Driving Efficiency in Manufacturing with Actuation
Hydraulic cylinders are fundamental components in countless industrial applications, playing a pivotal role in modern manufacturing. These devices convert hydraulic power into linear mechanical force and motion, enabling heavy lifting, pressing, clamping, and precise positioning tasks. Their robust design and ability to generate significant force make them indispensable for operations requiring reliability and high performance across various sectors, from automotive production lines to heavy construction equipment. Understanding their principles and applications is key to optimizing industrial processes.
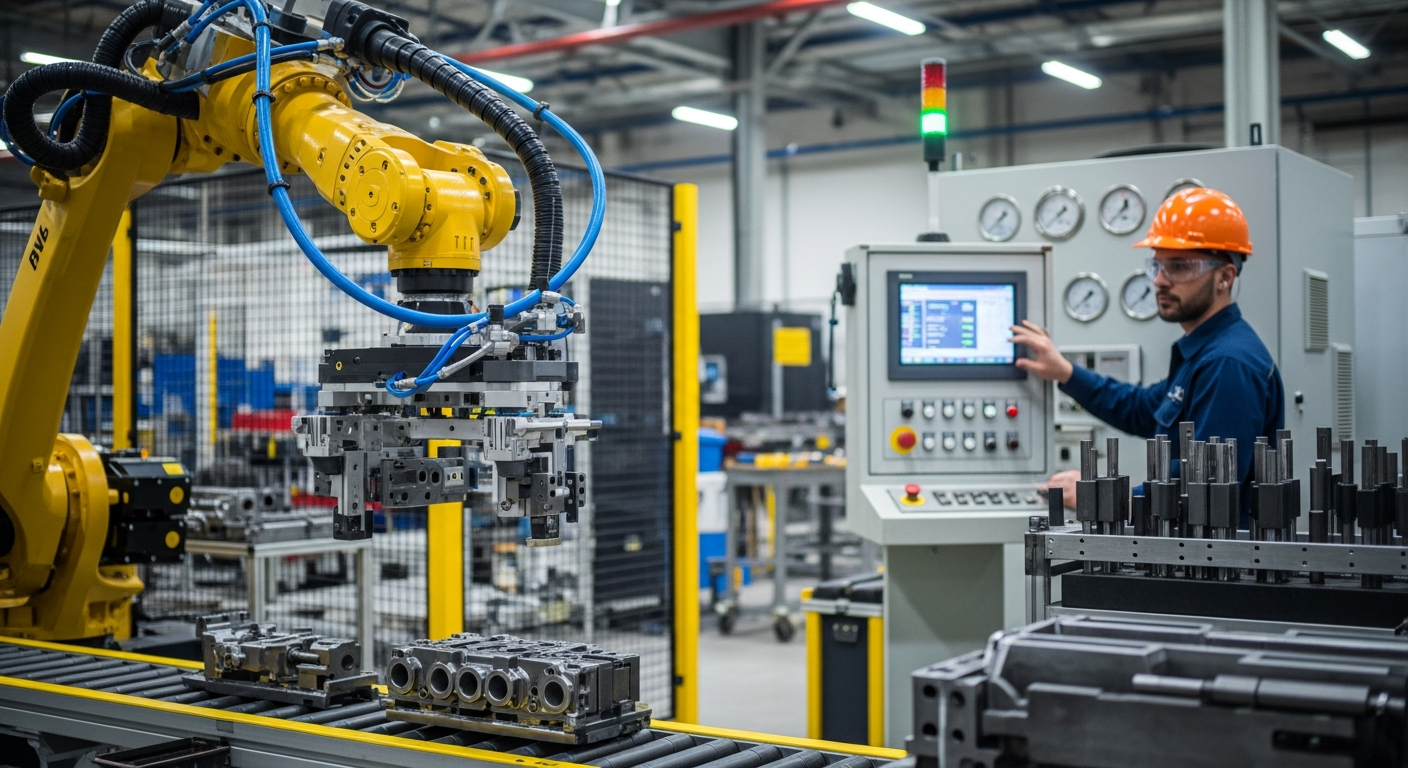
What is Fluid Power and Actuation in Industrial Machinery?
