Understanding Atopic Dermatitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Atopic dermatitis, commonly known as eczema, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. This persistent and often frustrating condition can cause itchy, dry, and inflamed skin, leading to discomfort and a reduced quality of life for those who suffer from it. In this article, we'll explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for atopic dermatitis, providing valuable insights for those seeking to manage this condition effectively.
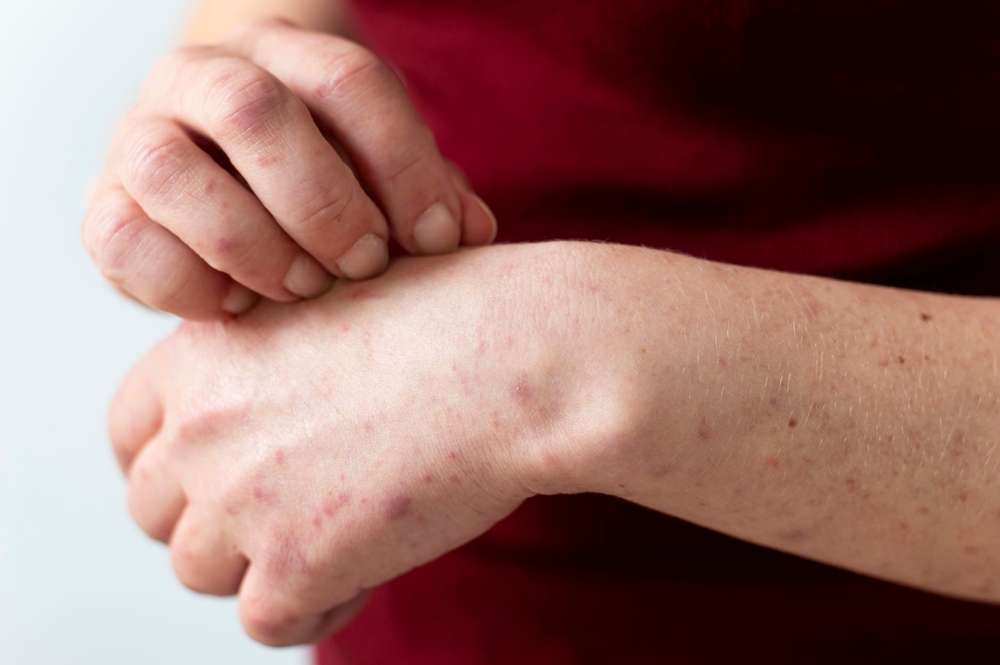
What are the common symptoms of atopic dermatitis?
The symptoms of atopic dermatitis can vary from person to person but typically include:
-
Dry, itchy skin
-
Redness and inflammation
-
Rough, scaly, or leathery patches
-
Small, raised bumps that may ooze or crust over when scratched
-
Thickened or cracked skin
-
Increased skin sensitivity and irritation
These symptoms often appear in specific areas of the body, such as the face, hands, feet, and the creases of elbows and knees. The intense itching associated with atopic dermatitis can lead to a cycle of scratching and further skin damage, making proper management essential.
How is atopic dermatitis diagnosed?
Diagnosing atopic dermatitis typically involves a thorough examination of the skin and a review of the patient’s medical history. A dermatologist or healthcare provider will look for characteristic signs of the condition, such as dry, itchy, and inflamed skin in typical areas. They may also inquire about family history, allergies, and potential triggers. In some cases, additional tests like skin biopsies or allergy tests may be necessary to rule out other skin conditions or identify specific triggers.
What are the available treatment options for atopic dermatitis?
Managing atopic dermatitis often requires a multi-faceted approach, combining various treatment options to provide relief and prevent flare-ups. Here are some common strategies:
-
Topical medications: Corticosteroid creams and ointments are often prescribed to reduce inflammation and itching. Non-steroidal options like calcineurin inhibitors may also be used for long-term management.
-
Moisturizers: Regular use of emollients and moisturizers helps maintain skin hydration and improve barrier function.
-
Systemic medications: For severe cases, oral medications such as immunosuppressants or biologics may be prescribed to manage symptoms and reduce inflammation.
-
Phototherapy: Controlled exposure to specific wavelengths of light can help reduce inflammation and improve skin condition in some patients.
-
Lifestyle modifications: Identifying and avoiding triggers, using gentle skincare products, and maintaining proper hygiene practices can help manage symptoms.
How can I manage atopic dermatitis at home?
While medical treatments are essential for managing atopic dermatitis, there are several steps you can take at home to alleviate symptoms and prevent flare-ups:
-
Moisturize regularly: Apply fragrance-free moisturizers immediately after bathing to lock in hydration.
-
Use gentle skincare products: Choose mild, unscented soaps and avoid harsh detergents or irritating fabrics.
-
Take lukewarm showers: Hot water can strip the skin of its natural oils, exacerbating dryness.
-
Identify and avoid triggers: Keep a diary to track potential triggers such as certain foods, stress, or environmental factors.
-
Manage stress: Practice stress-reduction techniques like meditation or yoga, as stress can worsen symptoms.
-
Maintain a cool, humid environment: Use a humidifier to add moisture to the air, especially in dry climates.
-
Wear breathable clothing: Choose loose-fitting, cotton clothing to minimize skin irritation.
By combining these home management strategies with prescribed treatments, many individuals with atopic dermatitis can effectively manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic condition that requires ongoing management and care. While there is no cure, advances in treatment options and a better understanding of the condition have made it possible for many people to effectively control their symptoms. If you suspect you have atopic dermatitis or are struggling to manage your symptoms, consult with a dermatologist or healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan tailored to your needs.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.






