Advancements in Diagnosing Intracranial Tumors
Understanding the complexities of intracranial tumors, often referred to as brain tumors, is crucial for effective patient care. These growths within the skull can significantly impact neurological function, making early and accurate detection paramount. Recent progress in medical technology and diagnostic methodologies offers new hope for improved outcomes, providing clinicians with more precise tools to identify, characterize, and monitor these challenging conditions. This article explores the evolving landscape of diagnostic techniques that are transforming the approach to intracranial tumor management globally.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.
Intracranial tumors represent a diverse group of growths originating within the brain or its surrounding structures. The intricate nature of the central nervous system means that even benign tumors can cause significant health issues due to pressure on vital brain regions. The journey from initial symptoms to a definitive diagnosis can be complex, involving a multidisciplinary approach that integrates insights from neurology, oncology, and advanced medical imaging. Ongoing research continues to shed light on the cellular mechanisms driving tumor growth and development, paving the way for more targeted diagnostic strategies.
Understanding Intracranial Tumor Growth and Types
Intracranial tumors can be primary, originating in the brain, or secondary, metastatic tumors that have spread from cancers elsewhere in the body. The diverse cellular origins lead to a wide spectrum of tumor types, each with unique characteristics regarding growth rate, location, and potential for malignancy. Glioblastoma, for instance, is a highly aggressive primary cerebral tumor, while meningiomas, often benign, arise from the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord. Accurate classification of these tumors is fundamental for predicting their behavior and guiding treatment decisions. Studying the specific patterns of tumor growth is a key area of research, helping to differentiate between various types and predict their progression.
Modern Medical Imaging for Tumor Detection
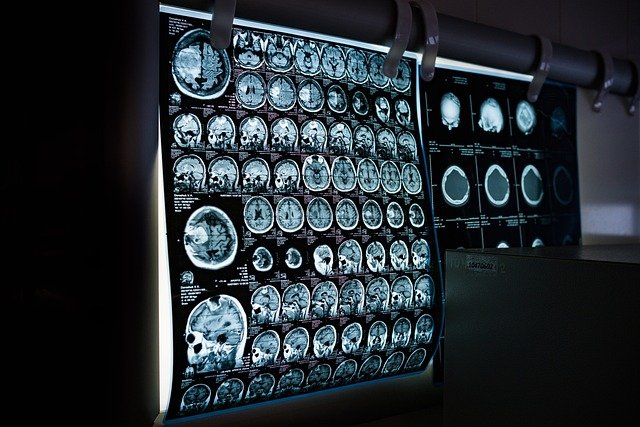
The cornerstone of intracranial tumor detection lies in advanced medical imaging techniques. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) remains the gold standard, offering high-resolution images of brain structures and tumor morphology. Newer MRI sequences, such as diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) and perfusion-weighted imaging (PWI), provide functional information about cellular density and blood flow, aiding in tumor characterization and distinguishing active tumor tissue from treatment-related changes. Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scans, often combined with CT or MRI, can detect metabolic activity within tumors, helping to identify aggressive lesions and assess treatment response. These imaging modalities contribute significantly to the initial diagnosis and ongoing monitoring of intracranial tumors.
Advances in Diagnosis and Molecular Profiling
Beyond structural imaging, the field of oncology has seen remarkable advancements in molecular diagnostics. Biopsy remains essential for definitive diagnosis, allowing pathologists to examine tumor tissue under a microscope. However, modern approaches extend this by performing comprehensive molecular profiling, identifying specific genetic mutations, epigenetic alterations, and protein expressions within the tumor cells. Techniques like next-generation sequencing (NGS) can detect a broad range of biomarkers that influence tumor behavior and predict response to specific therapies. This detailed molecular diagnosis provides a more personalized understanding of each patient’s tumor, moving towards precision medicine in neurological care.
Evolving Treatment and Therapy Approaches
The insights gained from advanced diagnosis directly influence the evolving landscape of treatment and therapy for intracranial tumors. Surgical intervention remains a primary approach for resectable tumors, with neurosurgeons employing sophisticated navigation systems and intraoperative imaging to maximize tumor removal while preserving neurological function. Radiation therapy, including focused techniques like stereotactic radiosurgery, precisely targets tumor cells. Chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and targeted molecular therapies are increasingly tailored based on the tumor’s molecular profile, offering more effective and less toxic options. These integrated strategies aim to improve patient outcomes and quality of life.
The Role of Research in Neurological Care
Continuous research is the driving force behind the advancements in diagnosing and treating intracranial tumors. Scientific inquiry spans basic laboratory studies investigating cellular pathways of tumor development, to clinical trials evaluating new diagnostic tools and therapeutic agents. Collaborative efforts among neurologists, oncologists, radiologists, and pathologists worldwide contribute to a deeper understanding of these complex diseases. This ongoing commitment to research helps refine current medical practices, introduces innovative technologies, and ultimately translates into improved health outcomes for individuals affected by brain tumors, ensuring that the field of neuro-oncology continues to progress.
Specialized Institutions and Collaborative Care
Patients with intracranial tumors often benefit from care at specialized institutions that bring together multidisciplinary teams of experts. These centers typically offer access to advanced diagnostic equipment, specialized neurosurgical expertise, and a wide array of therapeutic options, including clinical trials. Such collaborative environments facilitate comprehensive treatment planning, integrating the latest research findings into patient care. The coordinated approach ensures that each aspect of the patient’s condition, from initial detection to long-term follow-up, is managed with specialized knowledge and resources. These institutions are pivotal in pushing the boundaries of what is possible in neuro-oncology.
Advancements in the diagnosis of intracranial tumors have significantly improved the ability of healthcare professionals to detect, characterize, and monitor these challenging conditions. The integration of high-resolution imaging, sophisticated molecular profiling, and collaborative multidisciplinary care pathways underscores a future where diagnosis is more precise and treatment strategies are increasingly personalized. This ongoing progress offers considerable promise for enhancing the prognosis and quality of life for individuals affected by these complex neurological conditions.



