Understanding Hair Loss: Causes, Prevention & Treatments
Hair loss affects people of all ages and genders, from subtle thinning to clear balding patterns. Learn how to spot early signs, understand common receding patterns, and explore prevention tips and treatment options — from at-home remedies to medical procedures — to make informed choices about your hair health.
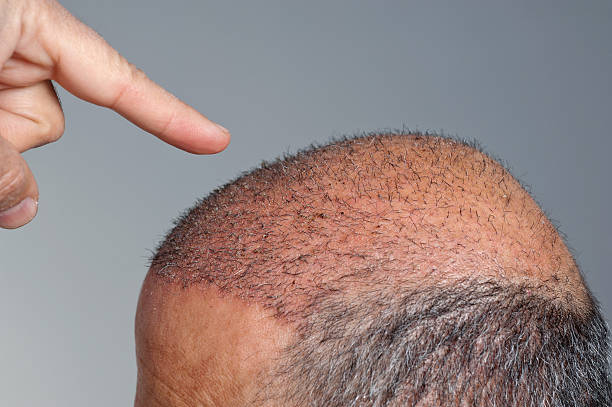
Hair loss is a common concern that can affect confidence and daily life. Whether you notice gradual thinning, a changing hairline, or more visible scalp, recognizing the signs early and understanding available options helps you take practical steps. This guide explains how to detect early thinning, identifies typical receding patterns, offers brushing best practices to reduce breakage, and outlines treatment choices from over-the-counter remedies to clinical procedures.
How to Spot Early Thinning
Early detection starts with simple monitoring. While losing about 50 to 100 hairs each day is normal, persistent increases in shedding or changes in hair density deserve attention. Red flags include finding noticeably more hair in your brush or shower drain, a widening part, and the scalp showing through in areas that used to be covered.
A reliable method for tracking progress is to take photos of your hairline and the crown from the same angles every few months. Comparing images over time makes gradual changes easier to spot than relying on memory alone. Keep in mind that temporary factors such as stress, illness, medications, or seasonal shedding can increase hair loss, so trends over several months are most informative.
Recognizing Receding Hairline Patterns
Hairline changes follow recognizable patterns that can indicate the underlying cause. In men, a receding hairline often begins at the temples and forms an M-shaped pattern as it progresses. The crown is another common starting point for male pattern hair loss.
Women tend to experience diffuse thinning across the top of the scalp rather than a sharply receding hairline. The part may become wider and the crown area may look less dense. Identifying whether hair loss is localized or generalized helps guide treatment choices and expectations.
Brushing Practices That Protect Your Hair
Daily habits influence how much breakage you experience. Choose a brush suited to your hair type — natural bristles or flexible, wide-tooth combs usually cause less damage than stiff metal bristles. When detangling, start at the ends and gently work upward to the roots; pulling through knots from the top down can rip out strands.
Avoid brushing wet hair unless you use a detangling product, because hair is more elastic and fragile when wet. If you must comb damp hair, use a wide-tooth comb and proceed slowly. Minimize tight hairstyles and excessive heat styling, both of which can weaken follicles and increase shedding.
Treatment Options and Professional Solutions
A range of treatments exists for addressing hair loss, from topical remedies to surgical options. The right choice depends on the cause, severity, and your personal goals. Below is a quick reference for common treatments and typical cost ranges.
| Treatment Type | Provider/Product | Average Cost Range |
|---|---|---|
| Minoxidil | Rogaine (OTC) | $20-45/month |
| Finasteride | Prescription | $10-80/month |
| Hair Transplant | Medical Clinics | $4,000-15,000/procedure |
| Laser Therapy | Home or clinical devices | $200-1,000/device |
| PRP Treatment | Medical Spas/Clinics | $500-2,500/session |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Topical minoxidil is an FDA-approved option for many types of hair thinning and can be used by men and women. It often needs continuous use to maintain results and may take several months to show visible improvement. Finasteride is an oral prescription medication typically used for men; it can slow hair loss and promote regrowth for some users but carries potential side effects and should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
For those seeking longer-term restoration, hair transplantation moves hair follicles from denser regions to thinning areas. Results can be natural and lasting, but the procedure is more costly and requires recovery time. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy uses a person’s own blood components to stimulate follicles; some patients see benefits after a series of sessions, although evidence and outcomes vary.
Low-level laser therapy devices are available for home use or in clinics and aim to stimulate hair growth with light energy. Their effectiveness differs between individuals, and regular use is necessary to maintain any gains.
Choosing the Right Approach
Effectiveness varies by cause, age, and individual biology. A consultation with a dermatologist or hair restoration specialist can clarify the diagnosis — whether it’s androgenetic alopecia, telogen effluvium, traction alopecia, or another condition — and help you weigh risks, benefits, and costs.
Combine professional guidance with sensible daily care: avoid harsh chemical treatments, reduce heat styling, maintain a balanced diet, and manage stress where possible. Tracking changes with photos, being patient with treatments that can take months to produce results, and following medical advice will improve the chance of a successful outcome.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.






