Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the joints, causing pain, swelling, and stiffness. This condition occurs when the body's immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues, particularly the synovium, the lining of the membranes surrounding the joints. While RA can affect people of all ages, it most commonly develops in middle-aged and older adults. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for rheumatoid arthritis is crucial for managing this condition effectively and improving quality of life.
-
Environmental triggers: Exposure to certain viruses, bacteria, or environmental pollutants may trigger the onset of RA in genetically predisposed individuals.
-
Hormonal factors: Women are more likely to develop RA than men, suggesting a possible hormonal influence.
-
Smoking: Cigarette smoking has been linked to an increased risk of developing RA and may also worsen the severity of the condition.
What are the common symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis?
Rheumatoid arthritis typically affects the small joints of the hands and feet first, but it can progress to larger joints as well. The most common symptoms of RA include:
-
Joint pain and tenderness
-
Swelling and stiffness in the affected joints
-
Symmetrical joint involvement (affecting the same joints on both sides of the body)
-
Morning stiffness that lasts for 30 minutes or longer
-
Fatigue and general weakness
-
Low-grade fever
-
Loss of appetite and weight loss
It’s important to note that RA symptoms can vary in severity and may come and go in cycles, known as flares and remissions.
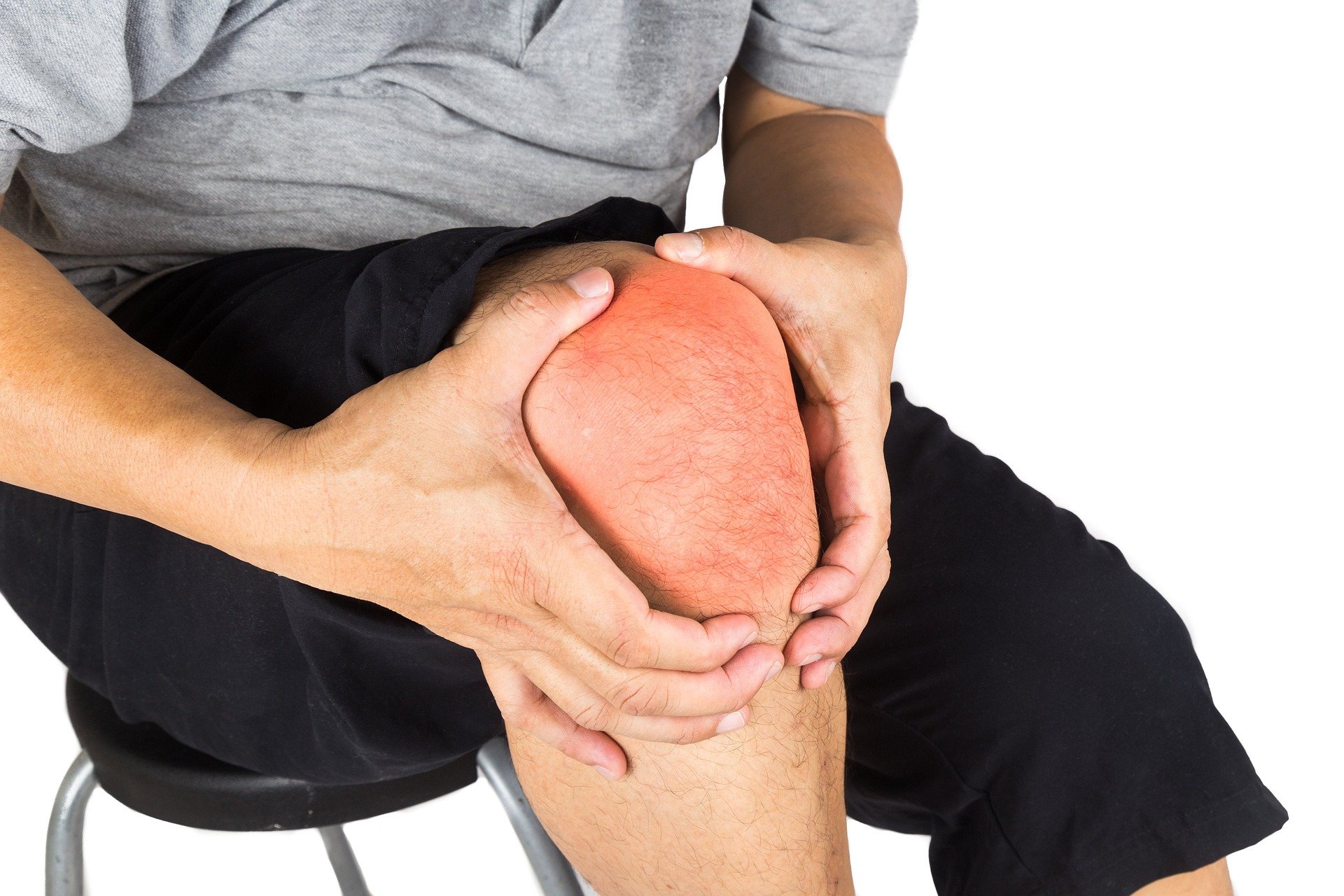
How does rheumatoid arthritis affect the hands and knees?
The hands and knees are among the most commonly affected areas in rheumatoid arthritis. In the hands, RA typically affects the joints at the base of the fingers (metacarpophalangeal joints) and the middle joints of the fingers (proximal interphalangeal joints). This can lead to:
-
Swelling and tenderness in the finger joints
-
Difficulty gripping or pinching objects
-
Reduced range of motion in the fingers
-
Deformities such as ulnar deviation (fingers bending towards the little finger)
In the knees, RA can cause:
-
Pain and stiffness, especially when walking or climbing stairs
-
Swelling and warmth around the knee joint
-
Instability or a feeling of the knee “giving way”
-
Reduced range of motion in the knee
What treatment options are available for rheumatoid arthritis?
While there is no cure for rheumatoid arthritis, various treatment options can help manage symptoms, slow disease progression, and improve quality of life. The main goals of RA treatment are to:
-
Reduce inflammation and pain
-
Prevent or slow joint damage
-
Improve physical function and overall well-being
Treatment options for RA may include:
-
Medications:
-
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for pain relief
-
Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) to slow disease progression
-
Biologic agents that target specific components of the immune system
-
Corticosteroids for short-term relief of inflammation and pain
-
-
Physical and occupational therapy:
-
Exercises to improve joint flexibility and muscle strength
-
Techniques to protect joints and maintain function
-
Assistive devices to help with daily activities
-
-
Lifestyle modifications:
-
Regular exercise and physical activity
-
Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce stress on joints
-
Stress management techniques such as relaxation and meditation
-
Applying heat or cold to affected joints for pain relief
-
-
Surgery:
- In severe cases, joint replacement surgery may be necessary to restore function and reduce pain
How can individuals manage rheumatoid arthritis pain and swelling?
Managing pain and swelling associated with rheumatoid arthritis is crucial for maintaining quality of life. Some strategies that can help include:
-
Adhering to prescribed medication regimens
-
Practicing joint protection techniques to reduce stress on affected joints
-
Using assistive devices for daily activities when necessary
-
Engaging in low-impact exercises such as swimming or cycling
-
Applying heat or cold therapy to affected joints
-
Maintaining a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods
-
Getting adequate rest and managing stress levels
-
Working closely with healthcare providers to adjust treatment plans as needed
By combining these strategies with medical treatments, individuals with rheumatoid arthritis can often effectively manage their symptoms and maintain an active, fulfilling lifestyle.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.






