Detecting Cerebral Growths: Current Methodologies
Understanding the methods used to identify cerebral growths is a crucial aspect of modern healthcare. These growths, which can manifest in various forms, require precise and timely detection to inform appropriate medical strategies. This article explores the current diagnostic techniques and the multidisciplinary approaches involved in their identification, offering a comprehensive overview for those seeking to understand the detection process.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.
The detection of cerebral growths involves a sophisticated array of medical techniques designed to identify abnormal cell formations within the brain. These methodologies are continuously evolving, aiming for greater accuracy and earlier intervention. The journey from initial suspicion to a confirmed diagnosis often involves several steps, each contributing vital information to the overall picture of a patient’s condition.
What are Intracranial Growths and Lesions?
Intracranial growths and lesions refer to any abnormal tissue mass or area of damage found within the skull. These can range from benign (non-cancerous) to malignant (cancerous) tumors, or even other conditions such as infections, cysts, or vascular malformations. Understanding the nature of these growths is paramount, as it dictates the subsequent management and treatment pathways. The brain’s enclosed environment means that any abnormal growth can exert pressure on surrounding delicate tissues, potentially leading to a range of symptoms depending on its size, location, and rate of growth.
Symptoms associated with intracranial growths can be varied and often depend on the specific area of the brain affected. They might include persistent headaches, seizures, changes in vision, speech difficulties, weakness or numbness in limbs, and alterations in personality or cognitive function. Recognizing these signs is an important first step, prompting further medical evaluation to determine the underlying cause and facilitate a timely diagnosis.
How is a Diagnosis of Cerebral Growths Made?
The diagnostic process for cerebral growths typically begins with a thorough medical history and a neurological examination. During this examination, healthcare professionals assess a patient’s reflexes, muscle strength, coordination, balance, and sensory responses. Any abnormalities noted during this initial assessment can provide clues about the location and potential nature of a growth within the brain.
Following the physical examination, a series of imaging tests are often ordered to visualize the brain’s internal structures. These tests are critical for confirming the presence of a growth, determining its size and exact location, and sometimes even offering insights into its potential type. Further specialized tests may be required to gather more detailed information, guiding the medical team toward the most appropriate course of action.
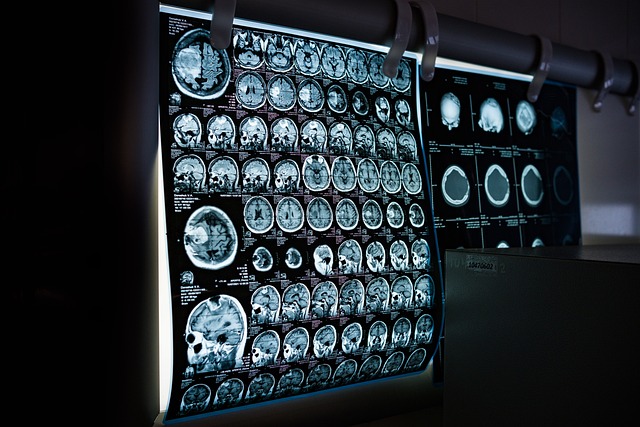
Understanding Imaging Techniques for Detection
Several advanced imaging techniques play a crucial role in the detection and characterization of cerebral growths. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is frequently considered the gold standard due to its ability to produce highly detailed images of soft tissues, distinguishing between healthy brain tissue and abnormal growths. Functional MRI (fMRI) can also be used to map brain activity, which is particularly useful for surgical planning.
Computed Tomography (CT) scans are another common imaging modality, often used for initial evaluations, especially in emergency settings, as they can quickly detect significant growths or bleeding. Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scans, sometimes combined with CT or MRI (PET-CT, PET-MRI), can help identify metabolically active areas, which is useful in differentiating between types of growths and assessing their aggressiveness or response to therapy. Angiography may also be used to visualize blood vessels and detect any vascular abnormalities associated with the growth.
The Role of Neurology and Oncology in Management Pathways
The management of cerebral growths typically involves a multidisciplinary team, with neurology and oncology specialists playing central roles. Neurologists are experts in disorders of the nervous system and are often involved in the initial diagnosis and ongoing monitoring of patients. They assess symptoms, interpret imaging results, and coordinate care. Oncologists specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of cancer, and their expertise is vital when a growth is confirmed to be malignant.
Together with neurosurgeons, radiation oncologists, neuropathologists, and other healthcare professionals, these specialists collaborate to develop a comprehensive management plan. This plan considers the specific characteristics of the growth, the patient’s overall health, and their preferences. The goal is to provide the most effective treatment while minimizing potential side effects and preserving quality of life.
Ongoing Research and Support for Brain Conditions
Research into cerebral growths and related brain conditions is continuously advancing, leading to new diagnostic tools, treatment options, and a deeper understanding of these complex diseases. Scientists and medical professionals worldwide are exploring novel imaging biomarkers, genetic profiling of tumors, and innovative therapeutic approaches, including targeted therapies and immunotherapies. These ongoing efforts aim to improve early detection, enhance treatment efficacy, and ultimately improve outcomes for individuals affected by these conditions.
Beyond medical advancements, a robust network of support is available for patients and their families. This includes patient advocacy groups, counseling services, and rehabilitation programs designed to address the physical, emotional, and cognitive challenges that can arise. Access to accurate information and comprehensive support systems is an integral part of navigating the journey through diagnosis and management of cerebral growths.
In conclusion, the detection of cerebral growths relies on a combination of clinical assessment and advanced imaging technologies. A collaborative approach involving multiple medical specialties ensures a thorough diagnosis and the development of personalized management strategies. Continuous research and accessible support systems are vital components in improving the outlook for individuals with these complex brain conditions.