Fluid power is a technology that deals with the generation, control, and transmission of power using pressurized fluids. In the context of hydraulic cylinders, this fluid is typically oil. Actuation refers to the process of putting something into action or motion, and hydraulic cylinders are prime examples of actuators. They are crucial components in a wide range of industrial machinery and equipment, providing the necessary muscle for automated systems. The principles of fluid power allow for the transmission of considerable force over distances, making it an efficient method for many demanding industrial tasks.
How do Hydraulic Cylinders Generate Linear Motion and Force?
Hydraulic cylinders operate on Pascal’s principle, which states that pressure applied to an enclosed fluid is transmitted undiminished to every portion of the fluid and the walls of the containing vessel. When hydraulic fluid is pumped into one side of the cylinder, it exerts pressure on the piston. This pressure, acting over the surface area of the piston, generates a significant force that drives the piston rod in a linear motion. The direction of motion depends on which side of the piston the fluid is introduced. This mechanism allows for precise control over the speed and force of the linear movement, essential for many manufacturing processes.
Understanding Hydraulic Pressure Systems and Engineering
A hydraulic pressure system consists of several interconnected components: a reservoir to hold the hydraulic fluid, a pump to generate flow and pressure, control valves to direct the fluid, and the hydraulic cylinder itself to convert fluid power into mechanical work. The engineering behind these systems focuses on optimizing efficiency, safety, and durability. Proper system design considers factors such as fluid viscosity, operating temperature, pressure ratings, and material compatibility to ensure reliable performance. Advanced engineering also involves designing cylinders for specific applications, considering stroke length, bore size, and mounting configurations.
The Role of Control and Automation in Hydraulic Equipment
Modern hydraulic equipment often integrates sophisticated control and automation systems. These systems allow operators to precisely manage the movement, speed, and force exerted by hydraulic cylinders. Through the use of proportional valves, servo valves, and electronic controllers, hydraulic cylinders can be seamlessly incorporated into automated production lines and robotic systems. This level of control enhances operational accuracy, reduces manual intervention, and improves overall productivity. Automation in hydraulic applications is vital for repetitive tasks and those requiring high precision, contributing significantly to manufacturing efficiency.
Enhancing Performance in Manufacturing with Hydraulic Systems
Optimizing the performance of hydraulic systems in manufacturing involves several considerations. Regular maintenance, including fluid checks and seal replacements, is crucial for longevity and preventing efficiency losses. The selection of the right hydraulic cylinder for a specific task—considering factors like required force, speed, and environmental conditions—also directly impacts performance. Furthermore, integrating diagnostic tools can monitor system health and predict potential failures, minimizing downtime. By focusing on these aspects, manufacturers can ensure their hydraulic equipment operates at peak efficiency, contributing to higher output and reliability in their production processes.
Key Considerations for Hydraulic System Longevity and Efficiency
To ensure the long-term viability and efficiency of hydraulic systems, several factors warrant continuous attention. The quality and cleanliness of the hydraulic fluid are paramount, as contaminants can lead to wear and tear on components, reducing system lifespan and performance. Regular filtration and fluid analysis are essential practices. Additionally, proper sizing of pumps, valves, and cylinders prevents overheating and unnecessary energy consumption. Training personnel on best operating practices and routine inspections can identify issues before they escalate, maintaining the system’s integrity and operational effectiveness. Adhering to manufacturer specifications for components and maintenance schedules contributes significantly to the overall reliability and cost-effectiveness of these powerful industrial tools.
Hydraulic cylinders are foundational to industrial operations, offering robust and precise actuation capabilities. Their ability to deliver high force and controlled linear motion makes them indispensable in a wide array of manufacturing and heavy industry applications. Through careful engineering, integration with automation, and diligent maintenance, hydraulic systems continue to drive efficiency and performance across global industries, underpinning many of the processes that shape our modern world.




