Senior Car Insurance Guide: Smart Coverage for Older Drivers
As you or a loved one age, car insurance needs evolve. Senior drivers often face different risks, discounts, and coverage choices than younger motorists. This article explains key considerations—coverage types, discounts, driving safety, vehicle choices, and how to compare local insurance options—so seniors can make confident, well-informed decisions about protecting themselves and their vehicles.
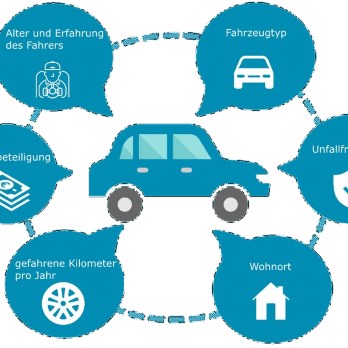
Car coverage options for seniors
Seniors typically need the same core coverages as other drivers—liability, collision, and comprehensive—but the balance and limits may change. Liability protects others if you’re at fault; collision pays for repairs to your vehicle after an accident; comprehensive covers non-collision losses such as theft, vandalism, or weather damage. Many seniors also consider higher bodily injury limits or medical payments/uninsured motorist coverage depending on health insurance coordination and state rules.
Beyond basics, consider optional coverages that can be valuable for older drivers: roadside assistance for breakdowns, rental reimbursement when your vehicle is in repair, and gap coverage if you carry a loan. Review policy deductibles carefully—higher deductibles lower premiums but increase out-of-pocket costs after a claim. Periodically reassess limits as driving habits, assets, and household health change.
Insurance discounts available to seniors
Insurers commonly offer age-related discounts and programs. Good-driver discounts, multi-policy savings (bundling auto and home), and low-mileage discounts are often applicable. Many companies provide discounts if a senior completes a defensive driving or mature driver course, which can also help update driving skills and refresh knowledge of road rules.
Other potential savings include multi-car discounts for family households, anti-theft device discounts if your vehicle has modern security systems, and loyalty discounts for long-standing customers. It’s worthwhile to ask insurers about all possible credits and to shop annually—discount availability and underwriting criteria can vary across providers and states.
Seniors and safe driving practices
Maintaining safe driving habits is one of the best ways for seniors to manage insurance risk and premiums. Regular vision and hearing checks, discussing medications with a physician that might affect driving, and adapting driving times to avoid night or rush-hour conditions can reduce accident risk. Consider vehicle modifications if mobility or dexterity is an issue—hand controls, swivel seats, and larger mirrors can improve safety and confidence behind the wheel.
Family conversations about driving ability are important but can be sensitive. Look for objective markers—near misses, tickets, or medical changes—that indicate a need for reassessment. Some communities offer driving evaluations and refresher courses tailored to older adults; these can provide constructive feedback and support safer independence.
Vehicle choice and insurance for seniors
The make and model of a vehicle significantly affect premiums. Generally, cars with good safety ratings, lower repair costs, and strong theft-deterrence features are cheaper to insure. Luxury cars, high-performance models, or vehicles with expensive replacement parts typically cost more to insure. For seniors who plan to keep driving for many years, choosing a vehicle with advanced driver-assistance systems (automatic emergency braking, blind-spot alerts, lane-keeping) can enhance safety and sometimes result in insurer discounts.
If mobility is a concern, consider vehicles with easier entry/exit, higher seating positions, or automatic transmissions. When evaluating a vehicle, check crash-test ratings from reliable sources and discuss potential insurance impacts with your agent.
Finding local insurance and comparing options
Shopping around remains essential. Coverage offerings, discounts, and customer service vary by provider and by state, so comparing quotes from multiple insurers in your area can reveal significant differences. Use an insurance checklist: confirm coverage limits, deductible amounts, exclusions, claim handling reputation, and whether any senior-specific programs are offered.
When reviewing an insurer, consider financial stability and complaint ratios in your state. Independent agents can help compare policies across companies, while direct insurers may offer lower rates if you’re comfortable managing policies online. Keep a record of quotes and renewal dates to prompt periodic review.
Conclusion
Senior car insurance is not one-size-fits-all. Understanding coverage types, seeking available discounts, practicing safe driving, choosing an appropriate vehicle, and comparing local insurance options will help seniors balance protection and cost. Regular reviews of driving habits and policy details ensure coverage remains aligned with changing needs, helping older drivers maintain mobility with confidence and clarity.