms, and proven treatment options — from medicated shampoos and topicals to systemic drugs and phototherapy — plus practical at-home care and when to see a dermatologist for lasting relief.
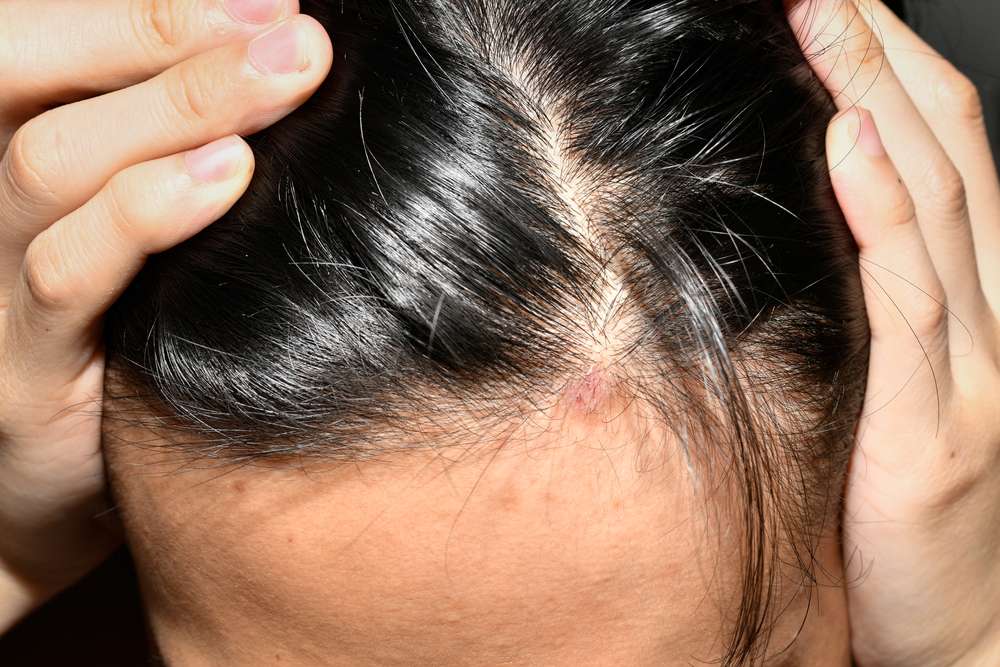
Scalp psoriasis is a chronic immune-related skin condition that speeds up the lifecycle of skin cells on the scalp, producing inflamed, scaly patches. Though it can be uncomfortable and visible, many people find meaningful symptom control with the right mix of medical treatments and self-care. This article outlines the main causes, how psoriasis can affect hair and skin, the most effective therapies, practical home strategies, and when to seek professional help.
What triggers scalp psoriasis?
Several factors can increase the likelihood of developing scalp psoriasis or provoke flare-ups:
-
Genetics: A family history of psoriasis is a strong risk factor. If relatives have psoriasis, your chance of developing it rises.
-
Stress: Emotional or physical stress frequently precipitates or worsens outbreaks, likely by affecting immune system balance.
-
Infections: Bacterial infections, especially streptococcal throat infections, have been associated with the onset of psoriasis in some people.
-
Climate: Cold, dry weather commonly makes symptoms worse by drying the skin, whereas warmer, more humid conditions often provide relief.
-
Certain medications: Some drugs, including lithium and certain beta-blockers, can trigger or exacerbate psoriasis in susceptible individuals.
Understanding your personal triggers helps in both preventing flares and tailoring treatment.
How scalp psoriasis affects the scalp and hair
Common signs and consequences include:
- Red, well-defined, scaly patches on the scalp
- Intense itching and burning sensations
- Dry flakes that may fall onto clothing or shoulders
- Thick, silvery-white scales that cling to the scalp
- Temporary hair thinning in areas exposed to severe inflammation or constant scratching
Scalp psoriasis itself rarely causes permanent hair loss. However, vigorous scratching, picking at scales, or aggressive removal techniques can damage hair follicles and lead to temporary hair shedding. Beyond the physical symptoms, visible scalp lesions can lower self-confidence and interfere with social or professional life, making effective management important for mental as well as physical health.
Most effective medical treatments
Therapy often combines several modalities to control inflammation, slow skin cell turnover, and relieve discomfort. Options include:
Topical treatments (applied directly to the scalp): - Corticosteroids: Reduce inflammation and itching; available in multiple strengths and formats for scalp use. - Vitamin D analogues: Slow abnormal skin cell growth and can be used alone or with steroids. - Salicylic acid: Helps dissolve thick scales so other treatments can penetrate. - Coal tar: Slows skin cell production and eases scaling and itching.
Systemic medications (for moderate to severe cases): - Methotrexate and cyclosporine: Oral immunosuppressants that decrease immune-driven inflammation. - Biologic agents: Injectable or infusion drugs such as adalimumab or etanercept target specific immune pathways and can be highly effective for resistant disease.
Phototherapy: - Controlled ultraviolet (UV) light exposure can reduce inflammation and slow the hyperproliferation of skin cells. Specialized devices and clinical settings ensure safe dosing.
Medicated shampoos and cleansers: - Formulations containing coal tar, salicylic acid, or antifungals like ketoconazole can reduce flaking and soothe the scalp when used as directed.
Lifestyle and trigger management: - Stress reduction, dietary attention, and avoiding known medication or environmental triggers contribute to better long-term control.
| Treatment type | Examples | Typical considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Topical therapies | Corticosteroids, vitamin D analogues, salicylic acid | Often first-line for mild-moderate disease; regular application needed |
| Medicated shampoos | Coal tar, ketoconazole, salicylic acid shampoos | Useful for flaking control; combine with topicals for best effect |
| Systemic agents | Methotrexate, cyclosporine, biologics (adalimumab) | For severe or widespread disease; require medical monitoring |
| Phototherapy | UVB light | Effective in clinics; multiple sessions required |
Cost disclaimer: Treatment costs vary widely by region, insurance coverage, and specific therapy. Consult your healthcare provider and insurance plan for accurate pricing and coverage details.
Practical at-home strategies
Many people reduce symptoms with everyday measures that complement medical care:
- Choose gentle, fragrance-free shampoos and conditioners to avoid irritating the scalp.
- Soften thick scales before attempting removal: apply mineral oil, coconut oil, or a medicated scalp oil, leave on for a short time, then gently loosen flakes with a soft brush or comb.
- Moisturize the scalp regularly to reduce dryness and flaking.
- Resist scratching; use cold compresses or anti-itch treatments if necessary to limit trauma to the skin.
- Adopt stress management practices such as meditation, yoga, or breathing exercises to help prevent stress-related flares.
- Use a humidifier during dry seasons to keep skin from becoming too dry.
- Opt for lukewarm showers rather than hot water to preserve the skin’s natural oils.
These measures can improve comfort and enhance the effectiveness of prescribed treatments.
When to consult a dermatologist
See a dermatologist if:
- Symptoms persist or worsen despite over-the-counter measures
- The condition is affecting your daily life or emotional well-being
- You experience severe itching, pain, or bleeding
- There are signs of infection, like increasing redness, warmth, swelling, or pus
- You’re unsure whether the problem is psoriasis or another scalp disorder
A dermatologist can confirm the diagnosis, rule out other causes, prescribe appropriate therapies (including systemic options), and tailor a treatment plan to your needs.
With a clear diagnosis and a combination of targeted treatments and sensible self-care, many people with scalp psoriasis achieve substantial improvement and maintain a better quality of life. Work closely with a healthcare provider to find the mix of therapies that works best for you.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.





