Maintaining Skin Health Through Fungal Prevention
Maintaining healthy skin is a continuous process that often involves safeguarding against various environmental factors, including common fungal infections. These conditions, while frequently mild, can cause discomfort and impact daily life if not properly addressed. Understanding the nature of fungal infections and implementing effective prevention strategies are crucial steps in preserving overall skin wellness.
Our skin, the body’s largest organ, acts as a primary barrier against external threats, including microscopic organisms. Among these, fungi are a common group that can lead to various skin conditions. While some fungi naturally reside on our skin without causing harm, an overgrowth or exposure to specific types can result in infections. These conditions are not only uncomfortable but can also spread if not managed effectively, underscoring the importance of vigilance and proactive care in maintaining skin health and preventing fungal issues.
Understanding Fungal Skin Infections and Dermatophytes
Fungal skin infections are primarily caused by a group of fungi known as dermatophytes. These microorganisms thrive on keratin, a protein found in skin, hair, and nails. Common examples of such infections include athlete’s foot, jock itch, and ringworm (despite its name, not caused by a worm). These conditions manifest when dermatophytes multiply rapidly, often in warm, moist environments, leading to symptoms like itching, redness, and flaking. Recognizing the specific type of fungal infection is important for effective treatment and management.
Recognizing Symptoms: Itch, Rash, and Skin Irritation
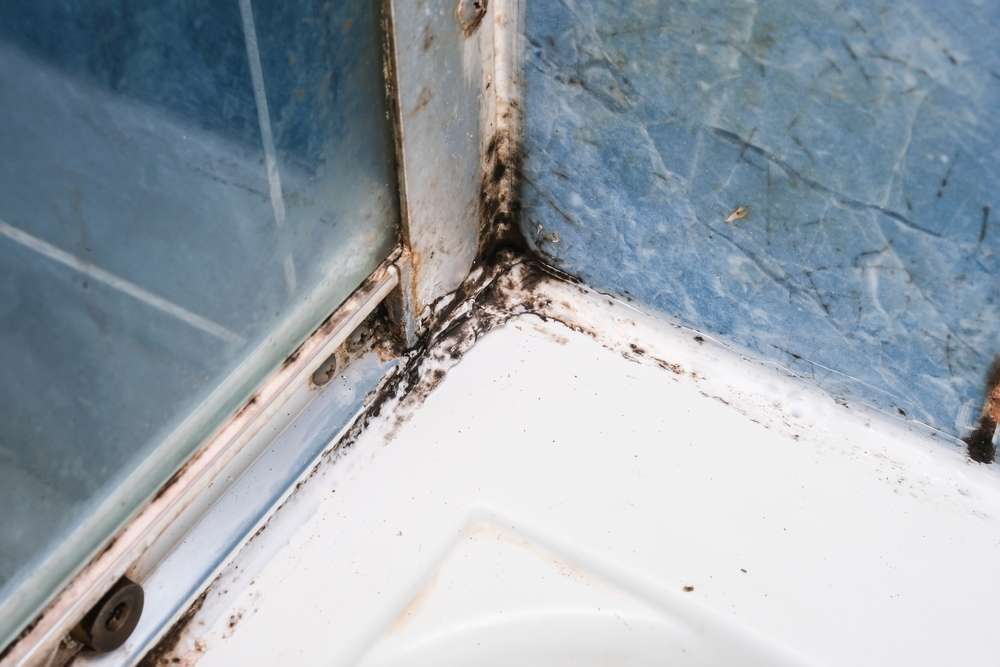
The signs of a fungal skin infection can vary but typically include a distinct itch, a visible rash, and general skin irritation. Ringworm, for instance, often presents as a circular, red, and scaly patch with raised edges, which can be intensely itchy. Other fungal infections might cause redness, flaking, peeling, or even small blisters, particularly in areas like the feet or groin. If any persistent or unusual skin changes occur, especially those accompanied by discomfort, it is advisable to seek professional advice for proper diagnosis.
Effective Anti-Fungal Treatment Approaches
Treating fungal skin infections typically involves anti-fungal medications, available in various forms. Over-the-counter (OTC) anti-fungal creams, powders, and sprays containing ingredients like clotrimazole, miconazole, or terbinafine are often effective for mild to moderate infections. For more persistent or widespread conditions, a healthcare professional might prescribe stronger topical medications or oral anti-fungal pills. The duration of treatment can vary, but it is important to complete the full course as directed, even if symptoms improve quickly, to ensure the infection is fully eradicated and to prevent recurrence.
Hygiene and Prevention Strategies for Skin Wellness
Preventing fungal infections largely revolves around good hygiene practices and reducing exposure to fungi. Keeping the skin clean and dry, especially in areas prone to moisture like between the toes, under the breasts, or in the groin, is fundamental. Wearing breathable fabrics, changing socks frequently, and avoiding sharing personal items like towels, shoes, or clothing can significantly reduce the risk of infection. Additionally, wearing sandals in public showers or locker rooms can help prevent exposure to fungi in communal areas. These simple steps contribute significantly to long-term skin health and wellness.
Fungal infections can be managed with various products and services, each with its own cost considerations. Over-the-counter topical anti-fungal creams and sprays are generally the most affordable option, while prescription-strength medications, whether topical or oral, typically incur higher costs, often covered partially by insurance. Professional consultations with a general practitioner or a dermatologist also come with fees, which can vary based on the clinic and the patient’s insurance coverage. Prices for treatments and consultations are estimates and can fluctuate.
| Product/Service | Provider | Cost Estimation (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| OTC Anti-Fungal Cream | Pharmacy brands (e.g., Lotrimin, Lamisil AT) | $8 - $20 |
| Prescription Topical Cream | Dermatologist/Pharmacy | $20 - $50+ (with insurance) |
| Oral Anti-Fungal Medication | General Practitioner/Pharmacy | $30 - $100+ (with insurance) |
| Dermatologist Consultation | Dermatology Clinic | $100 - $300+ (without insurance) |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Managing Fungal Conditions and Promoting Recovery
Effective management of fungal conditions extends beyond initial treatment to include strategies for preventing recurrence and promoting full recovery. This involves consistent adherence to hygiene practices, monitoring the skin for any new signs of irritation or rash, and addressing any underlying factors that might make one more susceptible to infections, such as compromised immune function or certain medical conditions. Regular skin care, including moisturizing when appropriate and avoiding harsh soaps, can also support the skin’s natural barrier function, contributing to overall skin health and reducing the likelihood of future fungal issues.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.
Maintaining healthy skin through diligent fungal prevention and timely treatment is an achievable goal for everyone. By understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and adopting proactive measures like good hygiene and appropriate anti-fungal care, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing uncomfortable skin conditions. Prioritizing skin health through consistent attention and informed choices contributes to overall wellness and comfort.




